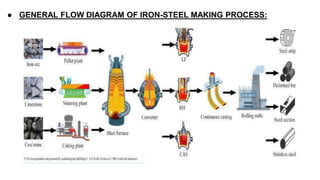
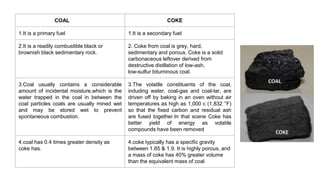
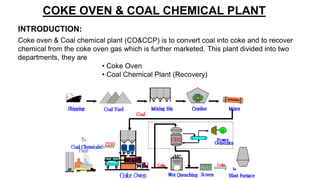
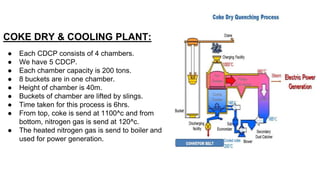
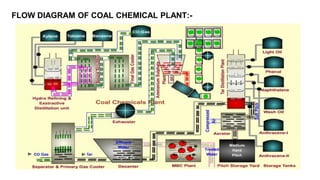
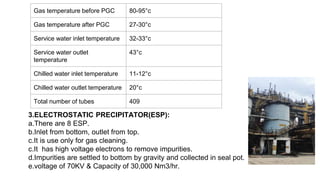
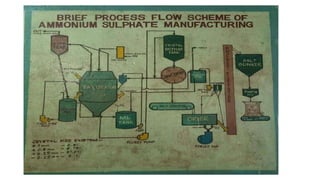
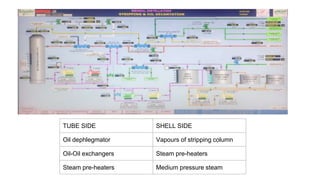
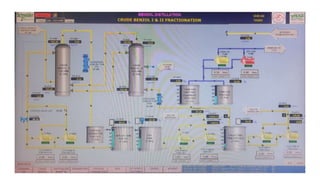
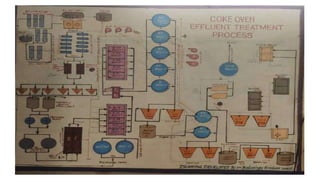
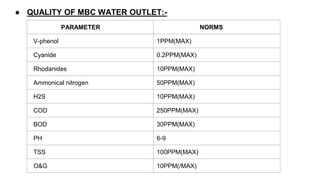
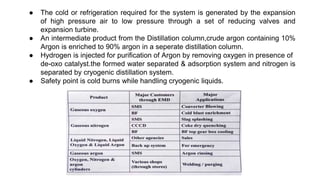
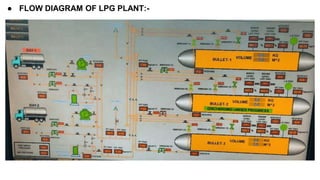
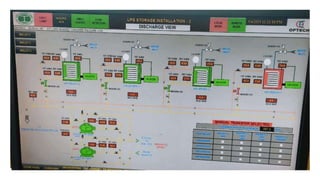
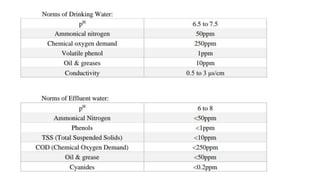
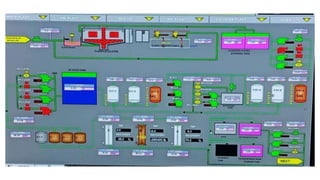
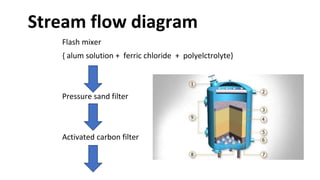
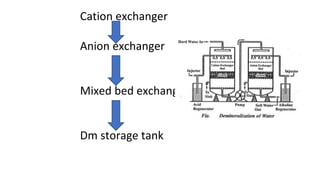
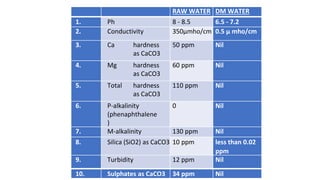
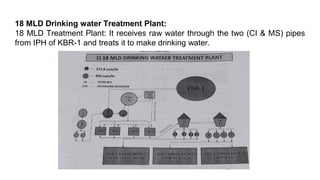
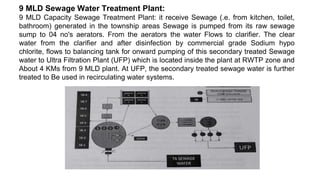
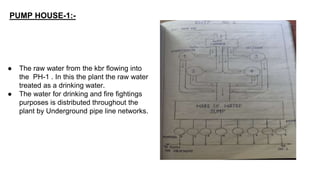
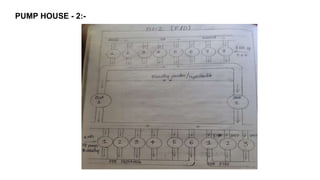
Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited (RINL) owns and operates Visakhapatnam Steel Plant (VSP), India's first shore-based integrated steel plant. VSP has a production capacity of 7.3 million tonnes per annum. The plant uses iron ore, coke, dolomite and limestone as raw materials and employs various processes like coke making, sintering, blast furnace production, and rolling mills to produce finished steel products. Trainees can receive on-site training in departments like coke ovens, utilities, quality control, power plant and water management.