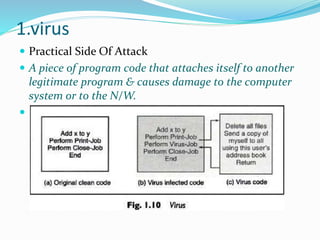
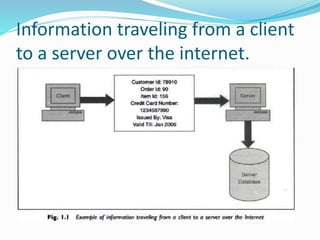
This document discusses various aspects of information security. It begins by explaining how recent events show that commercial, personal, and sensitive information is difficult to keep secure. An estimated 80% of data breaches are caused by staff rather than technical issues. Effective information security requires a management approach rather than just technical solutions. The document then outlines key principles of information security including confidentiality, integrity, authentication, non-repudiation, access control, and availability. It provides examples to illustrate these principles and how losses can occur when they are compromised or violated. Finally, it discusses the importance of security policies and techniques such as cryptography and authentication to help control threats and restrict unauthorized access.















![Principle/Goals Of Security
These r the 4 chief principles of security.
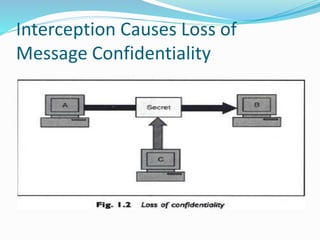
1. Confidentiality:- Is msg seen by someone else?
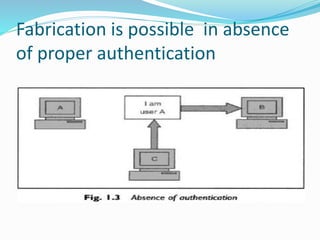
2. Authentication:- Do u trust the sender of msg?
3. Integrity:- Is the meg changed during transmit?
4. Non-repudiation:- Can sender refute the msg?
Above principles r related to a particular message.
There r 2 more linked to overall system as a whole.
5. Access Control:- Who can Access what? [ACL]
6. Availability:- Information should be available timely.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-1-is1-230212165508-2a28bd58/85/unit-1-is1-pptx-17-320.jpg)