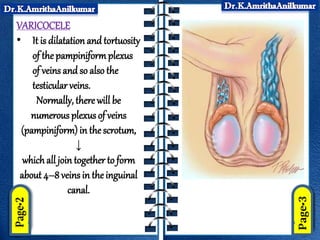
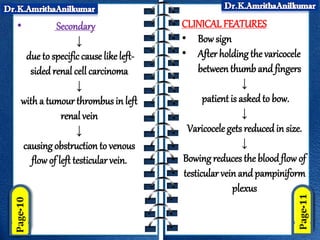
Varicocele is dilatation and tortuosity of the veins within the scrotum that drain blood from the testicles. It is more common on the left side where the left testicular vein drains directly into the left renal vein. Varicocele can cause increased temperature in the scrotum and impair sperm production. Treatment involves surgical ligation of the affected veins to repair blood flow and potentially improve fertility.