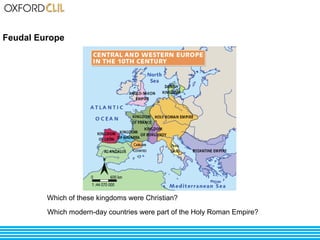
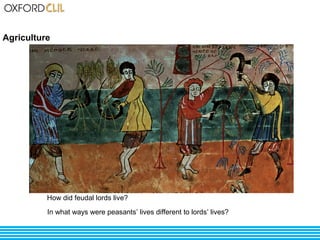
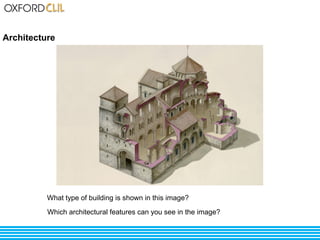
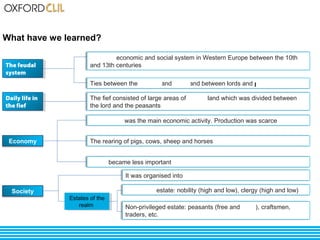
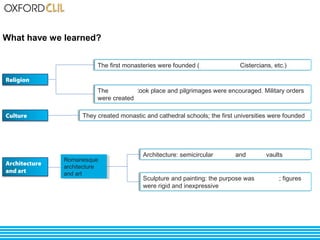
The document discusses life and society in feudal Europe between the 10th and 13th centuries. It describes the political, economic, and social system of feudalism, including the relationship between vassals and lords and between lords and peasants. Agriculture was the main economic activity, with peasants farming the lands of feudal lords in exchange for protection. Society was organized into estates including nobility, clergy, peasants, and craftsmen. Religion played a large role in culture and architecture during this period.