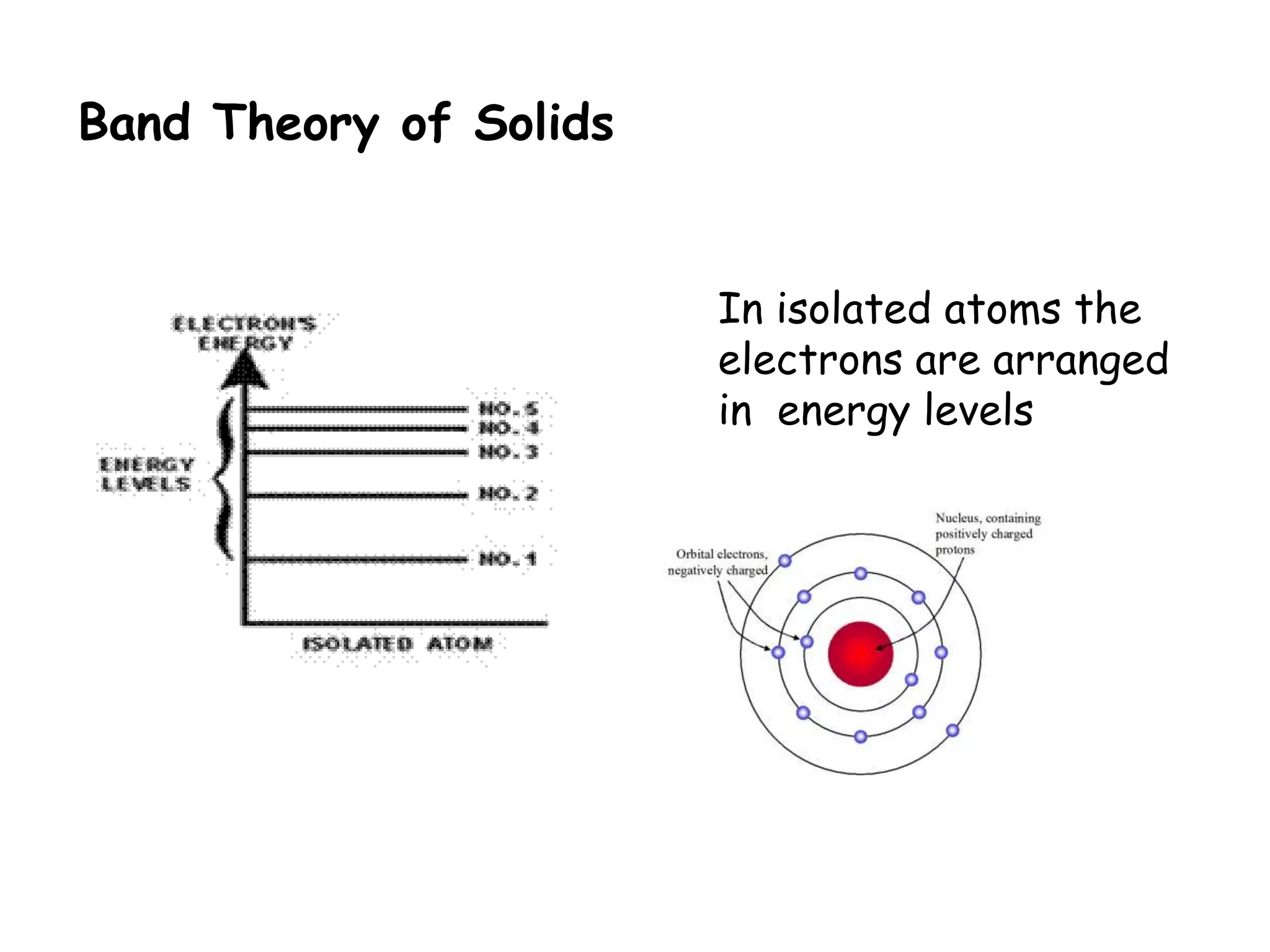
1) Band theory explains how materials can be conductors, insulators, or semiconductors based on their electron band structure.
