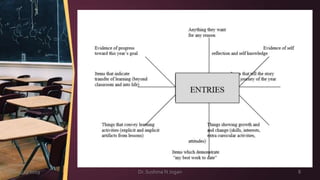
The document outlines guidelines for constructing student portfolios, emphasizing the need to identify purpose, select objectives, and choose appropriate entries. It highlights the importance of student involvement in selecting portfolio content and setting assessment criteria for both individual entries and the portfolio overall. Additionally, the guidelines suggest regular review and reflection on student progress toward established goals.