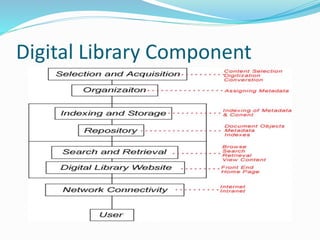
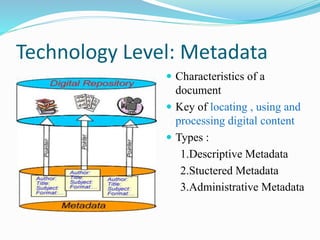
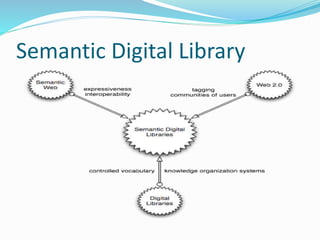
This document discusses the components and technologies of digital libraries. It describes the key components as selection and acquisition, organization through metadata assignment, indexing and storage in a repository, and search and retrieval via a digital library website. It then associates various technologies with these components, such as metadata standards, document formats, repository systems like DSpace and Fedora, and semantic technologies.