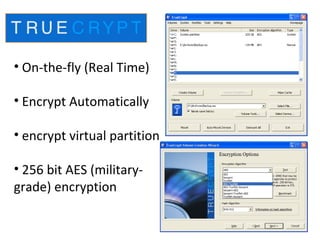
USB drives provide convenience but also security risks. Key risks include data corruption if improperly removed, virus transmission when transferring files between devices, loss of the media itself which can expose confidential data, and loss of confidentiality if stolen. Recommended solutions are to safely dismount drives, scan for viruses after transfers, attach drives to prevent loss, and encrypt data to protect against loss of confidentiality. Taking proactive steps like encryption can significantly reduce security risks from USB use.