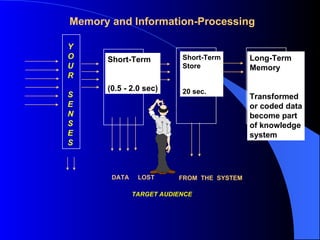
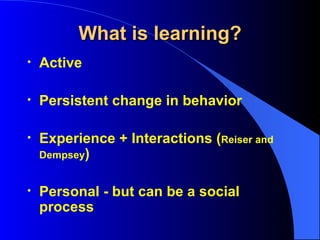
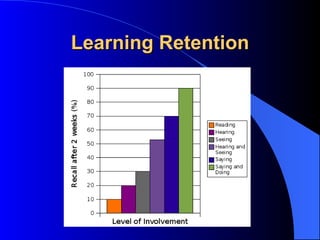
The document discusses instructional design unit 4 and learning theories. It provides an overview of conducting client surveys, with examples given. It also outlines the three domains of learning: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. Three learning theories - behaviorism, cognitive psychology, and constructivism - are explained in terms of their implications for instructional system design. Problem-based learning is also introduced as compatible with a constructivist approach.