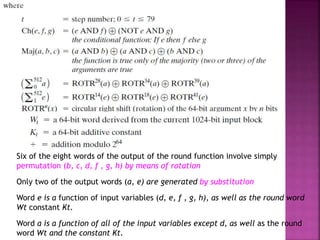
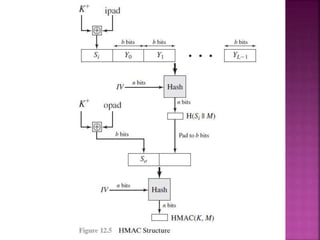
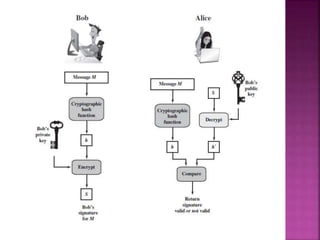
1. Digital signatures provide authentication of digital documents by using asymmetric cryptography techniques. A digital signature is generated using a private key and can be verified by anyone using the corresponding public key.
2. There are various types of attacks against digital signature schemes like key-only attacks, generic chosen message attacks, and adaptive chosen message attacks. The security goals are to prevent total key breaks or the ability to forge signatures selectively or existentially.
3. A secure digital signature scheme must produce signatures that depend on the message, use secret information to prevent forgery and denial, be efficient to generate and verify, and make forgery computationally infeasible. Timestamps can be included to require message freshness.












![ Brute-Force Attacks:
To attack a hash code Given a fixed message x with
n-bit hash code h = H(x),
a brute-force method of finding a collision is to pick a
random bit string y and check if H(y) = H(x).
The attacker can do this repeatedly off line
desired security property Computation resistance
Given one or more text-MAC pairs [xi, MAC(K, xi)], it is
computationally infeasible to compute any text-MAC
pair [x, MAC(K, x)] for any new input x ≠ xi.
the attacker would like to come up with the valid MAC
code for a given message x.
There are two lines of attack possible:
attack the key space and attack the MAC value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3-190706160823/85/Unit-3-13-320.jpg)




![ 1. Append padding bits:
The message is padded so that its length is congruent to 896
modulo 1024 [length = 896(mod 1024)].
the number of padding bits is in the range of 1 to 1024.
The padding consists of a single 1 bit followed by the necessary
number of 0 bits.
2. Append length:
A block of 128 bits is appended to the message.
3.Initialize hash buffer.
A 512-bit buffer is used to hold intermediate and final results of the
hash function.
The buffer can be represented as eight 64-bit registers (a, b, c, d,
e, f, g, h).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3-190706160823/85/Unit-3-18-320.jpg)