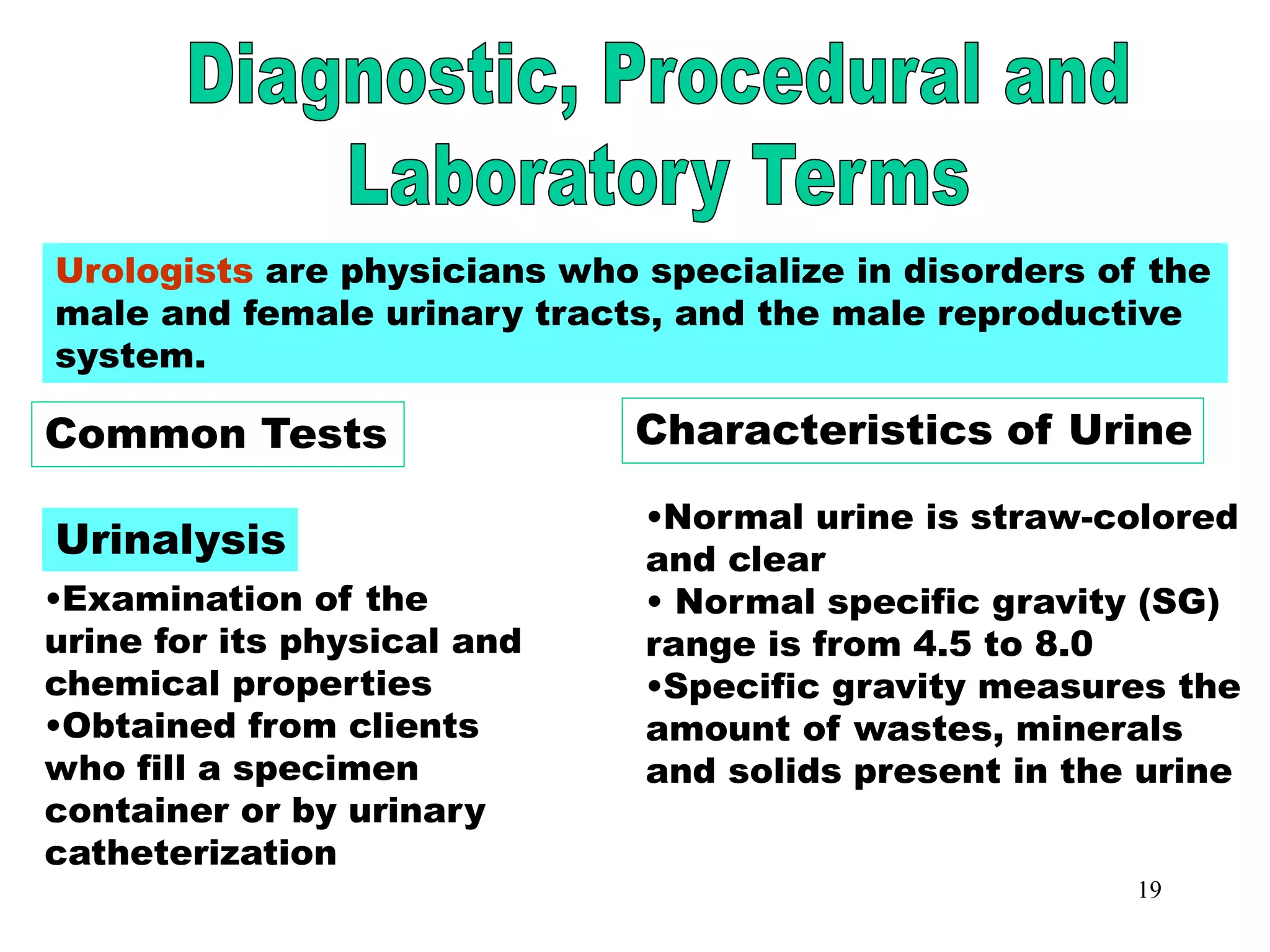
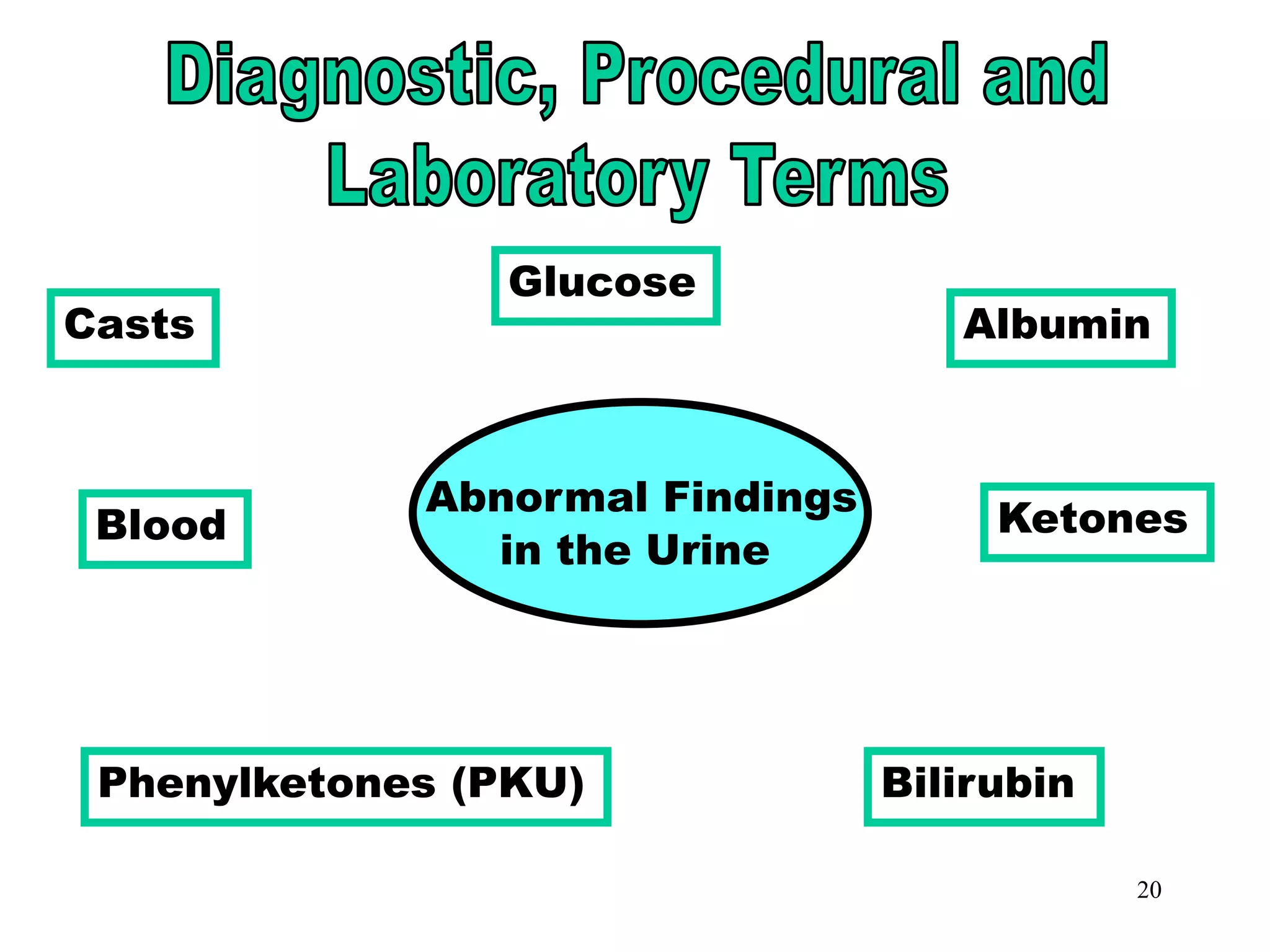
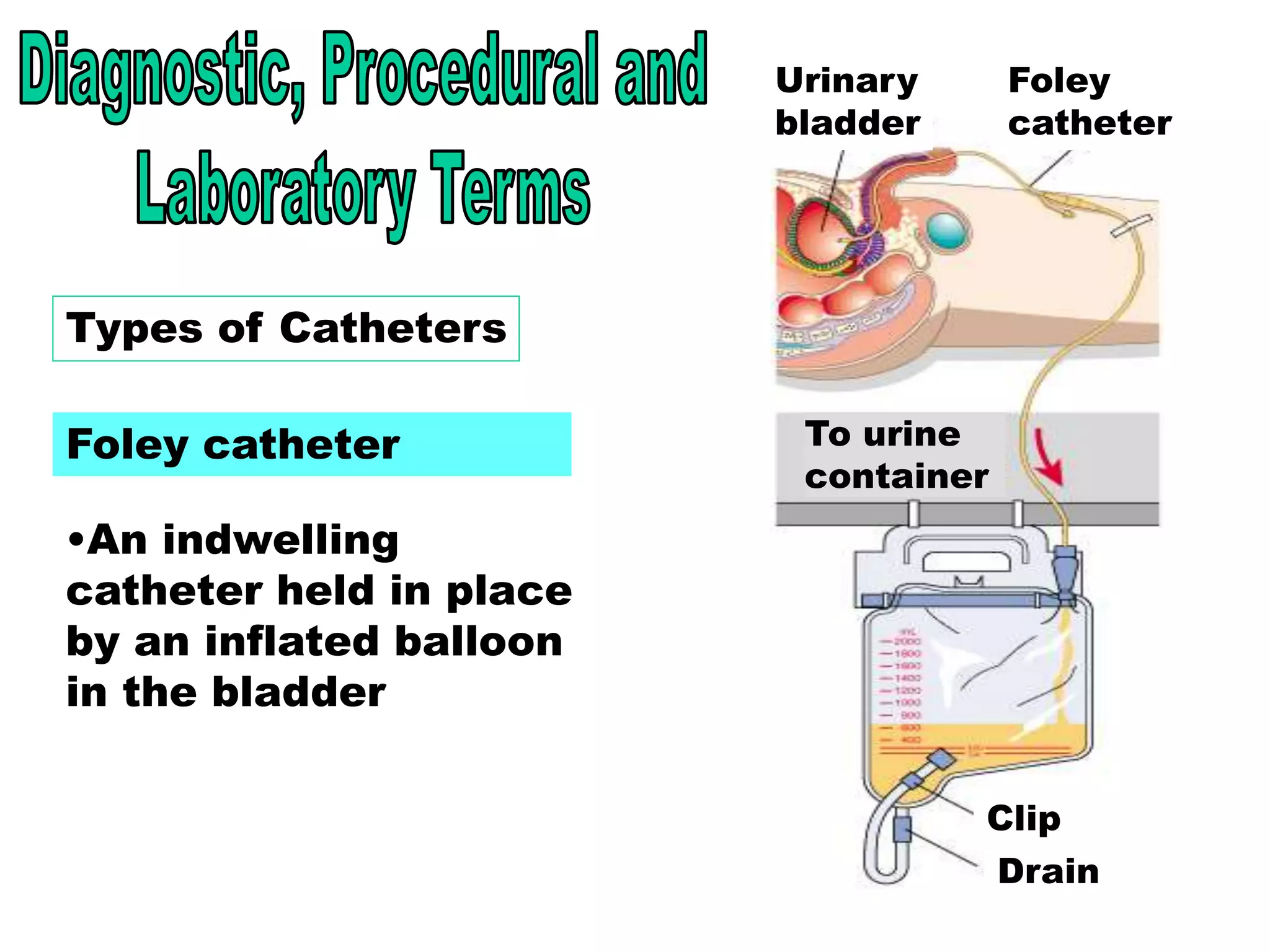
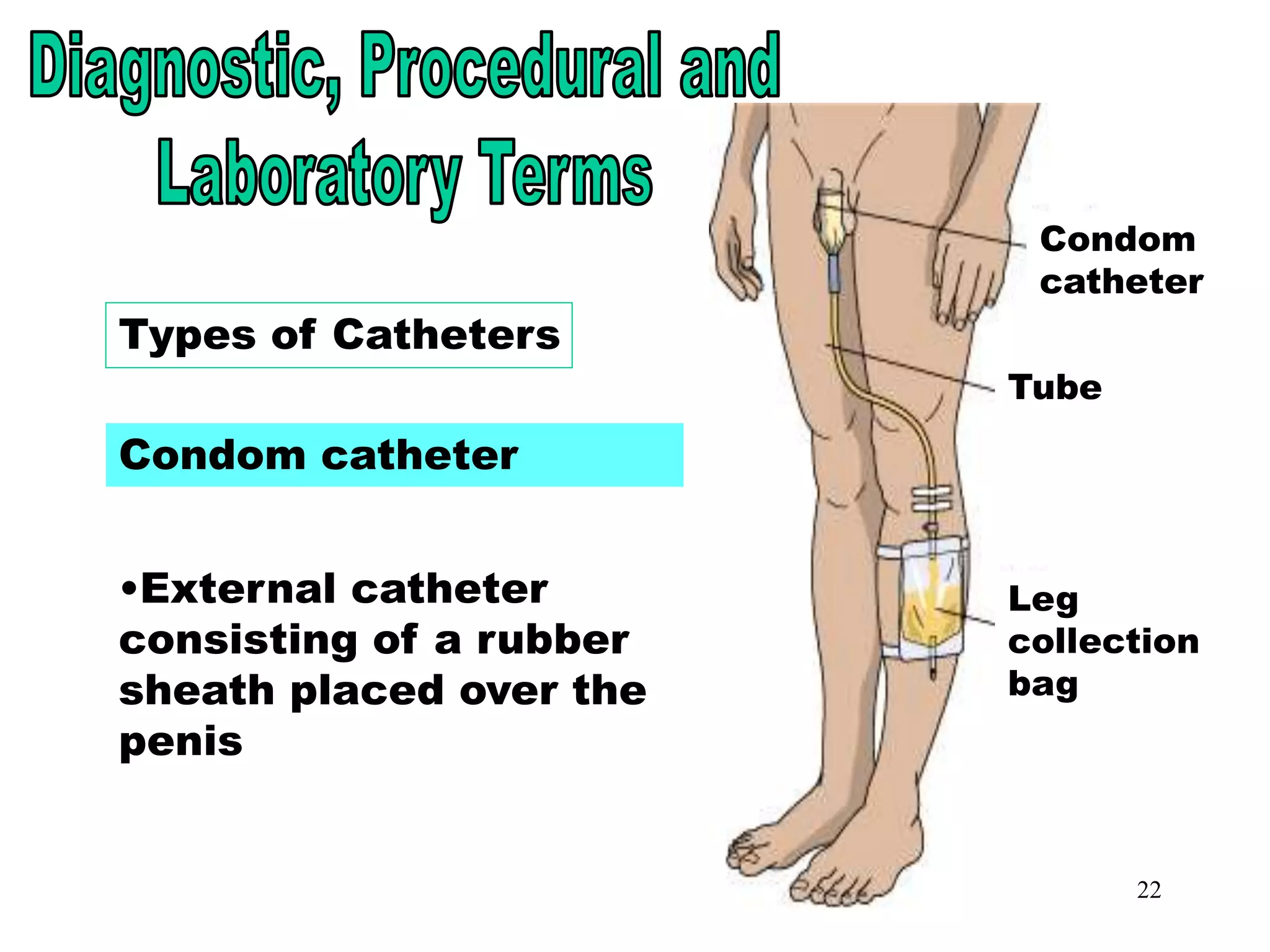
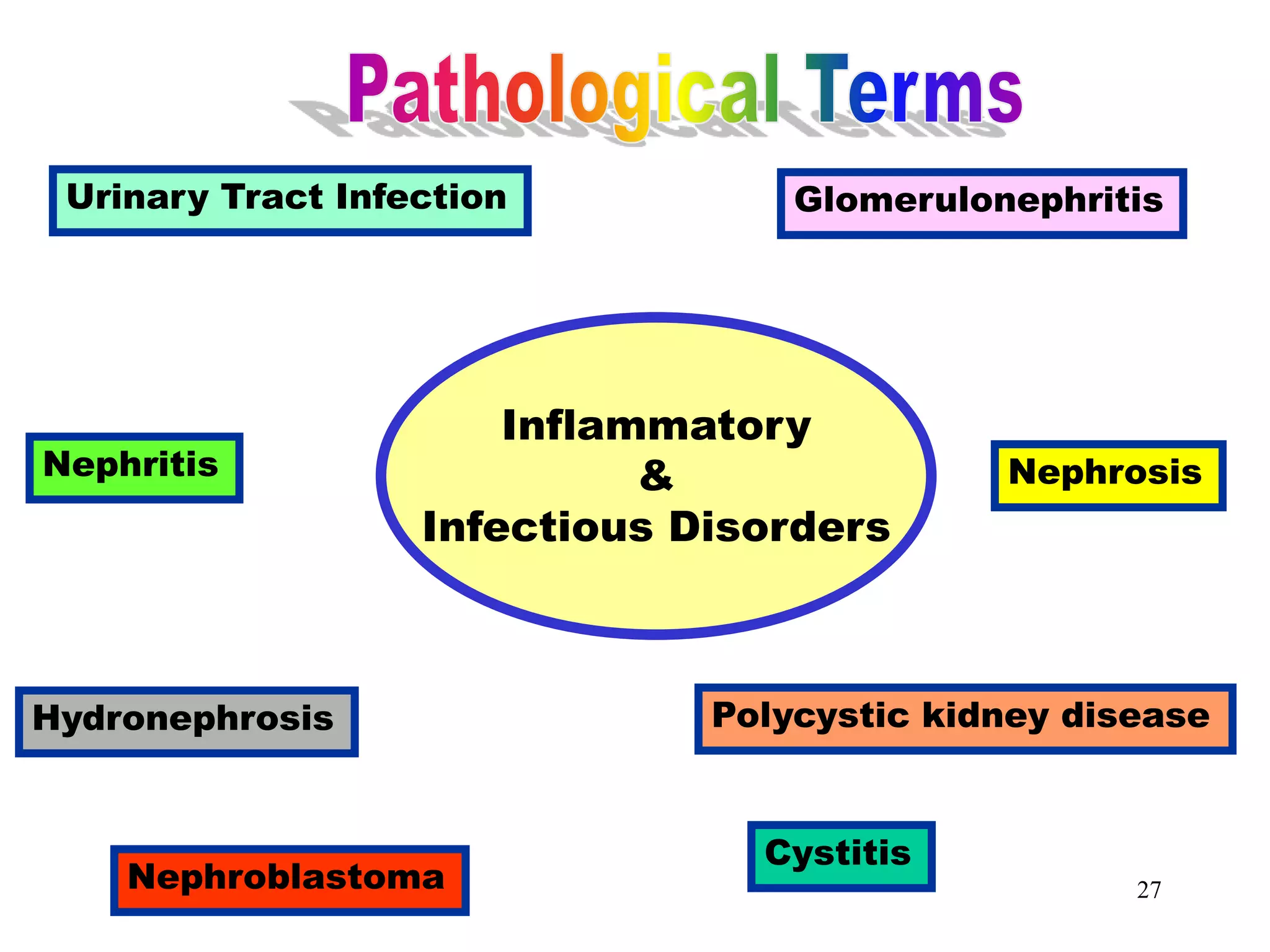
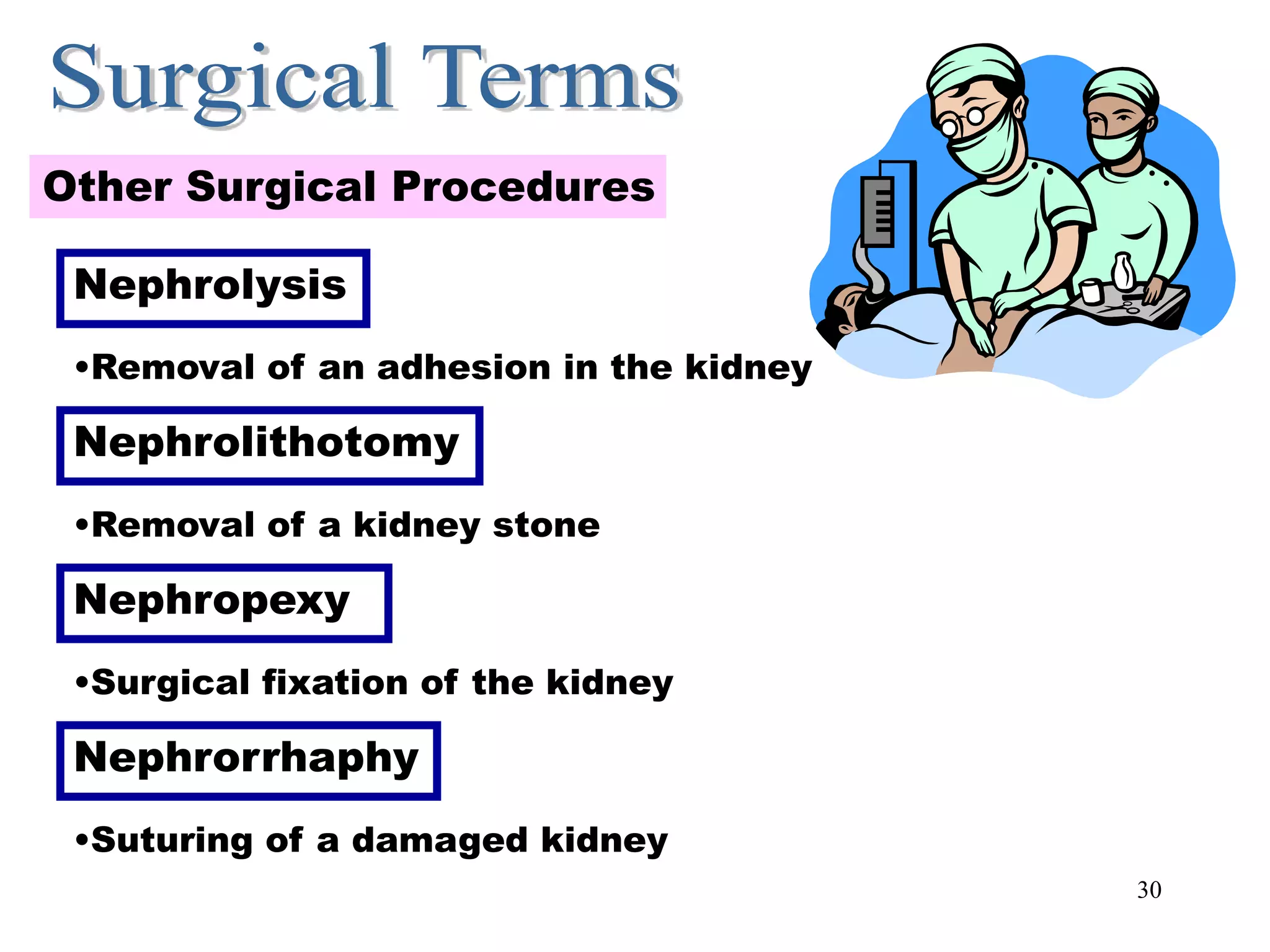
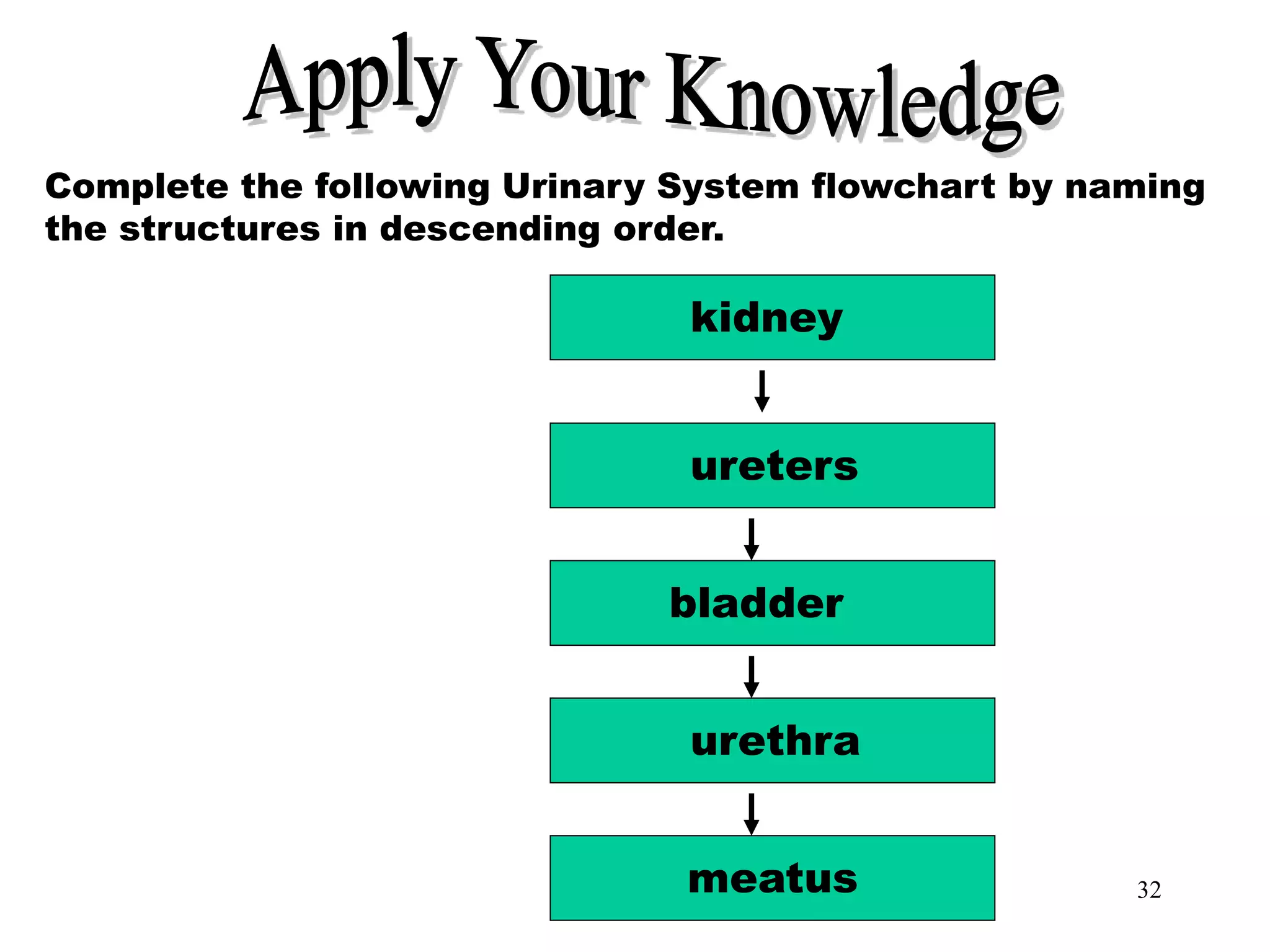
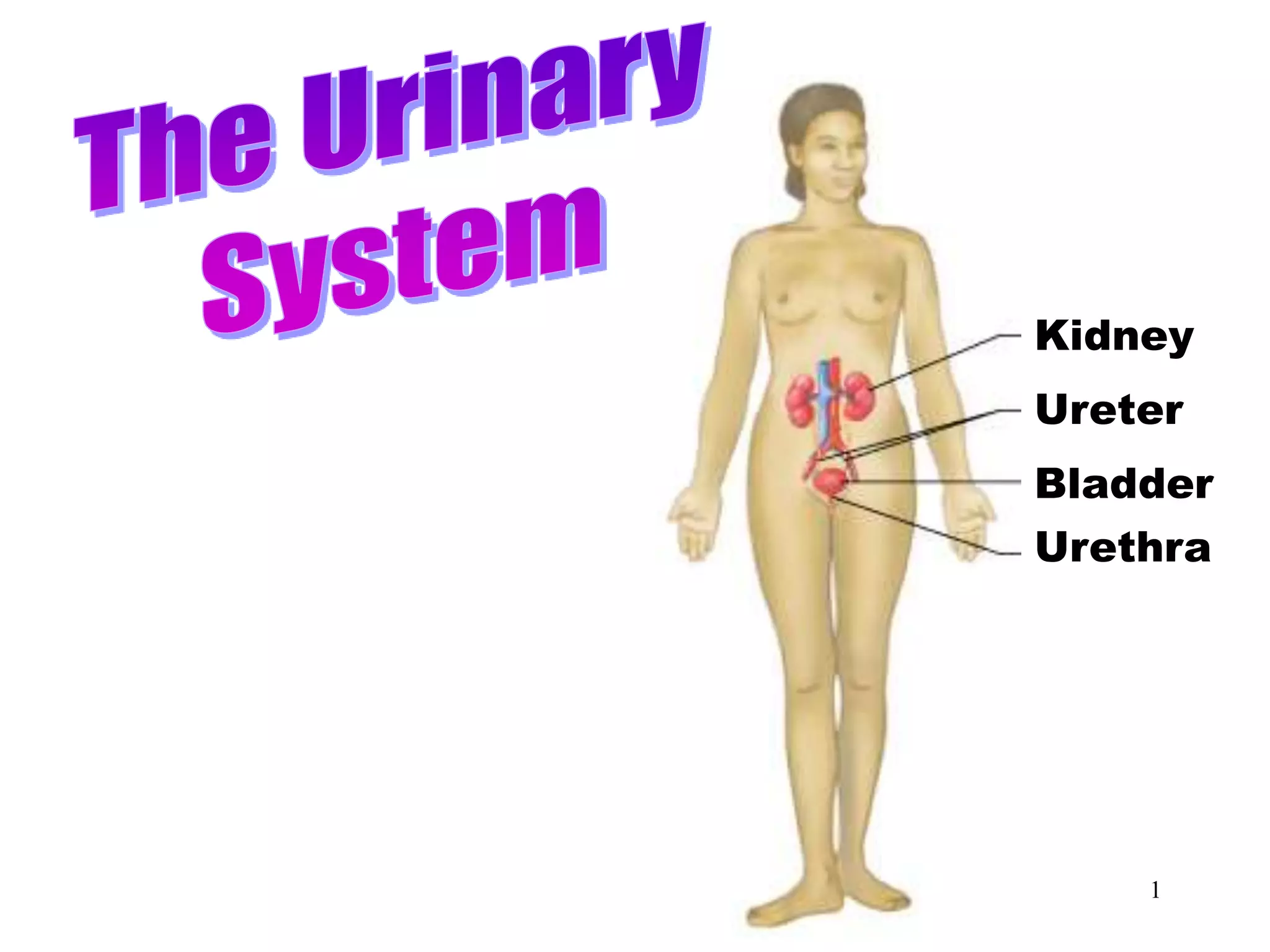
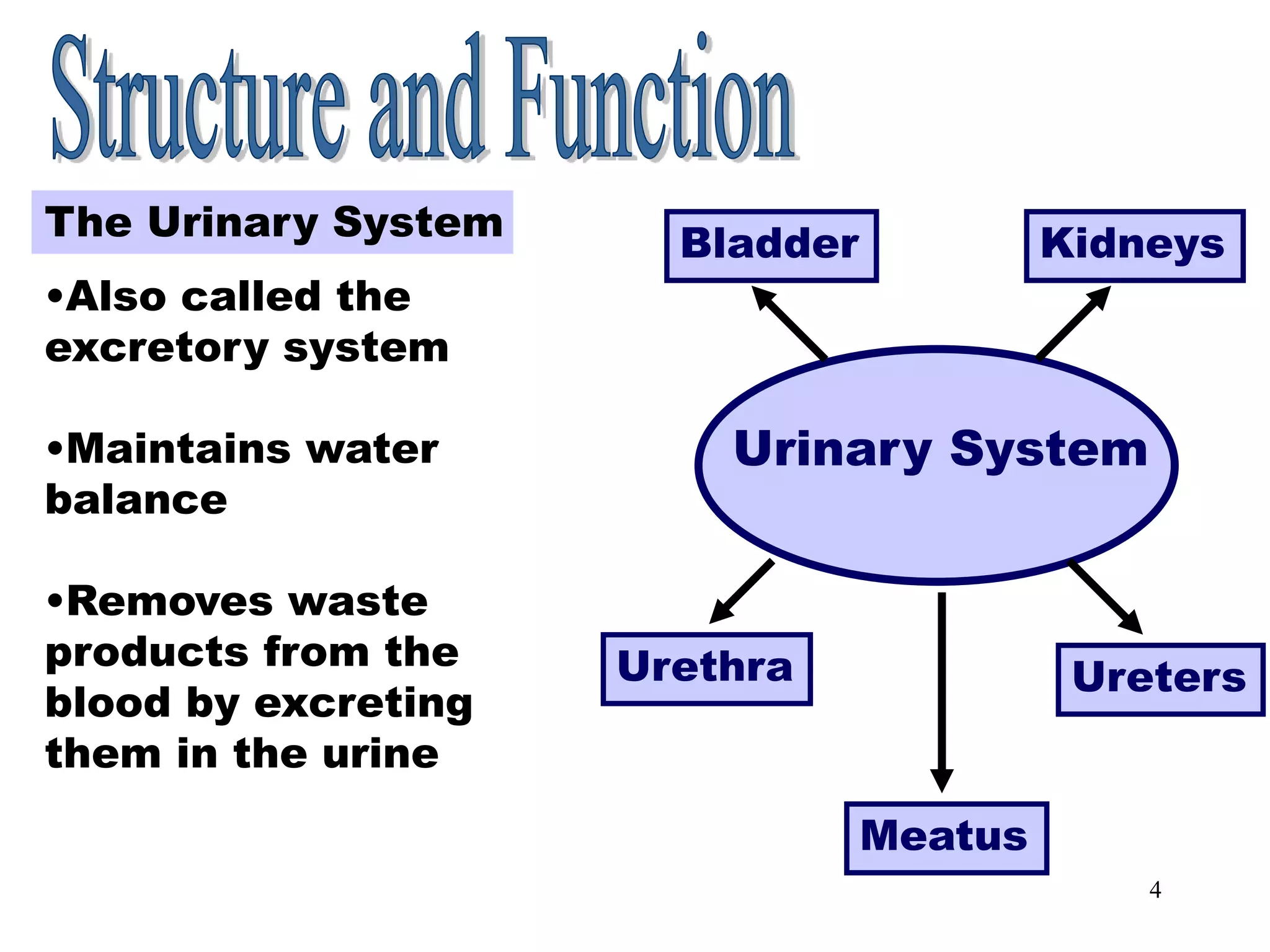
