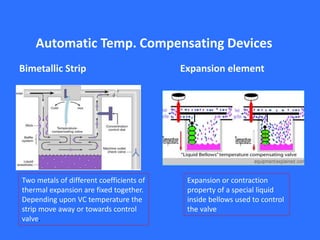
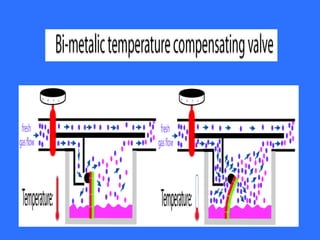
This document discusses vaporizers, which are instruments used to facilitate the vaporization of liquid inhalational anesthetic agents for controlled delivery during anesthesia. It covers the basic physics of vaporization, classifications of vaporizers, examples of older vaporizer models, and features of newer electronic vaporizers. Specifically, it describes the TEC-6 desflurane vaporizer, which is an electrically heated, dual circuit gas/vapor blender that maintains a constant temperature for precise desflurane delivery. Safety features of modern vaporizers are also outlined.


























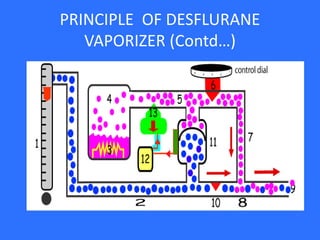
![TEC - 6
Flow meters [1]. The fresh gas travels through pipe [2]. None of the fresh gas goes to the vaporizing chamber [4]. The vaporizing chamber is
electrically heated [3]. Using sensors for feedback, the temperature is kept very constant. The heating causes the Desflurane to become a gas
under pressure [4] and this travels down pipe [5]. The flow of Desflurane is resisted by two valves [6,13]. Valve [6] is the valve that you
control when you set the dial to a particular concentration. When you increase the concentration setting, the valve [6] opens a bit and lowers the
resistance, allowing more Desflurane to flow through. Valve [13] is an electronically controlled valve. Computer [12], the vaporizer's "brain", is
able to also alter the flow of Desflurane by controlling valve [13]. i.e. both you and the computer can adjust the desflurane injection rate. The
Desflurane then goes via pipe [7] and meets the fresh gas at [8]. The Desflurane mixes with the fresh gas [8] and a final concentration emerges
from the exit of the vaporizer [9].Fresh gas flow resistor (10), Fresh gas flow & Desflurane vapor balancing unit(11)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hodvaporizerdr-150128030224-conversion-gate02/85/vaporizer-dr-s-p-34-320.jpg)