The document discusses selective decontamination of the digestive tract (SDD), a method used to prevent infections in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. It describes how SDD works by using topical antibiotics in the mouth and stomach to eliminate harmful bacteria while preserving normal flora. Meta-analyses of clinical trials show that SDD reduces ICU-acquired pneumonia rates by 60-70% and mortality by 10-30%. However, long-term antibiotic use may promote resistance. Overall, SDD is effective for preventing infections but its use requires consideration of local resistance patterns and strict hygiene protocols.










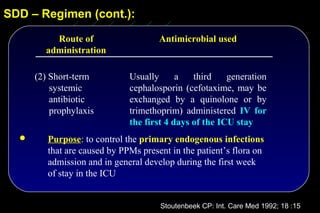












![The effect of topical and IV antibiotic prophylaxis on infections
and morbidity
Infections acquired in the ICU SDD vs. Control
Pneumonias:
6 vs. 29 ( P < 0.007)
Other lower resp. tract infections:
N=546
39 vs. 70 ( P < 0.007)
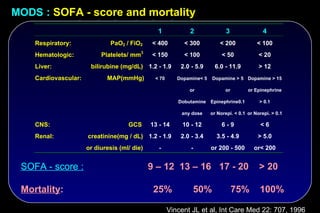
Bloodstream infections:
14 vs. 36 ( P < 0.007)
Urinary tract infections:
36 vs. 60 ( P < 0.042)
P < 0.001, RR 0.477,
95% CI [0.367 – 0.620]
Krueger WA et al AJRCCM 2002; 166: 1029-37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filos-selectivegutdecontamination-121223044416-phpapp01/85/K-S-Filos-MD-PhD-Selective-Gut-Decontamination-30-320.jpg)
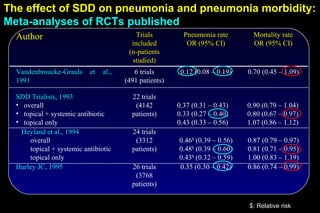
![The effect of topical and IV antibiotic prophylaxis on infections
and morbidity
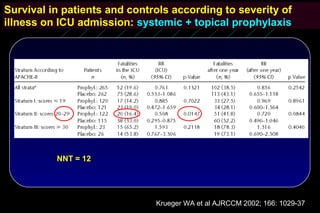
Multiorgan failure SDD vs. Control
Renal failure:
17 vs. 38 ( P < 0.018)
ARDS / ALI:
15 vs. 27 ( NS)
Circulation:
27 vs. 45 ( NS)
N=546
Liver:
26 vs. 29 ( NS)
Coagulation:
15 vs. 27 ( NS)
CNS:
P < 0.0051, RR 0.636, 3 vs. 5 ( NS)
95% CI [0.463 – 0.874]
Krueger WA et al AJRCCM 2002; 166: 1029-37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filos-selectivegutdecontamination-121223044416-phpapp01/85/K-S-Filos-MD-PhD-Selective-Gut-Decontamination-31-320.jpg)


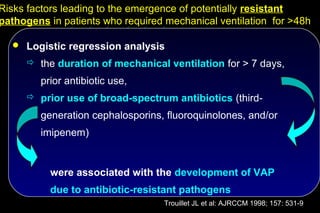
![The effect of topical and IV antibiotic prophylaxis on infections
and morbidity
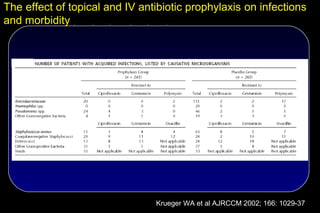
Multiorgan failure SDD vs. Control
Renal failure:
17 vs. 38 ( P < 0.018)
ARDS / ALI:
15 vs. 27 ( NS)
Circulation:
N=546 27 vs. 45 ( NS)
Liver:
26 vs. 29 ( NS)
Coagulation:
15 vs. 27 ( NS)
P < 0.0051, RR 0.636,
95% CI [0.463 – 0.874] CNS:
3 vs. 5 ( NS)
Krueger WA et al AJRCCM 2002; 166: 1029-37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filos-selectivegutdecontamination-121223044416-phpapp01/85/K-S-Filos-MD-PhD-Selective-Gut-Decontamination-35-320.jpg)



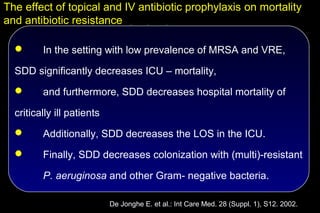
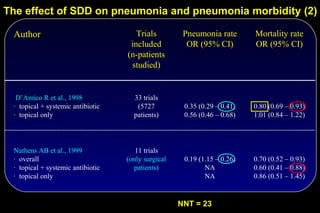
![The effect of topical and IV antibiotic prophylaxis on mortality
and antibiotic resistance
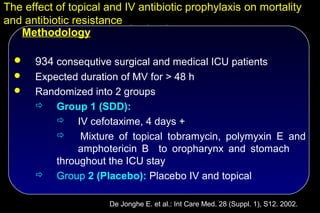
SDD Control Odds-ratio P-
(n = 468) (n=466) [95% C.I.] value
ICU-mortality (%) 14.8 22.9 0.6 [0.4 – 0.8] 0.002
Hospital-mortality (%) 24.2 31.2 0.7 [0.5 – 0.9] 0.02
ICU-LOS (days) 11.6 13.4 < 0.001
Tobramycin/P. aeruginosa 13 13 1.0 [0.5 – 2.3] NS
Tobramycin/other Gram neg. 20 47 0.4 [0.2 – 0.7] 0.001
Imipenem/ P. aeruginosa 1 16 0.1 [0.01 – 0.5] < 0.001
Imipenem/ other Gram neg. 1 10 0.1 [0.01 – 0.6] 0.01
Ciproflox./ P. aeruginosa 1 13 0.1 [0.01 – 0.6] 0.002
Ciproflox./ other Gram neg. 9 31 0.3 [0.1 – 0.6] 0.001
Vancomycin./ enterococcus 4 5 0.8 [0.2 – 3.1] NS
Methicillin./ S. aureus 0 0
De Jonghe E. et al.: Int Care Med. 28 (Suppl. 1), S12. 2002.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filos-selectivegutdecontamination-121223044416-phpapp01/85/K-S-Filos-MD-PhD-Selective-Gut-Decontamination-42-320.jpg)