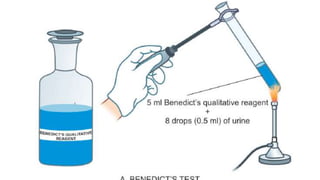
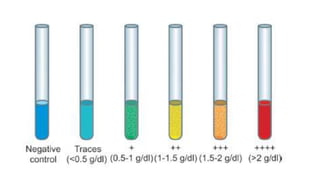
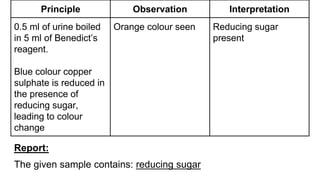
This document discusses urine analysis to detect reducing sugars using Benedict's test. Benedict's test involves adding urine to a blue copper sulfate solution. In the presence of reducing sugars like glucose, the cupric ion is reduced to a colored cuprous oxide precipitate. The color change can indicate the approximate concentration of reducing sugars, ranging from green (trace) to brick red (>2 g/dL glucose). Reducing sugars in urine, known as glycosuria, can be caused by conditions like diabetes mellitus. The document reviews the principle, procedure, interpretation and limitations of Benedict's test for qualitative and semi-quantitative detection of reducing sugars in urine samples.