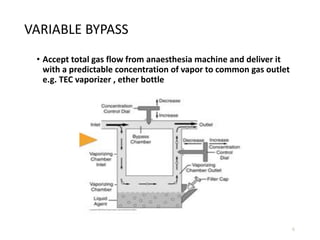
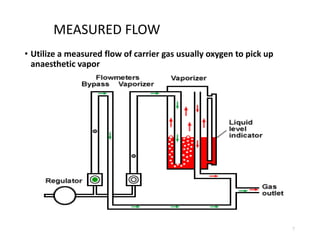
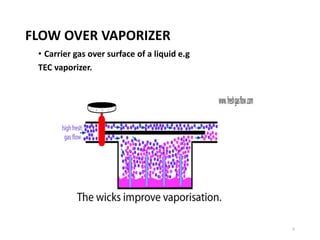
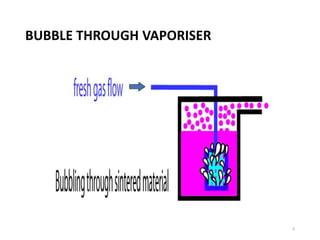
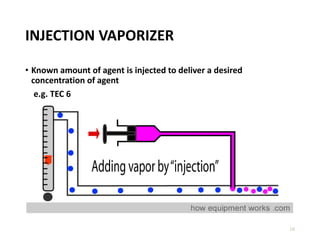
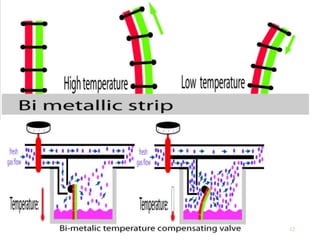
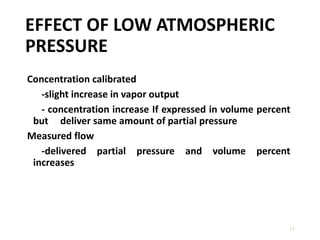
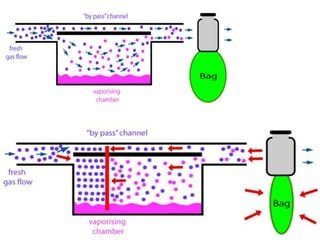
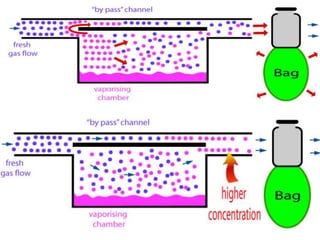
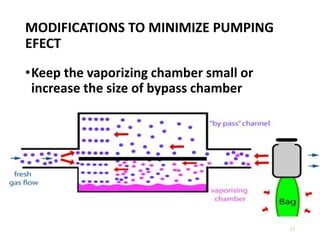
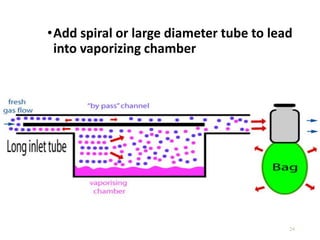
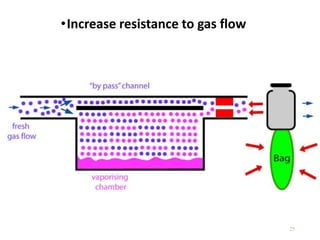
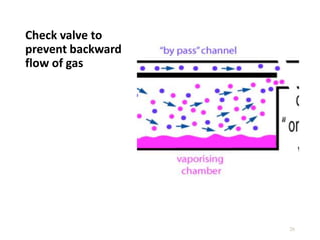
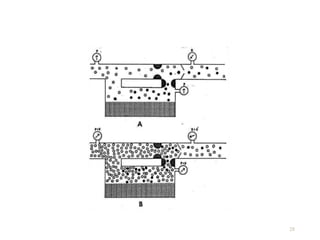
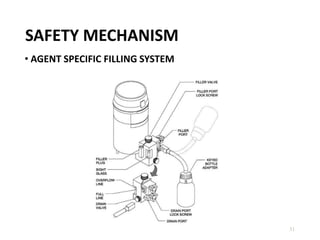
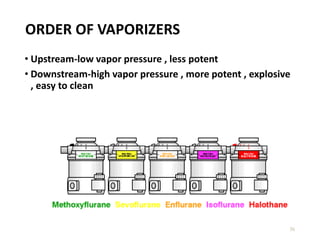
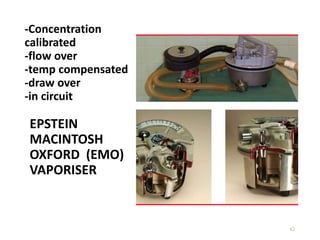
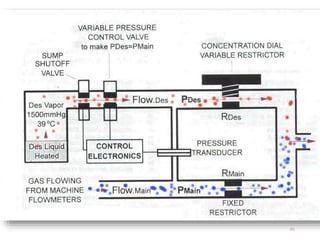
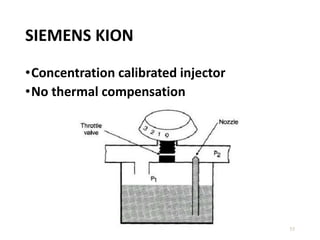
This document discusses different types of vaporizers used to deliver anesthetic gases to patients. It describes six classifications of vaporizers: 1) method of regulating output, 2) method of vaporization, 3) temperature compensation, 4) specificity, 5) resistance, and 6) location. Common vaporizers are then explained in more detail, including how they work, advantages, and disadvantages. Safety mechanisms are also reviewed to minimize risks from incorrect concentrations or agent delivery.