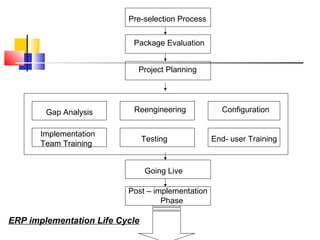
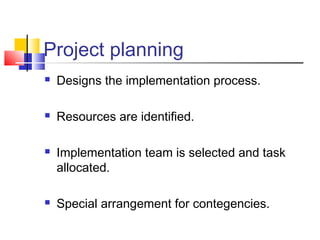
The document outlines the key phases in an ERP implementation life cycle. It begins with pre-evaluation screening to select suitable ERP packages. Next is a package evaluation to select the best package based on parameters like user friendliness and cost. A project plan is then made involving gap analysis, reengineering, and team training. Testing is followed by going live, end user training, and post-implementation maintenance. The goal is for organizations to maximize value by successfully adopting and effectively using the new ERP system.