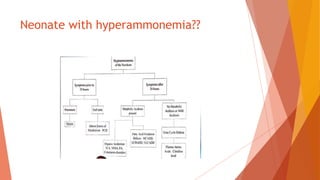
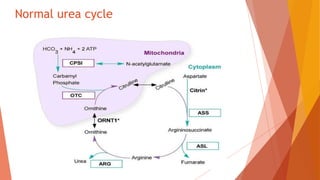
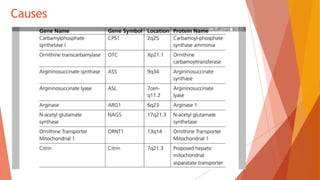
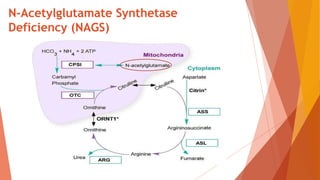
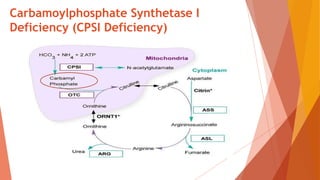
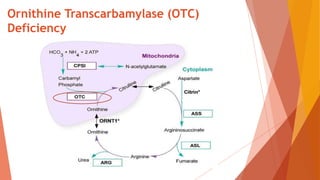
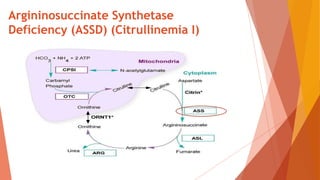
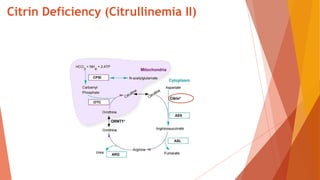
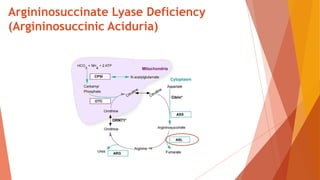
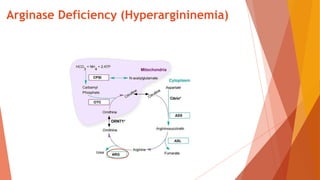
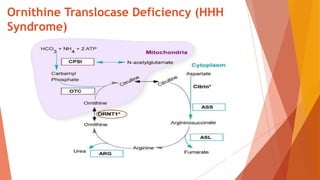
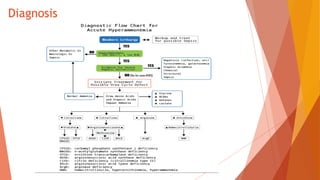
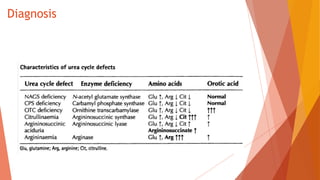
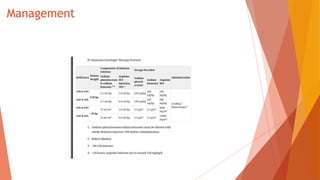
Urea cycle disorders result from defects in the metabolic pathway that converts nitrogen into urea for excretion. Symptoms range from hyperammonemia in newborns to neurological issues in older patients. Diagnosis involves measuring elevated ammonia levels and testing for specific enzyme deficiencies. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia through dialysis, nitrogen scavengers, and dietary protein restriction, as well as replacing deficient cycle intermediates. Long term management centers on minimizing nitrogen intake and promoting alternative excretion routes to prevent hyperammonemic crises.