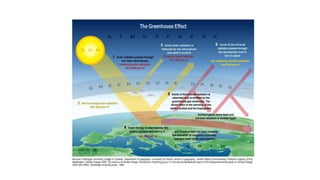
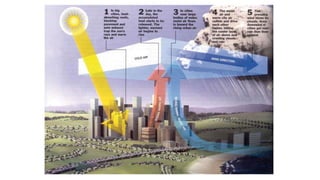
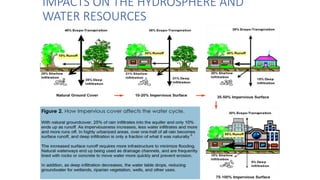
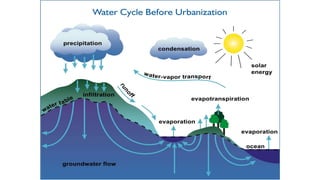
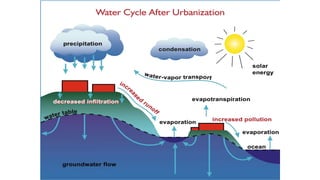
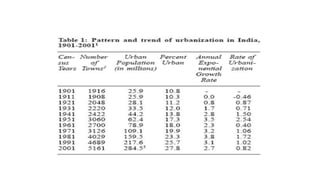
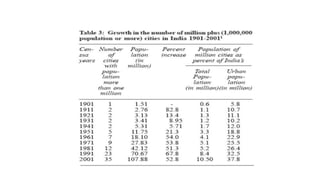
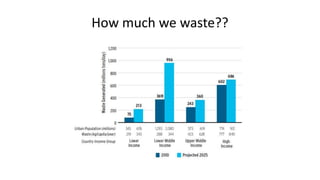
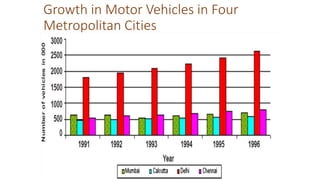
Urbanization has significant environmental impacts. It causes increased pollution in the form of greenhouse gases from fossil fuel combustion, acid rain from sulfur dioxide emissions, and degraded water quality from sewage. It also creates urban heat islands and modifies habitats. As more land is converted to urban uses, habitats are destroyed or fragmented and species are forced to adapt. Rapid urban growth in India is exacerbating these environmental problems as millions migrate to cities annually, and the urban population is expected to reach 74% of the total by 2025, placing huge demands on infrastructure and resources.