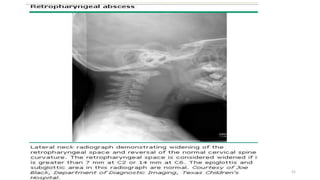
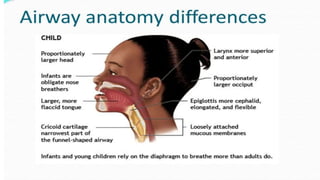
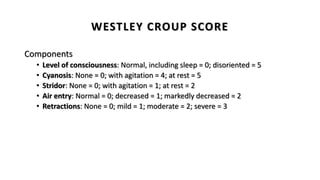
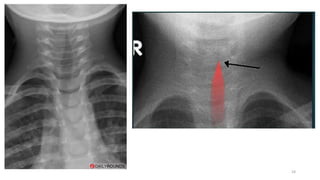
Upper airway obstruction is common in pediatric practice and can be serious. The airway is more prone to obstruction in children due to developmental anatomical features. Croup, an inflammation of the larynx and subglottic airway, is the most common cause of upper airway obstruction in children and is usually due to viral infection, most commonly parainfluenza virus. Croup presents with inspiratory stridor, barking cough, and hoarseness and is classified as mild, moderate, or severe using the Westley Croup Score to guide management and monitor for respiratory failure.






















![• Also receive supportive care including humidified air or oxygen,
antipyretics, and encouragement of fluid intake
• Dexamethasone (0.6 mg/kg, maximum of 16 mg)
• Administered by the least invasive route possible
• The oral preparation of dexamethasone (1 mg/mL) has an unpleasant taste.
• The IV preparation is more concentrated (4 mg per mL) and can be given
orally mixed with syrup.
• A single dose of nebulized budesonide (2 mg [2 mL solution] via nebulizer) is
an alternative option.
26
CROUP CONT…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtoupperairwayobstruction-180926121458/85/Approach-to-upper-airway-obstruction-26-320.jpg)