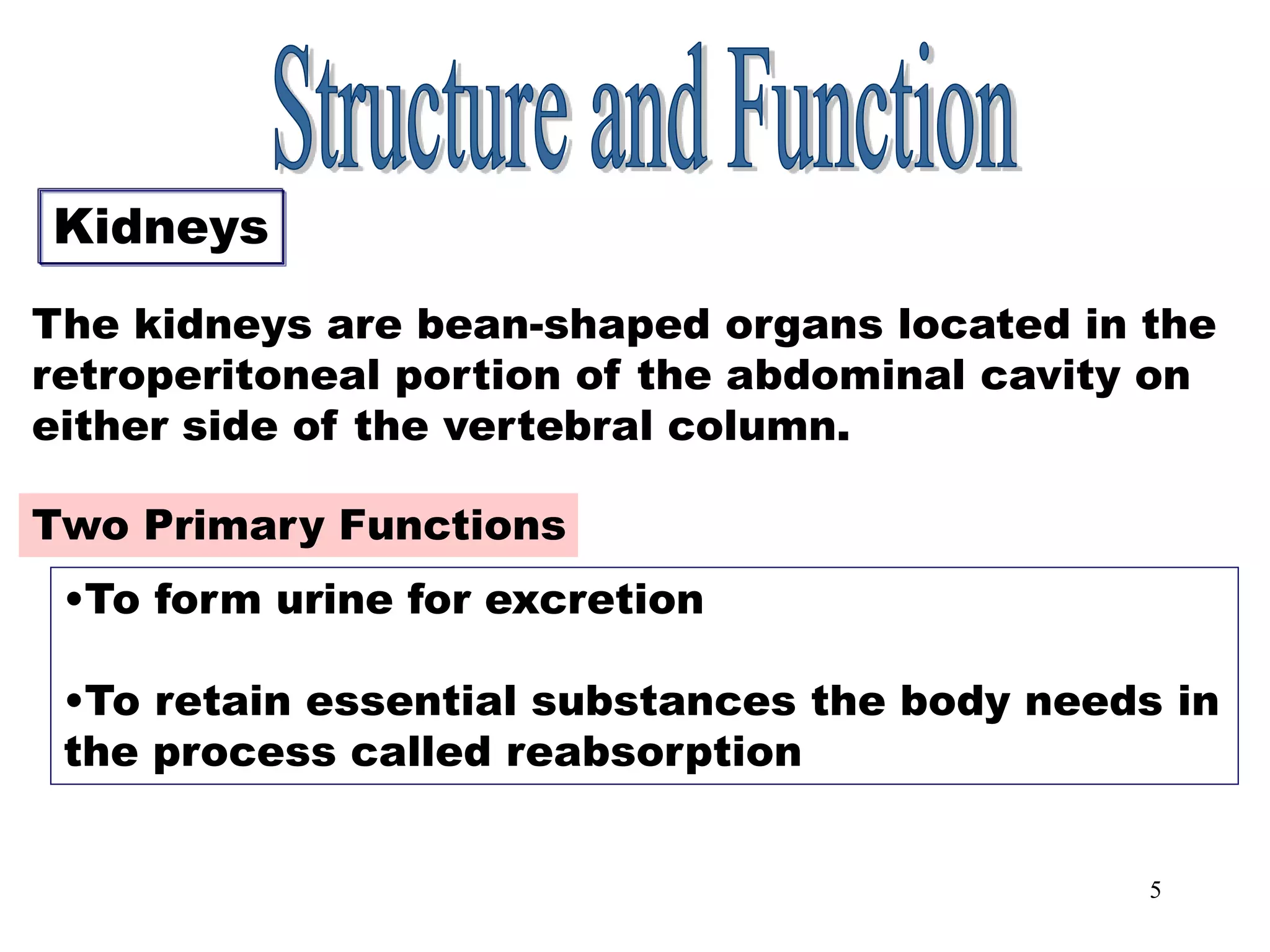
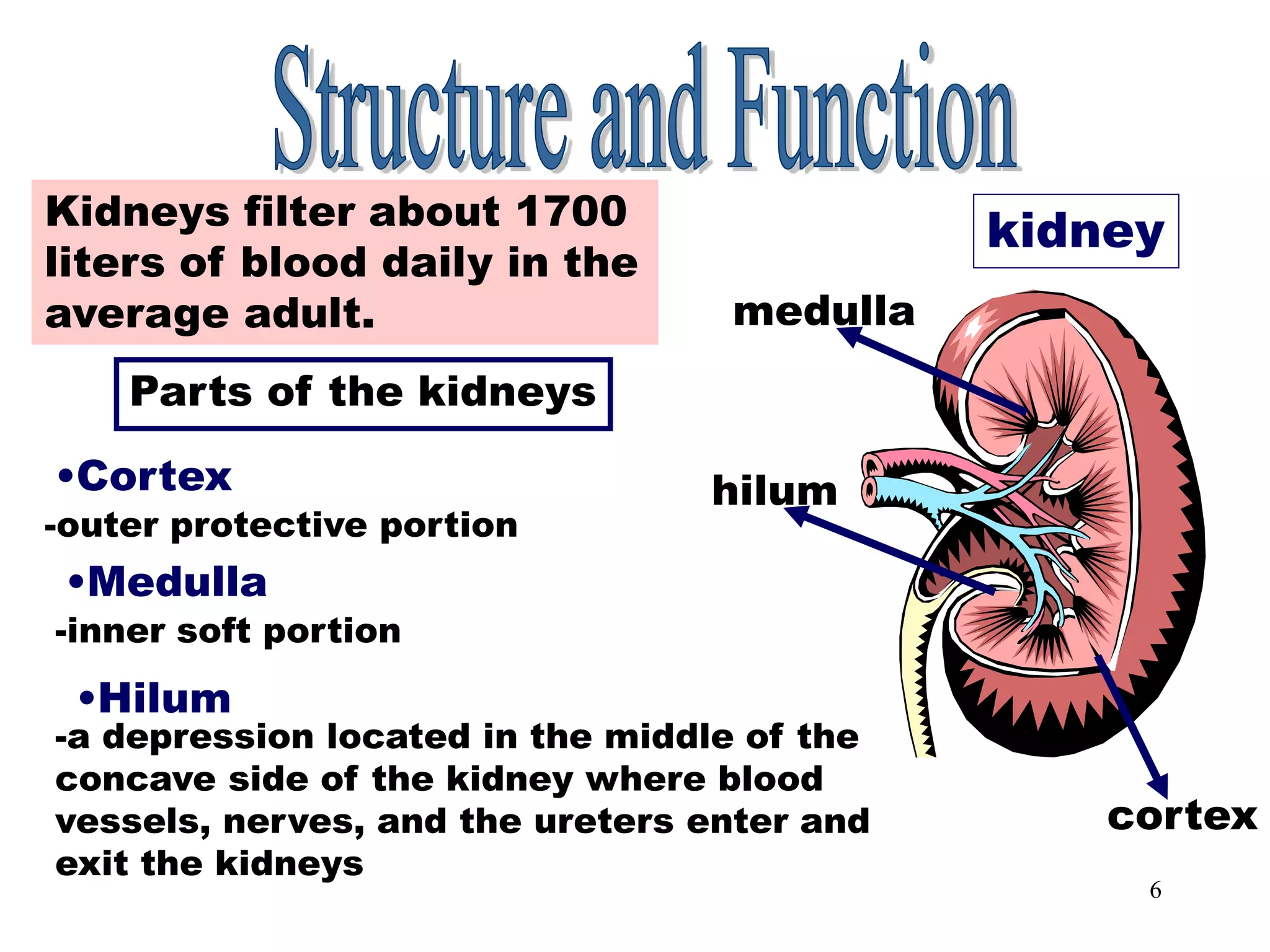
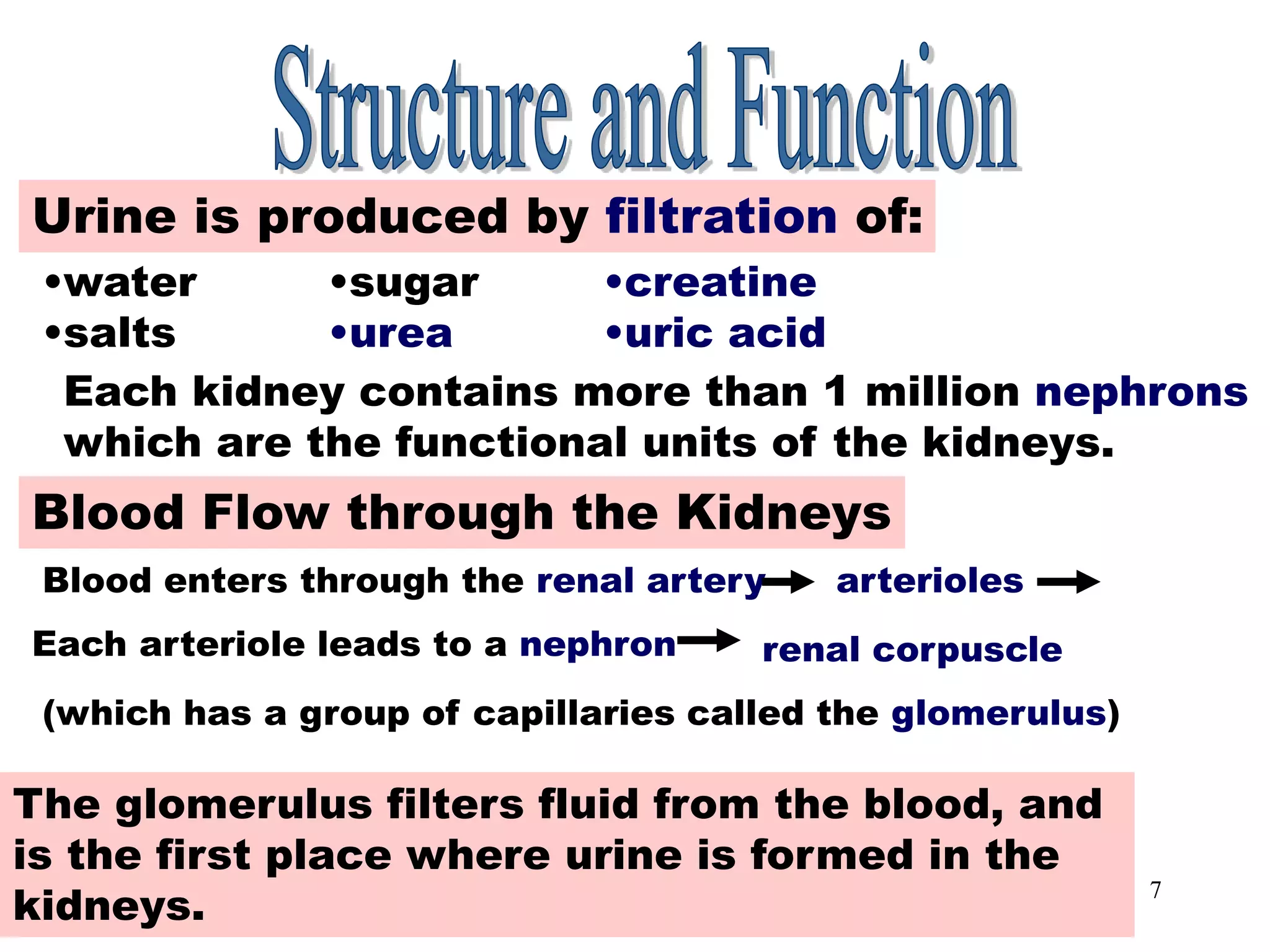
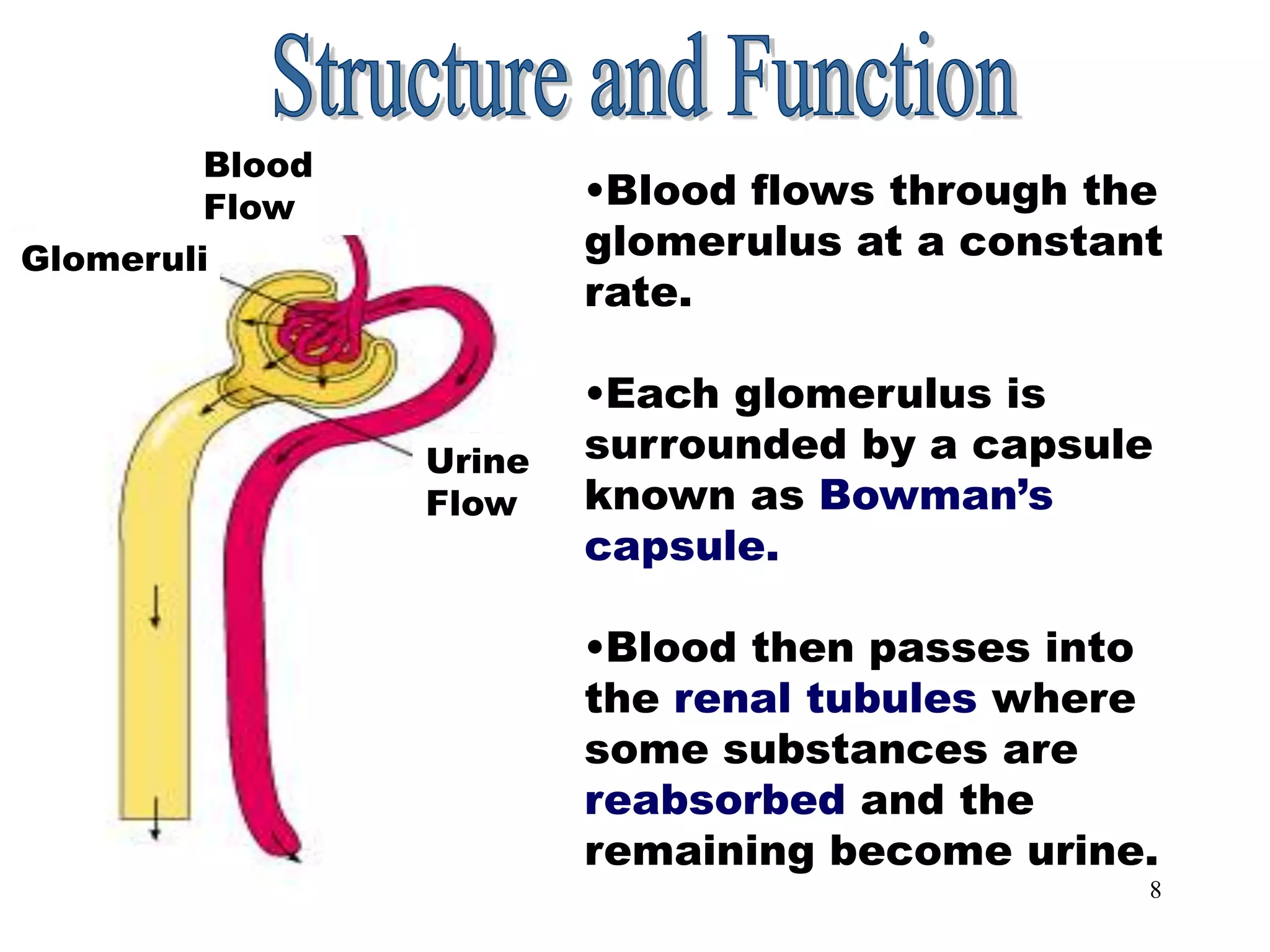
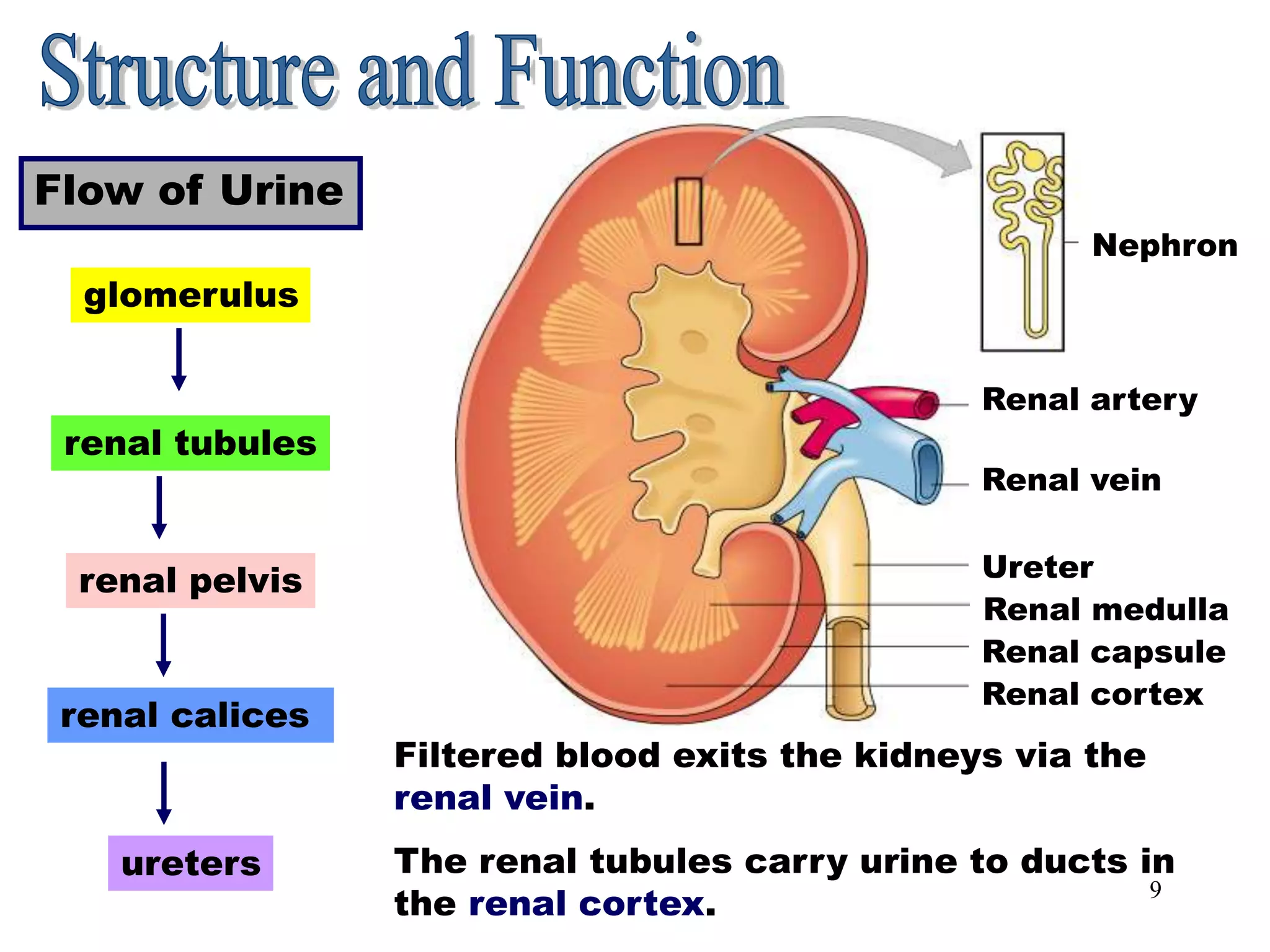
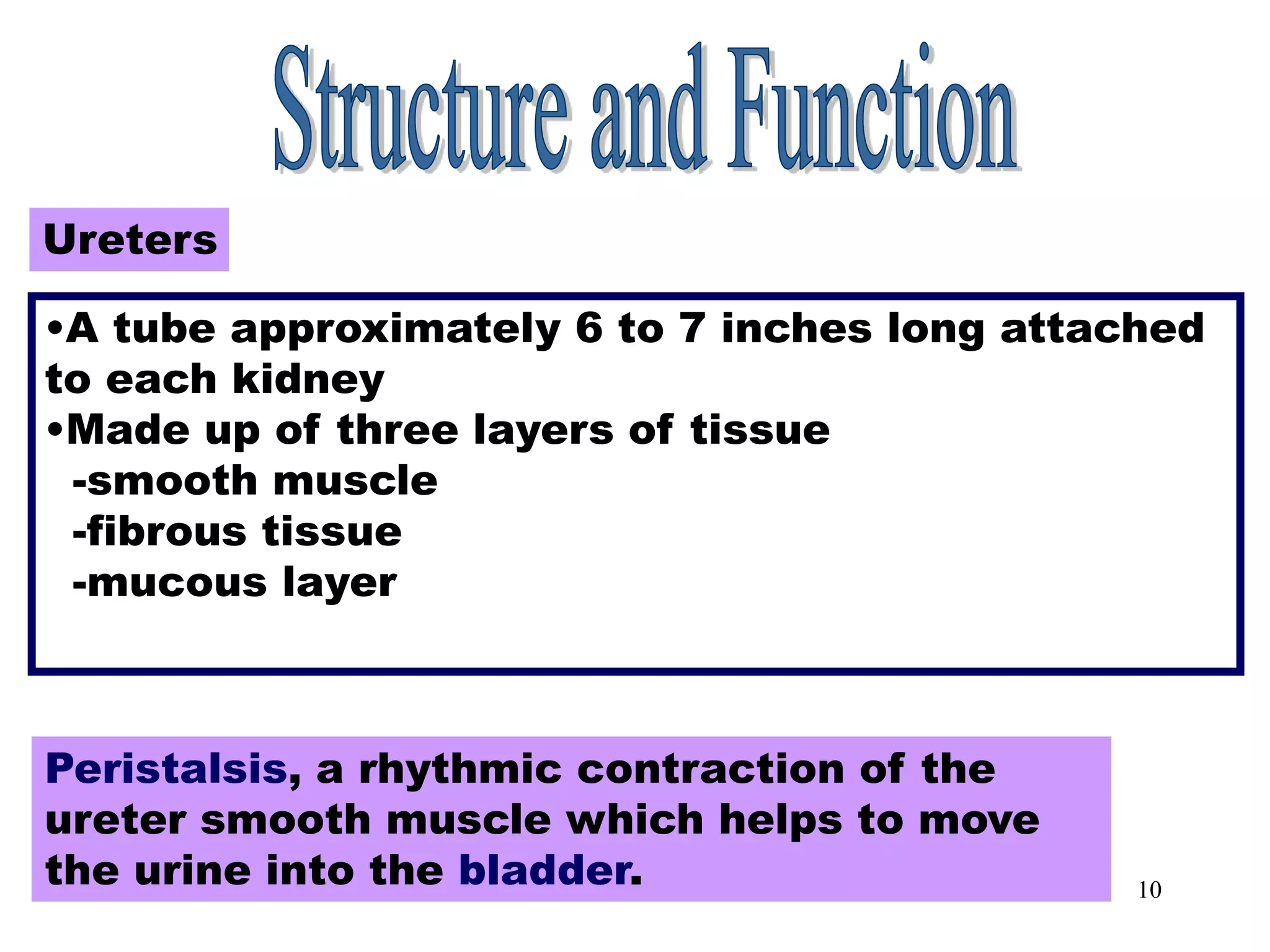
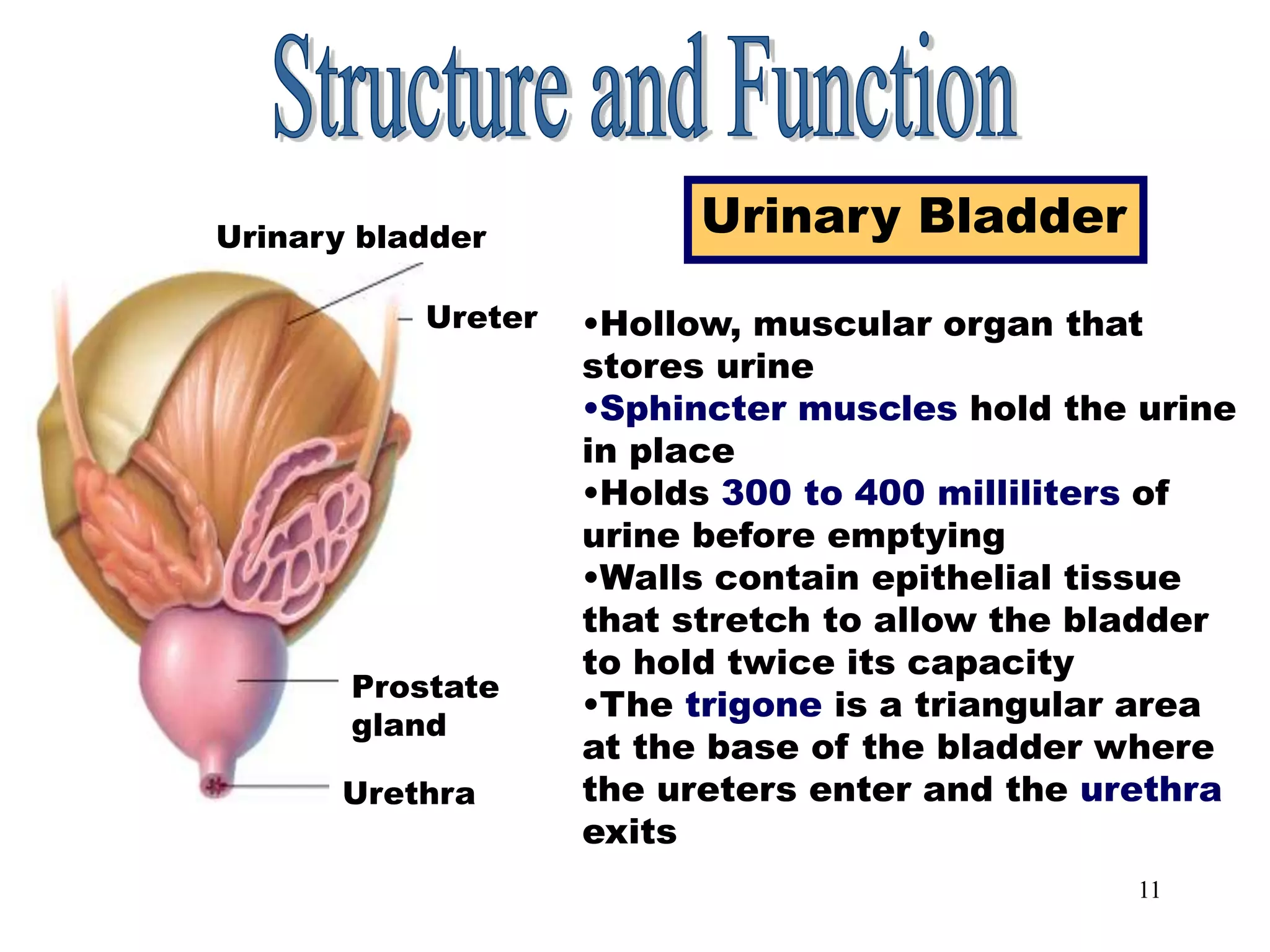
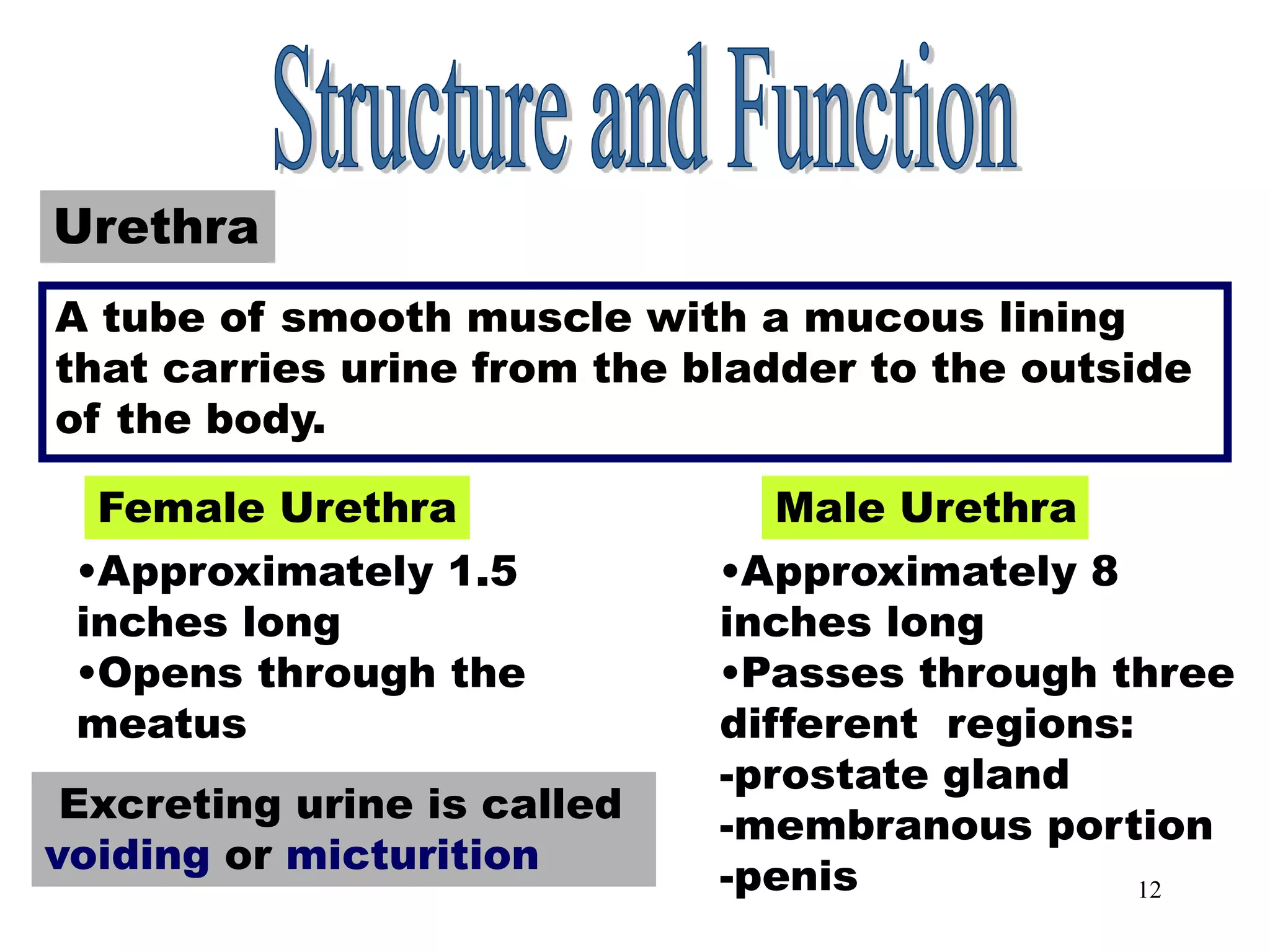
