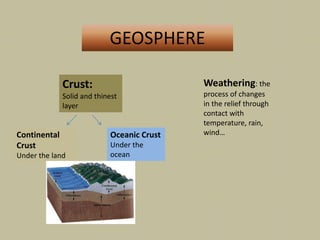
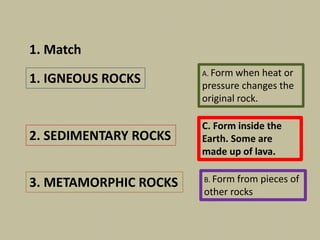
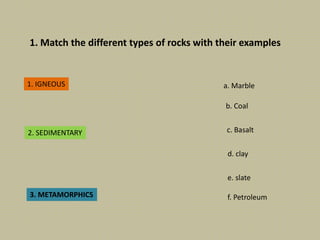
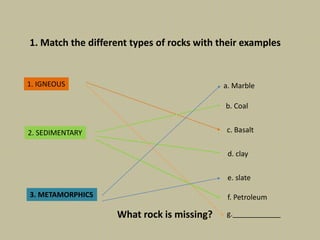
This document discusses rocks and landscapes. It describes the different layers of the Earth including the geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. The geosphere is divided into the crust, mantle, and core. The crust includes the continental crust under land and oceanic crust under the oceans. Rocks form the solid part of the Earth and can be igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. Igneous rocks such as granite form inside the Earth, sedimentary rocks like clay form from pieces of other rocks, and metamorphic rocks like marble form from heat or pressure changing original rocks. Rocks have various uses including providing energy through petroleum and building materials like marble and slate.