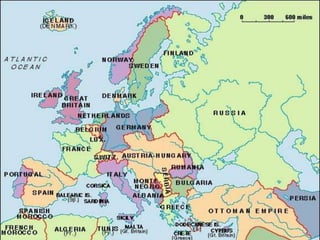
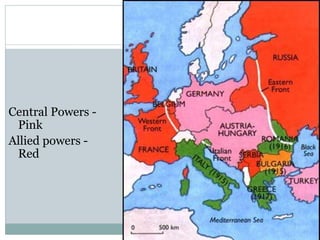
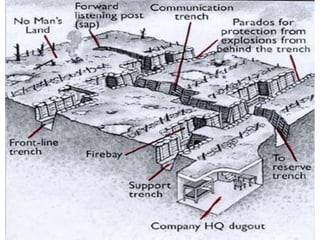
This document provides an overview of the topics and activities to be covered in a World History Honors class about World War I. It begins with a recap of the previous unit covering Industrialism, Nationalism, and Imperialism. It then outlines the day's lecture on WWI, including causes such as militarism, the Triple Alliance and Triple Entente, and the specific incident that sparked the war. Details are given on the new technologies of warfare and trench warfare on the Western Front. A short video is assigned for students to summarize about life in the trenches. The class period ends with assignments to label an Allied/Central Powers diagram and begin a timeline of significant WWI dates.