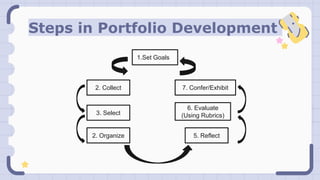
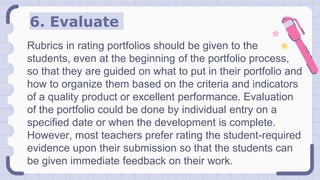
The document provides an overview of portfolio assessment, a dynamic and collaborative approach to evaluating student learning, emphasizing its advantages over traditional testing methods. It outlines the types of portfolios (e.g., process, product, showcase) and details the steps in portfolio development, including goal-setting, collecting, organizing, selecting, reflecting, evaluating, conferring, and exhibiting work. The goal of portfolio assessment is to offer a comprehensive, authentic view of student growth and learning while fostering responsibility and reflection.