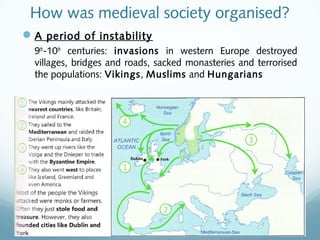
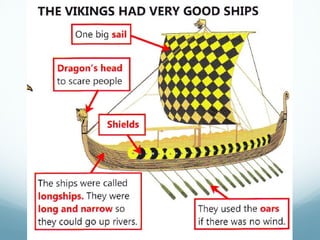
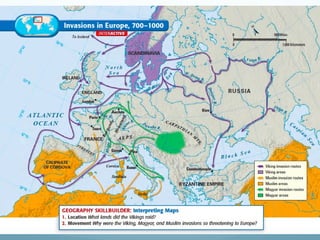
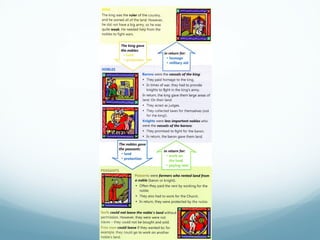
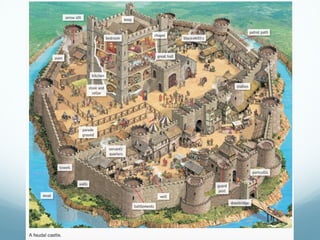
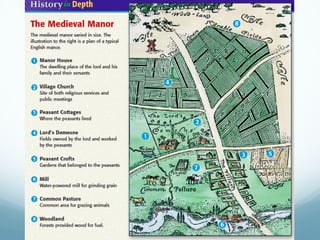
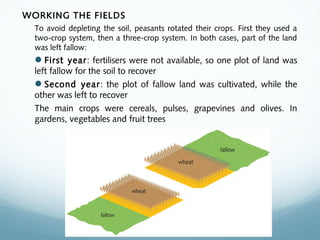
Feudal Europe was organized into a hierarchical feudal system following invasions in the 9th-10th centuries. Monarchs relied on nobles for protection and armies in exchange for land and power. Peasants pledged allegiance to nobles in exchange for protection and became serfs working the nobles' lands. Society was stratified with nobles and clergy owning most land and peasants working to support them. The system established relationships of loyalty between lords and vassals up to the king, though nobles often rebelled.