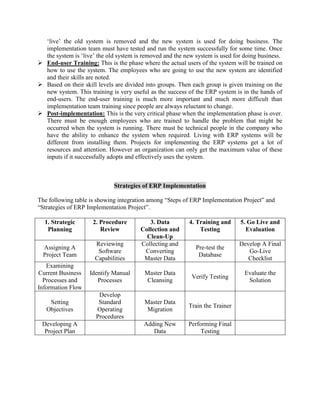
An ERP implementation project involves many complex phases and challenges to manage. The key phases include planning, gap analysis, configuration, testing, training, and post-implementation support. Some of the top challenges include the large project size, staffing issues, risk management, and organizational politics. Successful ERP implementations require strong executive support, focused project management, thorough testing and training, and change management to address resistance to the new system.