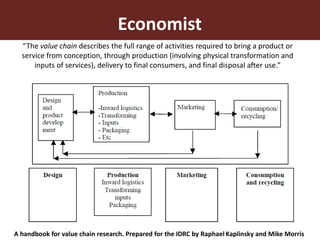
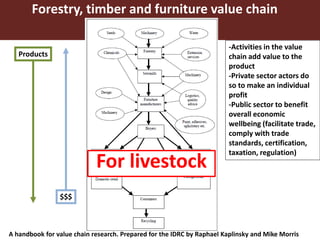
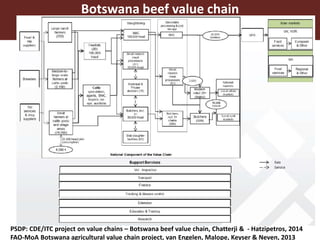
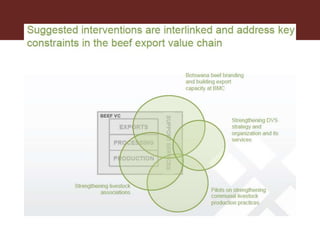
The document discusses the value chain approach in the context of livestock and beef trade, emphasizing its significance in enhancing product value and understanding the dynamics between various stakeholders. It highlights the need for careful analysis of production systems, stakeholder behavior, and risk management related to animal diseases to optimize trade efficiency. Various projects and methodologies are described to facilitate upgrading strategies within the Botswana beef value chain and improve economic outcomes.