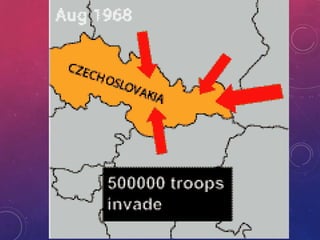
The document summarizes key events in the decline and fall of the Soviet Union. It describes the leadership of Brezhnev and his expansion of state control over citizens. It then discusses Gorbachev's reforms of glasnost and perestroika that gave citizens more freedoms and autonomy but also weakened central control. As reforms took hold, Soviet republics began demanding independence, which was accelerated after Yeltsin took power in Russia and declared independence, formally dissolving the USSR by the end of 1991.