1. The document discusses the basic components and concepts of digital communication systems including transmitters, channels, receivers, transceivers, attenuation, noise, and types of electronic communication such as simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex.
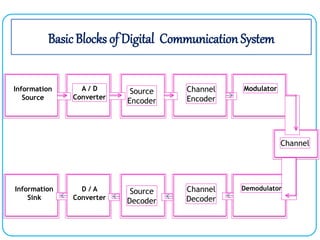
2. It also summarizes the basic blocks of a digital communication system including information sources, analog-to-digital conversion, source encoding, channel encoding, modulation, demodulation, channel decoding, source decoding, and digital-to-analog conversion.
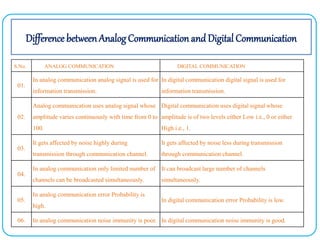
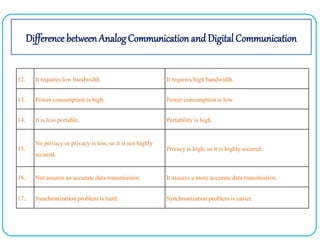
3. The key advantages of digital communication over analog communication are discussed such as ease of regeneration, noise immunity, error detection and correction capabilities, ability to multiplex signals, security, and flexibility of the system