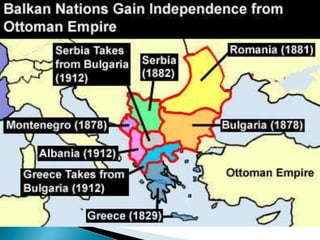
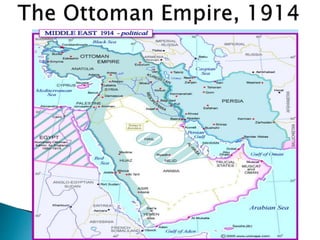
The document provides information about the Industrial Revolution:
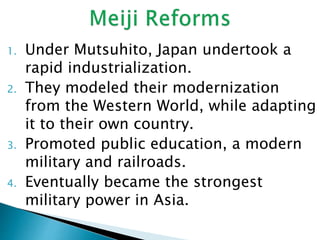
1. It began in Great Britain due to their natural resources and large population. Changes in agriculture and population growth created a large labor force for new factories.
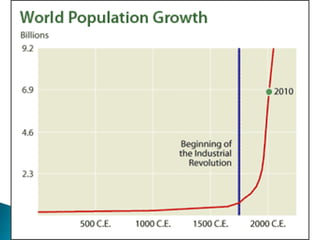
2. The increased food supply led to rapid population growth, providing more workers for factories. British colonies also provided new markets for manufactured goods.
3. The key resources needed for an industrial country were land, labor, and capital (wealth). New inventions like the spinning jenny and flying shuttle automated cotton production. Factories employing machines proliferated.