Anatomy of Flowering Plants, Important Notes - ExamPraxis
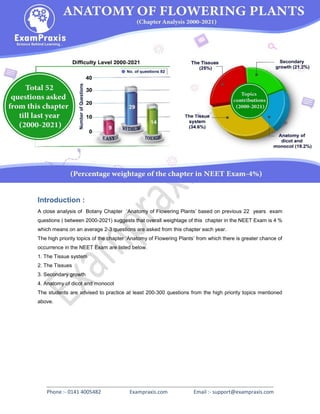
- 1. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com Introduction : A close analysis of Botany Chapter ‘Anatomy of Flowering Plants’ based on previous 22 years exam questions ( between 2000-2021) suggests that overall weightage of this chapter in the NEET Exam is 4 % which means on an average 2-3 questions are asked from this chapter each year. The high priority topics of the chapter ‘Anatomy of Flowering Plants’ from which there is greater chance of occurrence in the NEET Exam are listed below. 1. The Tissue system 2. The Tissues 3. Secondary growth 4. Anatomy of dicot and monocot The students are advised to practice at least 200-300 questions from the high priority topics mentioned above.
- 2. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com Noteworthy Points of the Chapter : 1. In plants, tissues are classified into two main groups, namely, meristematic and permanent tissues based on whether the cells being formed are capable of dividing or not. 2. Growth in plants is largely restricted to specialized regions of active cell division called meristems. 3. During the formation of leaves and elongation of stem, some cells ‘left behind’ from shoot apical meristem, constitute the axillary bud. 4. The meristem which occurs between mature tissues is known as intercalary meristem. 5. The meristem that occurs in the mature regions of roots and shoots of many plants, particularly those that produce woody axis and appear later than primary meristem is called secondary or lateral meristem. 6. Fascicular vascular cambium, interfascicular cambium and cork-cambium are examples of lateral meristems. 7. During the formation of the primary plant body, specific regions of the apical meristem produce dermal tissues, ground tissues and vascular tissues. 8. Permanent tissues made up of only one type of cells is called simple tissues. 9. Parenchyma includes isodiametric thin walled living cells with or without intercellular spaces. 10. The collenchyma occurs in layers below the epidermis in dicotyledonous plants. It includes thickened cells with deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin at corners. 11. Sclerenchyma consists of long, narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls having a few or numerous pits. 12. Sclerids are commonly found in the fruit walls of nuts; pulp of fruits like guava, pear and sapota; seed coats of legumes and leaves of tea. 13. Permanent tissues having many different types of cells are called complex tissues. 14. Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem. 15. The presence of vessels is a characteristic feature of angiosperms. 16. In flowering plants, tracheids and vessels are the main water transporting element.
- 3. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com 17. The first formed primary xylem elements are called protoxylem. 18. In roots, the protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies toward the centre. Such arrangement of primary xylem is called exarch. 19. Phloem in angiosperms is composed of sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibers. 20. The functions of sieve tubes are controlled by the nucleus of companion cells. 21. The companion cells are specialized parenchymatous cells, which are closely associated with sieve tube elements. 22. The sieve tube elements and companion cells are connected by pit fields present between their common longitudinal walls. 23. The companion cells help in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes. 24. Phloem parenchyma is absent in most of the monocotyledons. 25. Phloem fibres are made up of sclerenchymatous cells. 26. The first formed primary phloem consists of narrow sieve tubes and is referred to as protophloem. 27. The outside of the epidermis is often covered with a waxy thick layer called the cuticle which prevents the loss of water. Cuticle is absent in roots. 28. In dicots, each stoma is composed of two bean-shaped cells known as guard cells. In grasses, those cells are dumb-bell shaped. 29. The outer walls of guard cells are thin and the inner walls are highly thickened. 30. The stomatal aperture, guard cells and the surrounding subsidiary cells are together called stomatal apparatus. 31. On the stem the epidermal hairs are present called trichomes. 32. All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles constitute the ground tissue. 33. The ground tissue system forms the main bulk of the plant. It is divided into three zones cortex, pericycle and pith. 34. The wood is actually a secondary xylem.
- 4. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com 35. In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells and is called mesophyll. 36. The xylem and phloem together constitute the vascular bundles. 37. Vascular bundles due to presence of cambium possess the ability to form secondary xylem and secondary phloem, and hence called open vascular bundles. 38. In the monocotyledons, the vascular bundles have no cambium. They do not form secondary tissues hence are referred as closed. 39. In conjoint type of vascular bundles, the xylem and phloem are jointly situated at the same radius of vascular bundles. 40. The conjoint vascular bundles usually have the phloem located only on the outer side of xylem. 41. The innermost layer of cortex in dicot roots comprises a single layer of barrel-shaped cells without any intercellular spaces and is called endodermis. 42. The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells in cortex have a deposition of water impermeable, waxy material-suberin-in the form of casparian strips. 43. In dicot roots, the parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and phloem are called conjuctive tissue. 44. Dicot roots have usually 2-4 xylem and phloem patches. 45. All tissues on the inner side of the endodermis such as pericycle, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele. 46. There are usually more than six xylem bundles in the monocot root. 47. The outer hypodermis, consists of few layers of collenchymatous cells just below the epidermis, which provide mechanical strength to the young dicot stem. 48. The cells of the endodermis are rich in starch grains and the layer is also referred to as starch sheath. 49. A large number of vascular bundles are arranged in a ring; the ‘ring’ arrangement of vascular bundles is a characteristic of dicot stem. 50. The monocot stems have sclerenchymatous hypodermis, large number of scattered vascular bundles, each surrounded by sclerenchymatous bundle sheath and large conspicuous ground tissue.
- 5. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com 51. In dicot leaves, abaxial epidermis generally bears more stomata than the adaxial epidermis. 52. The size of the vascular bundles are dependent on the size of the veins. 53. In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells modify themselves into large, empty, colourless cells, called bulliform cells. 54. The meristem involved in secondary growth is lateral meristem i.e., vascular cambium and cork cambium. 55. In dicot stems, the cells of cambium present between primary xylem and primary phloem is the Intrafascicular cambium. 56. The cells of medullary rays adjoining intrafascicular cambium become meristematic and form the Interfascicular cambium. 57. The cambium is generally more active on the inner side than on the outer side. 58. In the spring season, cambium is very active and produces a large number of xylary elements having vessels with wider cavities. 59. The spring wood or early wood is lighter in colour and has a lower density. 60. In winter, cambium is less active and form fewer xylary elements that have narrow vessels. This wood is called autumn wood or late wood. 61. The two kinds of woods that appear as alternate concentric rings, constitute an annual ring. 62. In old trees, the greater part of secondary xylem is dark brown due to deposition of organic molecules like tannins, resins, oils, gums etc. 63. In old trees, the central region of secondary xylem comprising dead elements with highly lignified walls, is called heart wood. 64. The peripheral region of the secondary xylem is lighter in colour and is known as the sap wood. 65. The extra stellar cambium or phellogen develops in cortex region and divides to form cork (phellem) and secondary cortex (phelloderm). 66. The cork is impervious to water due to suberin deposition on the cell wall. 67. Phellogen, phellem, and phelloderm are collectively known as periderm. 68. Bark is a non-technical term that refers to all tissues exterior to the vascular cambium. When it is formed early in the season, it is called early or soft bark. 69. In the dicot root, the vascular cambium is completely secondary in origin.
- 6. Phone :- 0141 4005482 Exampraxis.com Email :- support@exampraxis.com