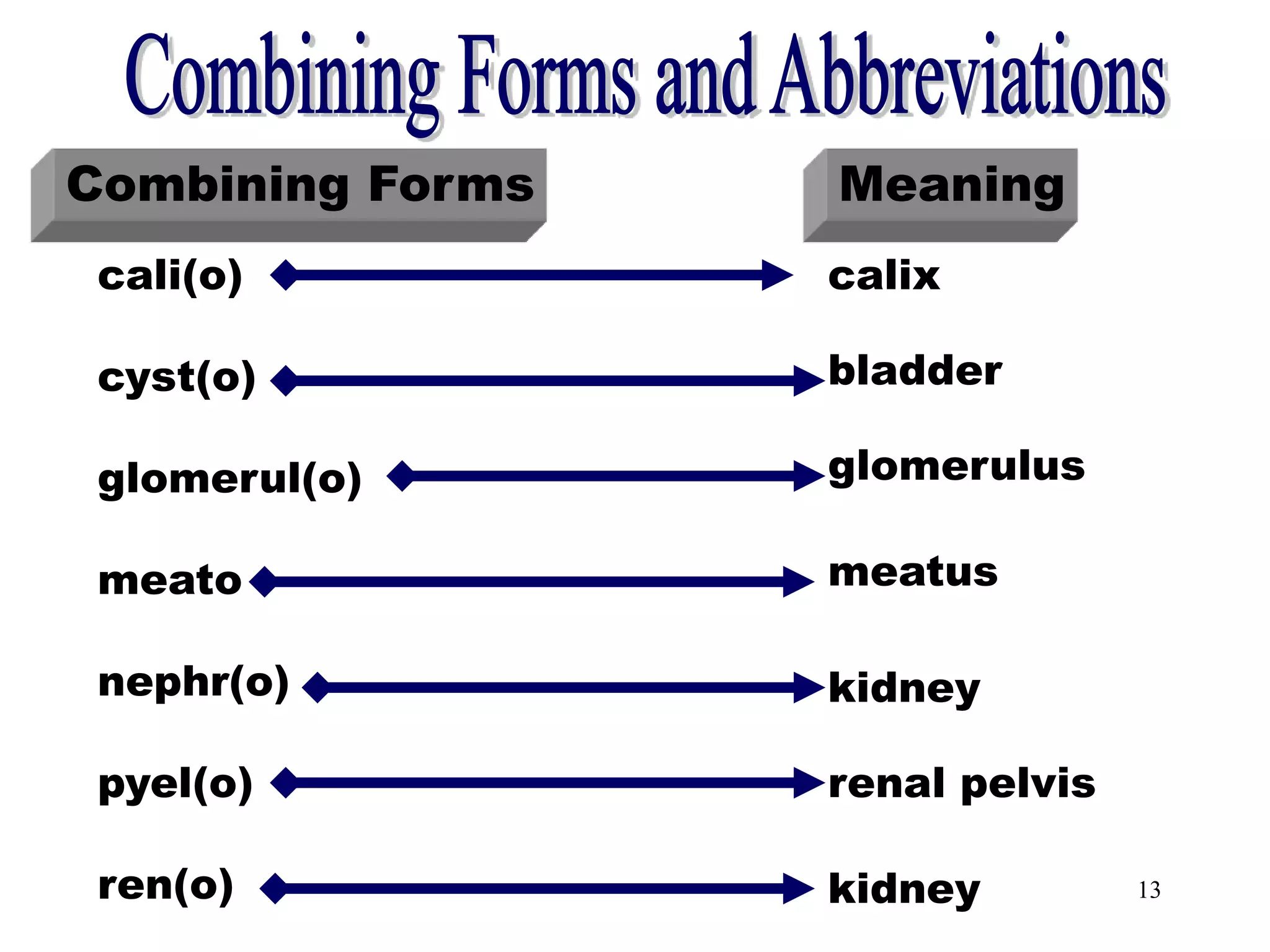
The document outlines the urinary system, including its components, functions, and related medical terminology. It details the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and covers diagnostic procedures, common disorders, and surgical procedures associated with urinary system pathologies. Additionally, it