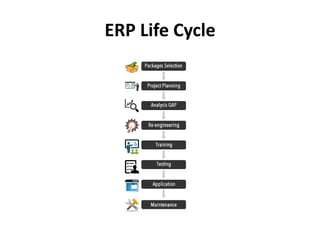
The ERP implementation life cycle involves several key stages: 1) selecting a suitable ERP package, 2) planning the implementation project, 3) analyzing any gaps between the current and desired systems, 4) reengineering business processes, 5) training employees, 6) testing the new system, 7) applying the new system, and 8) maintaining the system after implementation. Going through each stage of the life cycle carefully is important for a successful ERP project.