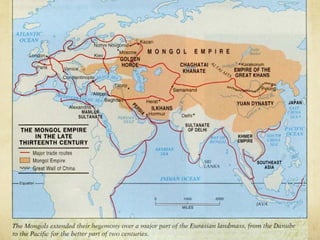
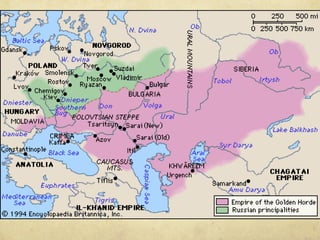
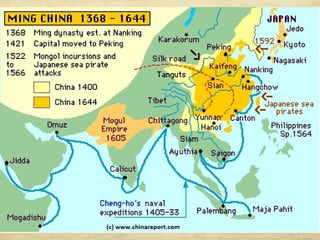
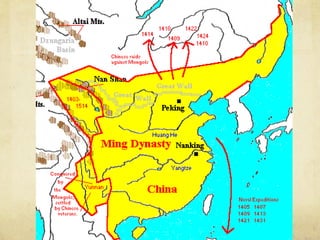
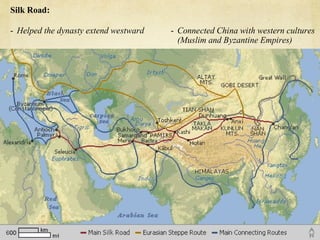
The document summarizes the origins and impacts of the Mongol Empire and Ming Dynasty in China. It discusses how Genghis Khan unified the Mongols and expanded their empire across Asia and into Eastern Europe. While the empire fragmented after Kublai Khan's death, the Mongols introduced Chinese culture and governance concepts to Russia and isolated it from Western Europe. The document also outlines the Ming Dynasty that replaced the Mongols in China and reasserted Chinese dominance, as well as cultural contributions from China, India, and Japan that still influence modern society, such as decimal numbers, gunpowder, and Buddhism.