discusses pharmacological treatments and includes questions to apply the knowledge gained.


![14
Combining Forms [trigon(o)]
Combining Forms Meaning
trigon(o)
urin(o)
ureter(o)
urethr(o)
vesic(o)
trigone
urine
ureter
urethra
bladder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap09-220913100511-0ed4e1c9/75/Chap09-ppt-14-2048.jpg)
![15
Combining Forms [ADH]
Abbreviation Meaning
ADH
A/G
AGN
ARF
ATN
BNO
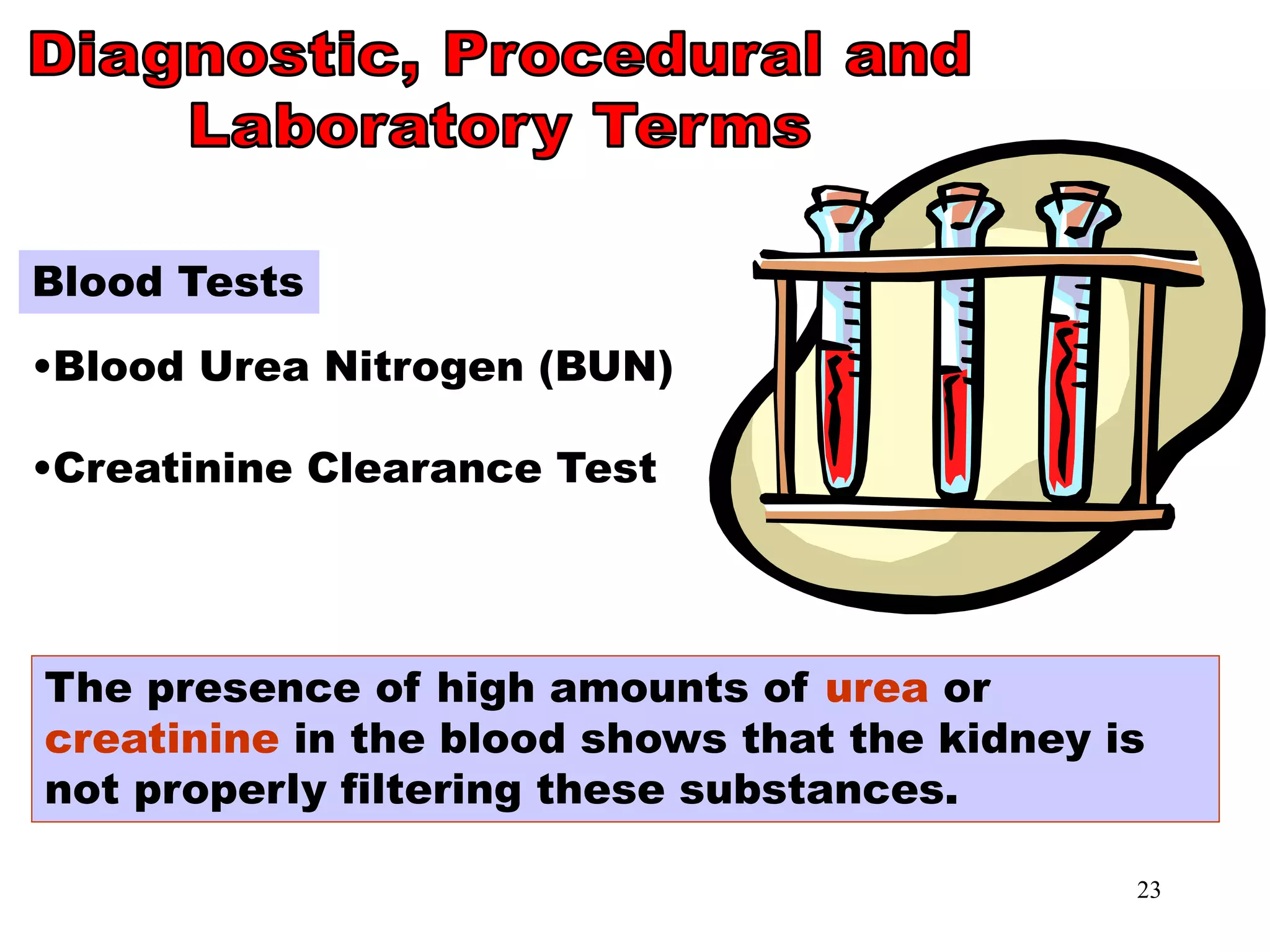
BUN
antidiuretic hormone
albumin/globulin
acute glomerulonephritis
acute renal failure
acute tubular nephrosis
bladder neck obstruction
blood urea nitrogen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap09-220913100511-0ed4e1c9/75/Chap09-ppt-15-2048.jpg)
