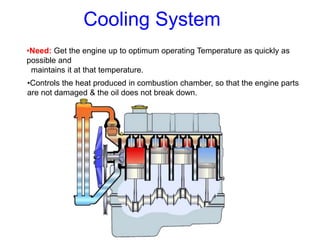
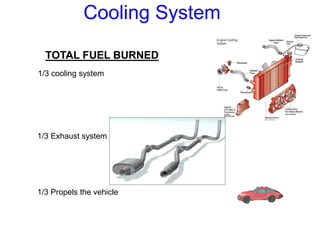
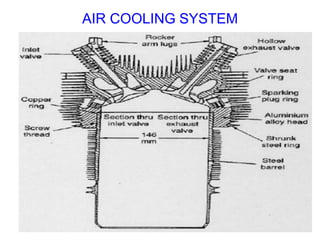
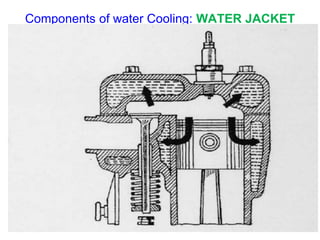
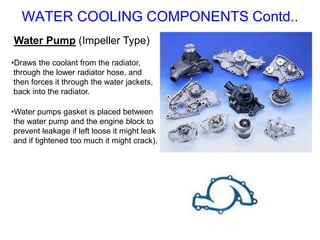
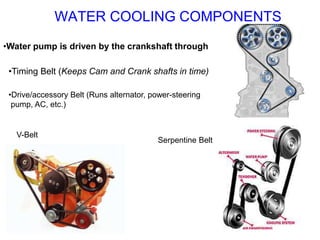
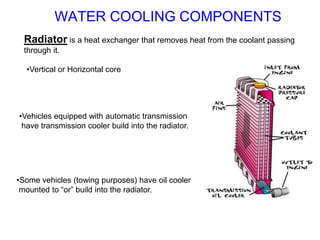
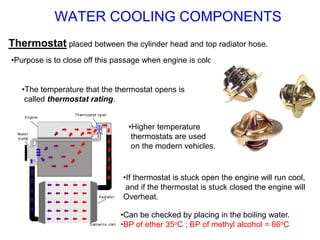
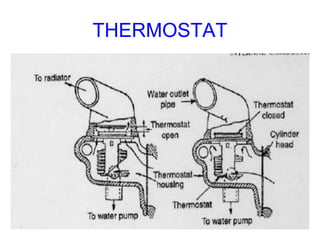
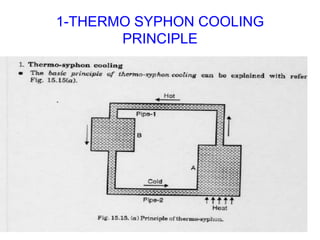
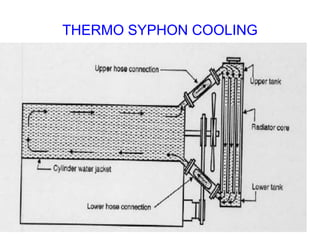
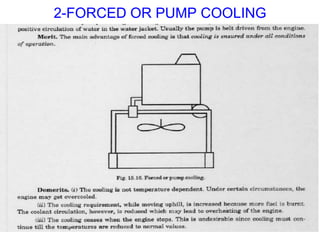
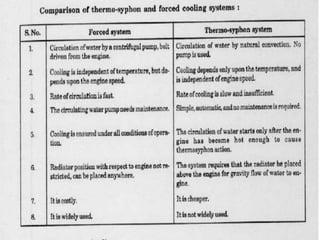
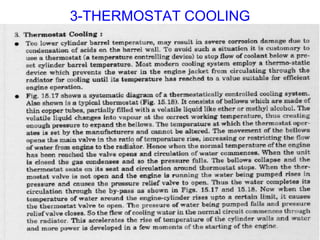
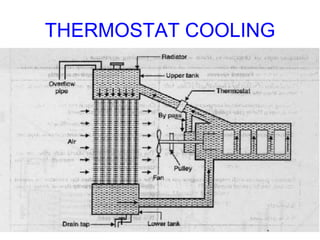
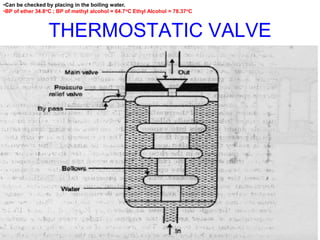
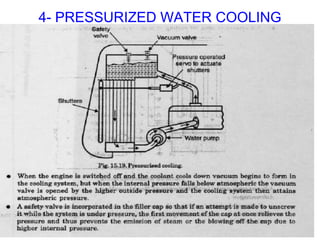
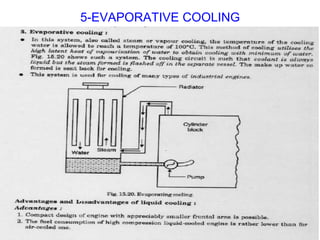
The document discusses the automobile cooling system. It notes that the cooling system serves to maintain the engine at an optimum operating temperature to prevent damage. It then describes the two main types of cooling systems - air cooling and liquid cooling. The liquid cooling system uses coolant to circulate through the engine and transfer heat to a radiator for dissipation. Key components of the liquid cooling system are then outlined, including the water jacket, water pump, radiator, thermostat, hoses, and pressure cap.