Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


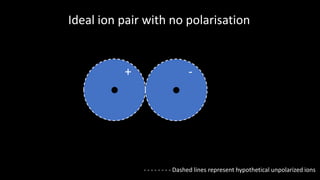
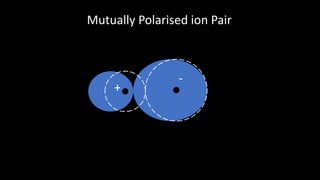
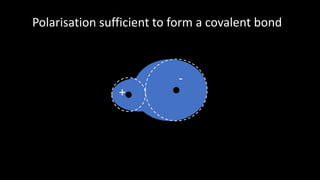

Polarisation occurs when the electron cloud of an atom or ion is distorted by the influence of a nearby positive atomic nucleus or electric field. Polarisability is the ability of an atom or ion to become polarized. Polarization can range from a slight distortion to a sufficient distortion that forms a covalent bond between ions. According to Fajans' Rules, ions with higher charges and smaller sizes polarize anions more, while ions with higher charges and larger sizes polarize cations more. Ions with partially filled d orbitals also polarize more than ions with noble gas configurations.





