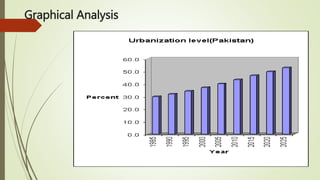
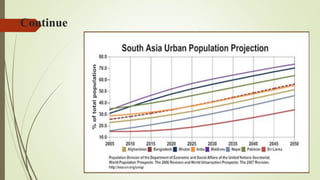
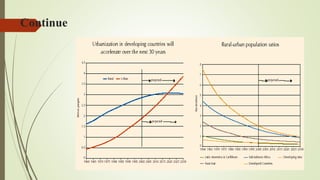
Urbanization is increasing rapidly around the world and having significant impacts on the environment. By 2050, 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. This rapid urban growth is causing problems like deforestation, air and water pollution, solid waste accumulation, and loss of agricultural land. Developing countries face more severe environmental impacts due to poor urban planning and inadequate infrastructure to handle the negative effects of urbanization. While urbanization enables economic growth, it also threatens the natural environment if not managed carefully through long-term planning and public-private partnerships that prioritize environmentally friendly development.