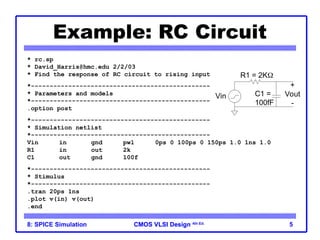
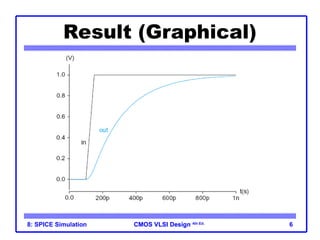
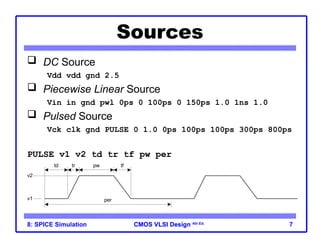
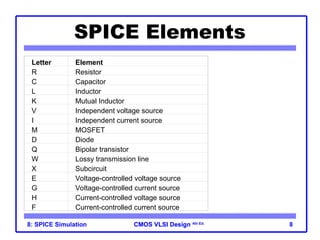
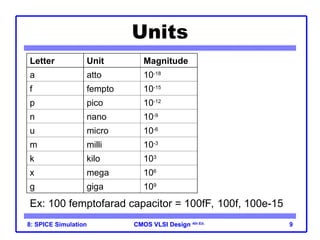
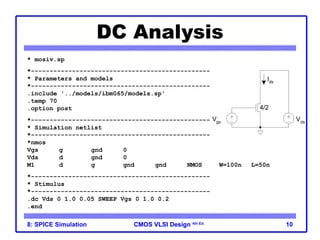
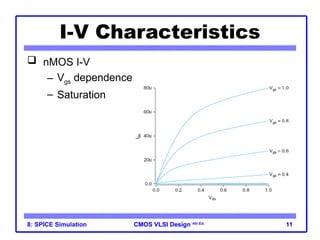
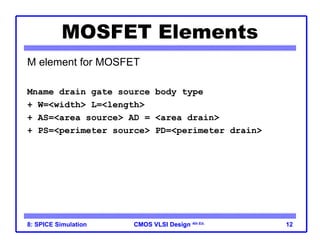
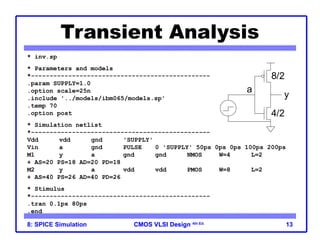
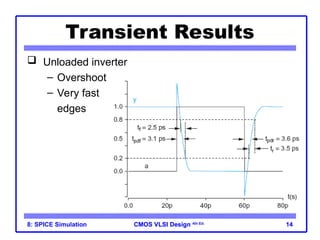
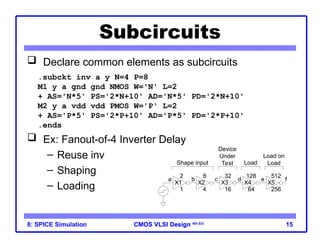
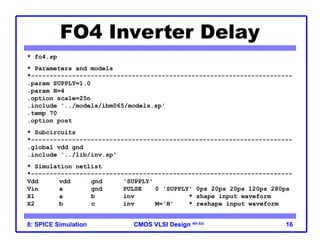
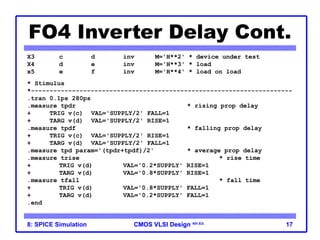
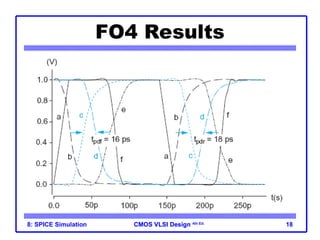
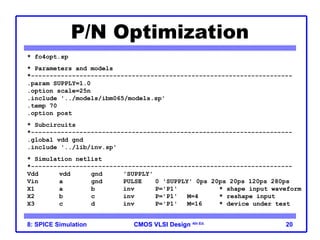
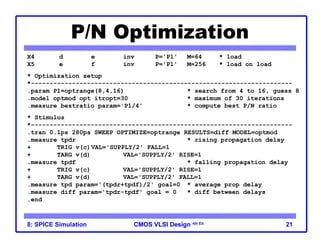
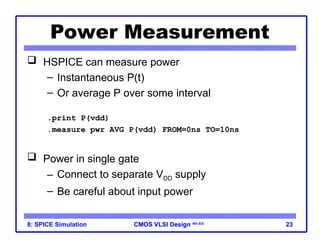
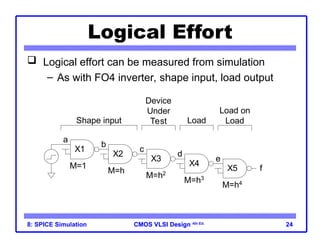
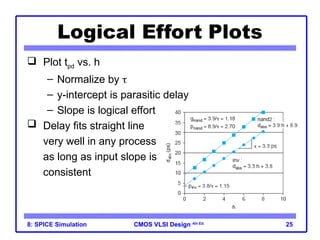
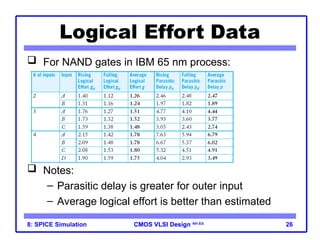
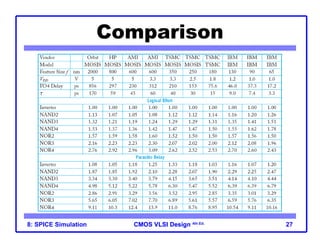
The document outlines the use of SPICE simulation in CMOS VLSI design, focusing on topics like DC and transient analysis, optimization, and power measurement. It provides details on writing SPICE decks, conducting simulations, and analyzing results, including logical effort characterization. Various examples are included to illustrate the simulation process and optimization techniques for circuit design.