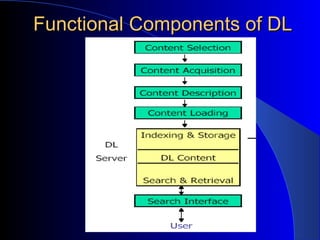
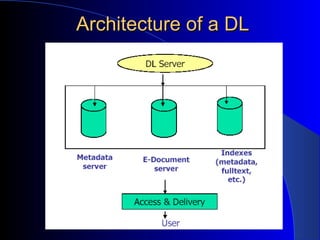
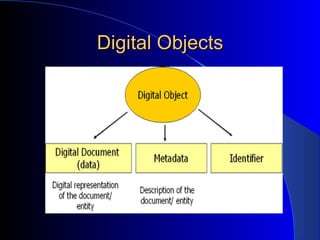
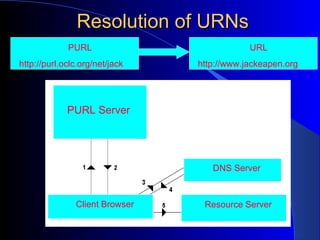
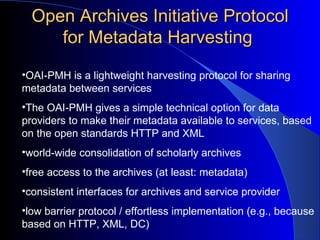
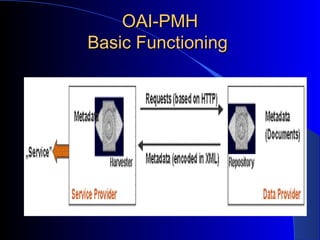
This document provides an overview of digital libraries, including definitions, benefits, limitations, components, standards, and challenges. It defines a digital library as a collection of information stored and accessed electronically, extending the functions of a traditional library digitally. Benefits include improved access and searchability, easier information sharing and preservation. Emerging technologies discussed include metadata standards, XML, and protocols like OAI-PMH for metadata harvesting. Common digital library software includes DSpace, Greenstone, and EPrints. Challenges involve digitization, description, legal issues, presentation of heterogeneous resources, and economic sustainability.
![Digital Libraries Jack Eapen [email_address] http://www.jackeapen.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitallibraries-100502121704-phpapp02/75/Digital-Libraries-1-2048.jpg)