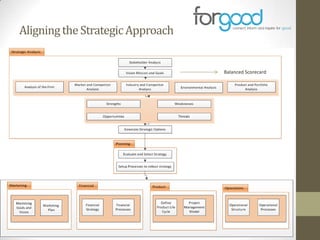
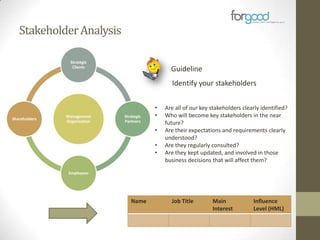
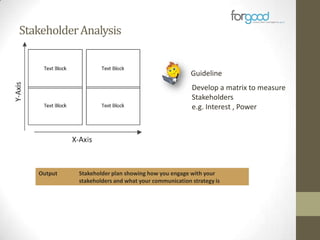
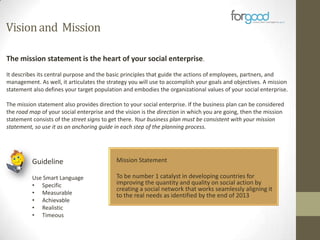
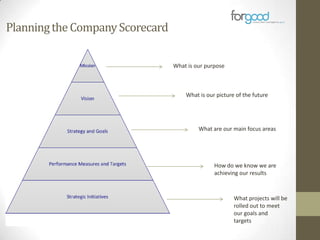
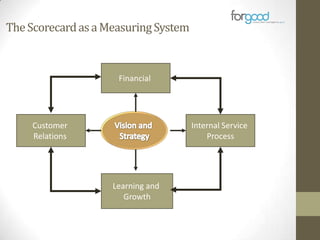
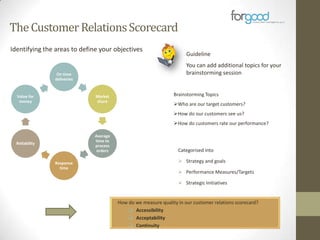
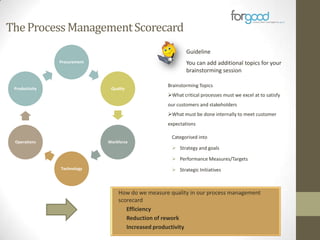
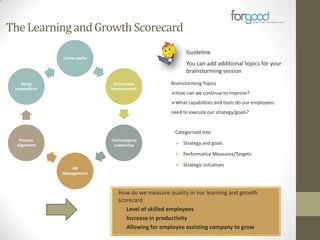
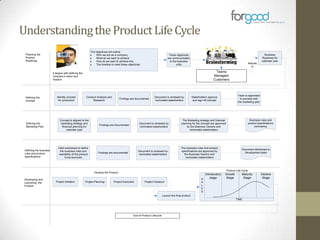
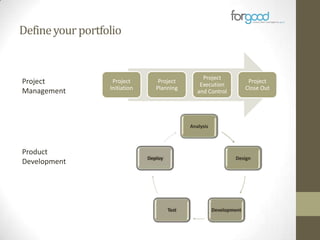
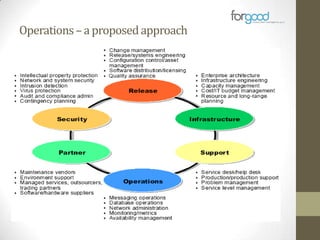
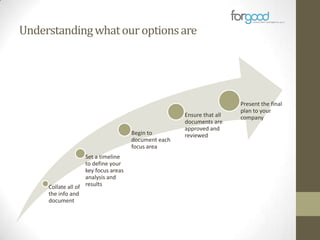
Strategic planning is one of the most important responsibilities of senior management as it sets the organizational vision, strategies, and resource deployment to achieve that vision. However, strategic plans are often misunderstood and poorly used, resulting in large documents that are not implemented. There are several common reasons for this, including senior management not following a defined process, the plan being delegated without true endorsement, and lack of communication and implementation guidelines. Properly developing a strategic plan requires involvement from senior leadership, understanding what the plan is designed to provide, and having a defined process and methodology to create the plan in a timely and efficient manner.