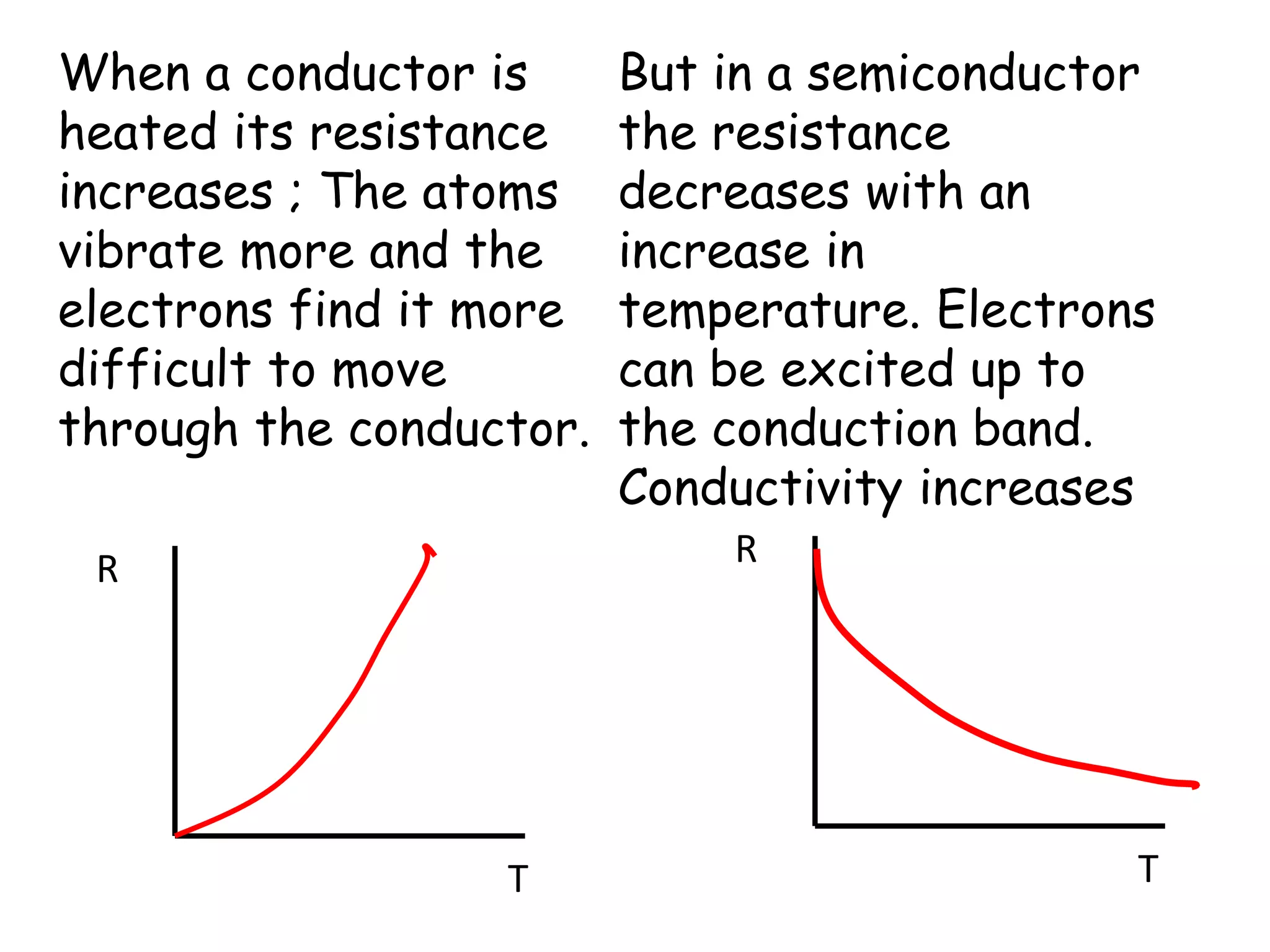
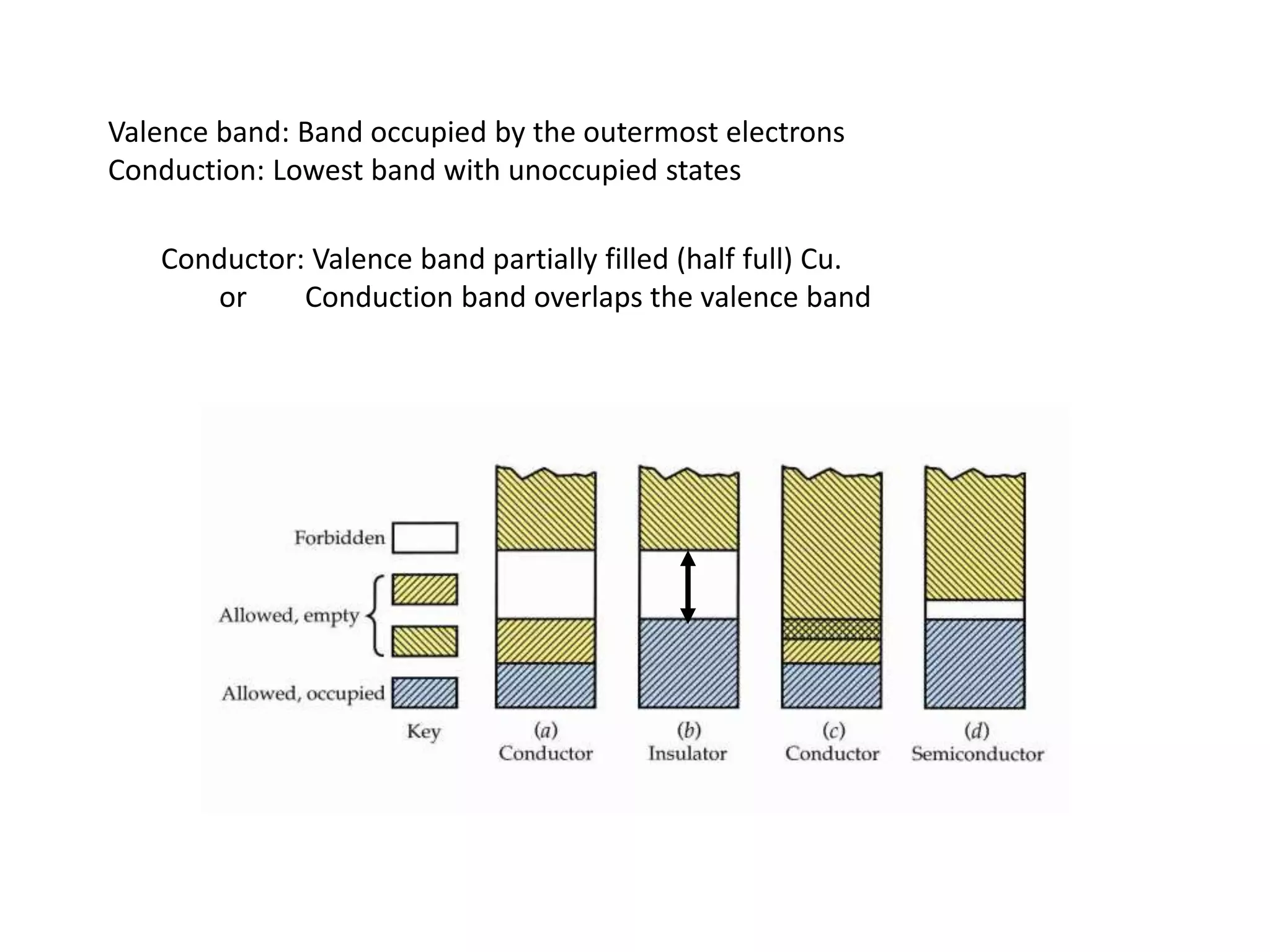
2) Conductors have overlapping or partially filled valence and conduction bands, allowing electrons to move freely. Insulators have a large gap between bands, preventing electron movement.
3) Semiconductors have a small gap that thermal energy can overcome, exciting some electrons into the conduction band and allowing some current flow.