![16
Combining Forms [CAPD]
Abbreviation Meaning
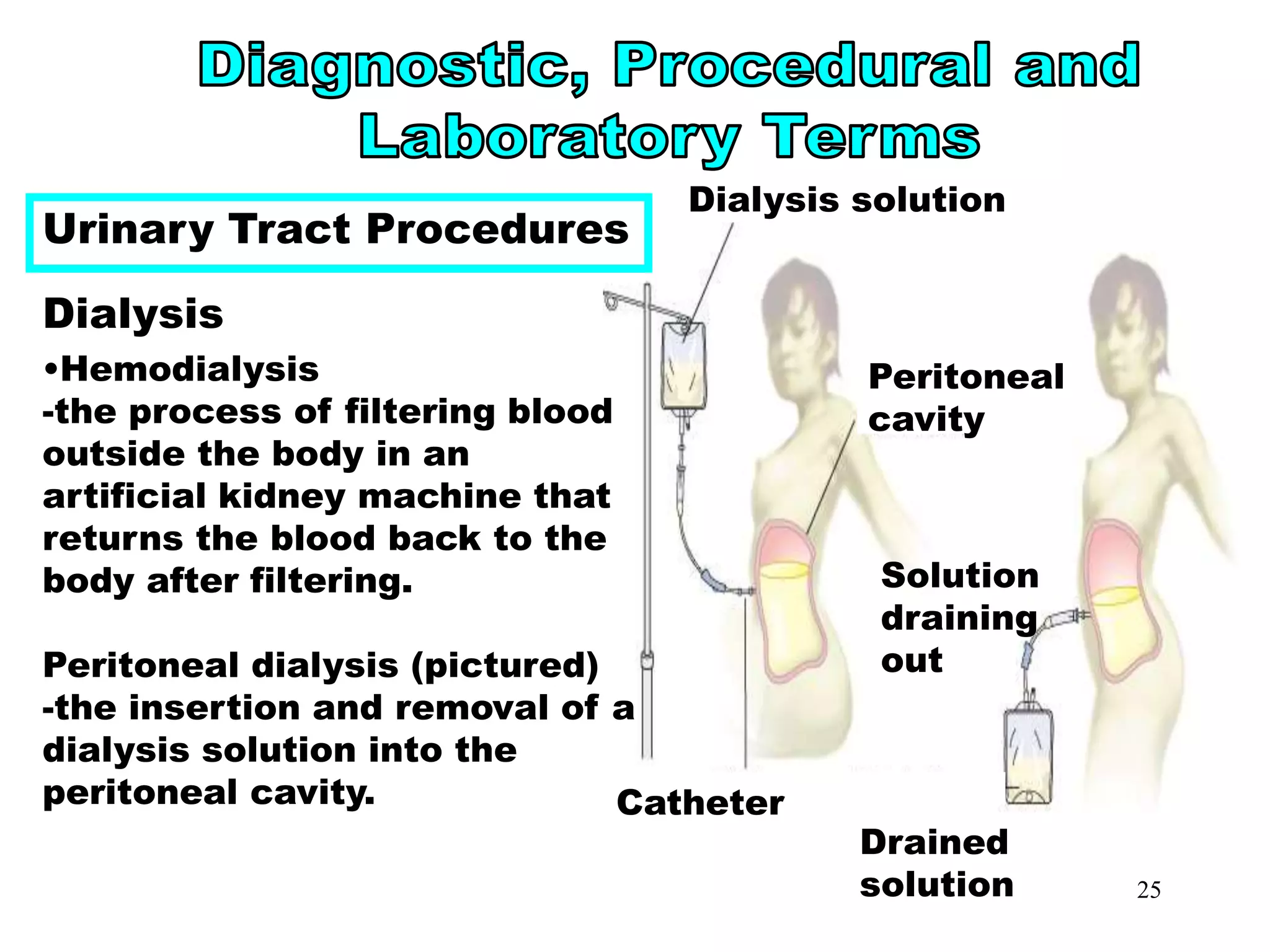
CAPD
Cath
Cl
CRF
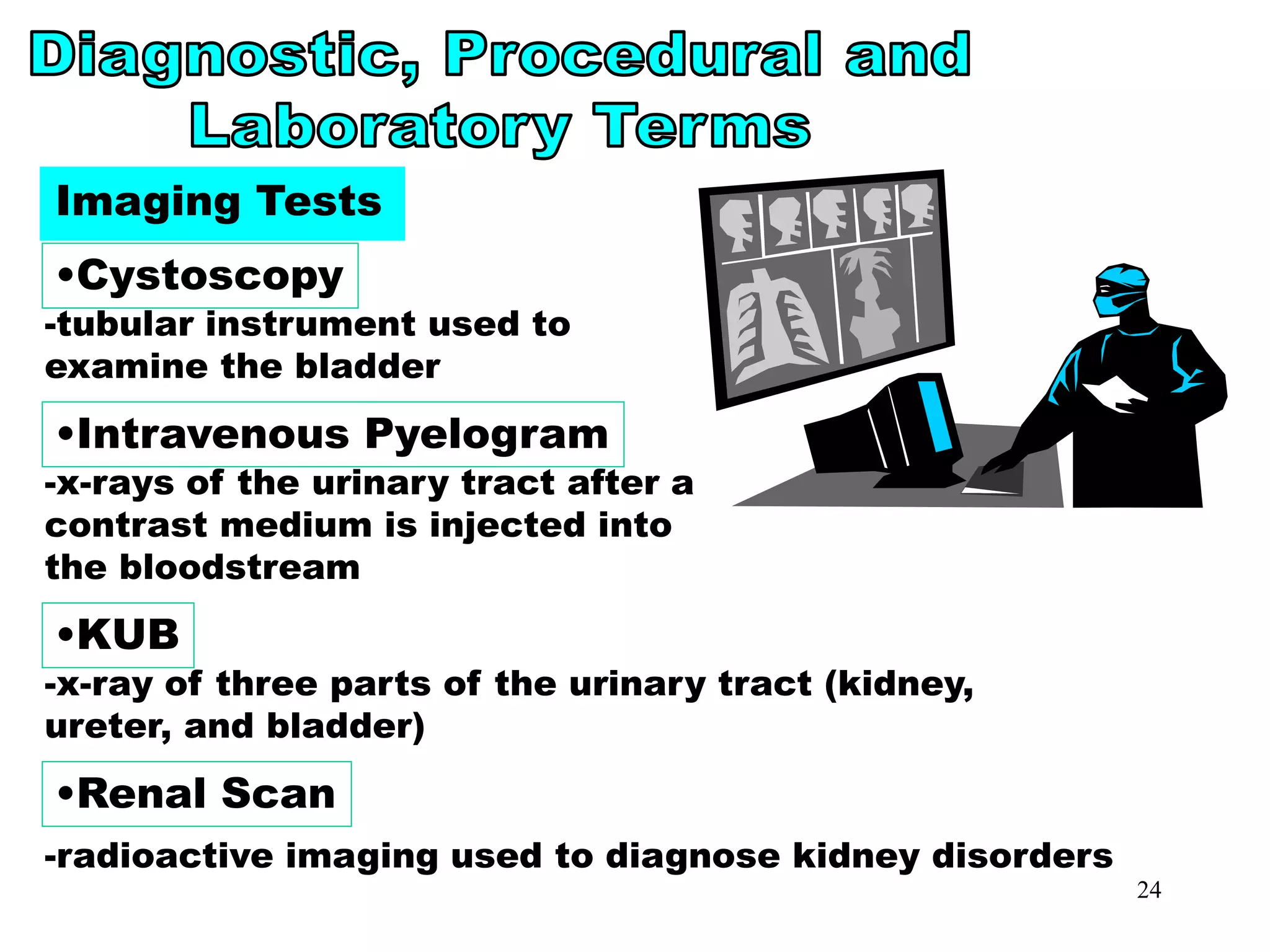
cysto
ESRD
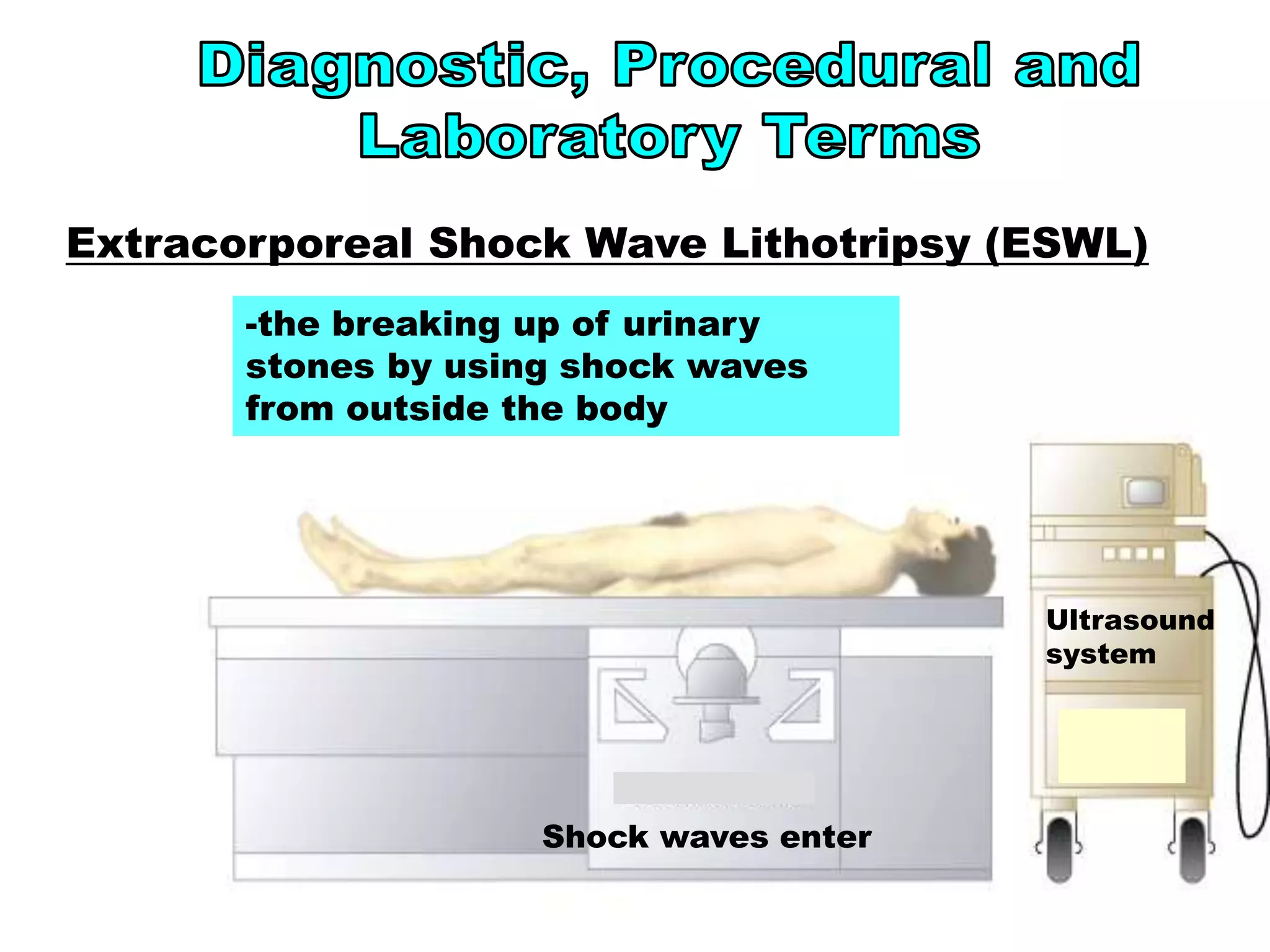
ESWL
continuous ambulatory peritoneal
dialysis
catheter
chlorine
chronic renal failure
cystoscopy
end-stage renal disease
extracorporeal shock wave
lithotripsy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap09-220913100511-0ed4e1c9/75/Chap09-ppt-16-2048.jpg)
![17
Combining Forms [HD]
Abbreviation Meaning
HD
IVP
K+
KUB
Na+
pH
PKU
hemodialysis
intravenous pyelogram
potassium
kidney, ureter, bladder
sodium
power of hydrogen
concentration
phenylketonuria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap09-220913100511-0ed4e1c9/75/Chap09-ppt-17-2048.jpg)
![18
Combining Forms [RP]
Abbreviation Meaning
RP
SG
UA
UTI
VCU
retrograde pyelogram
specific gravity
urinalysis
urinary tract infection
voiding cystourethrogram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap09-220913100511-0ed4e1c9/75/Chap09-ppt-18-2048.jpg)