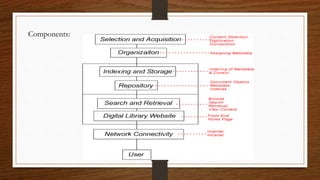
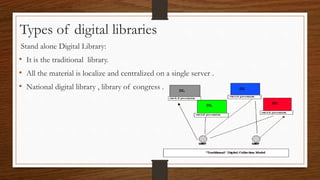
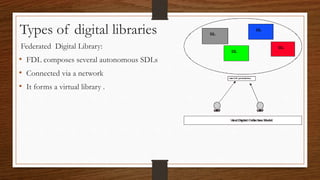
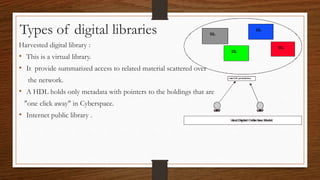
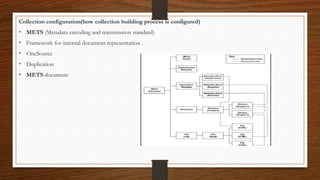
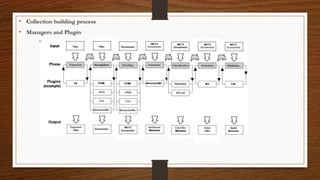
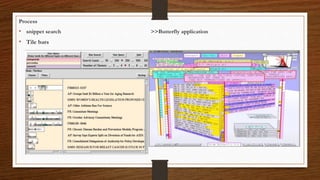
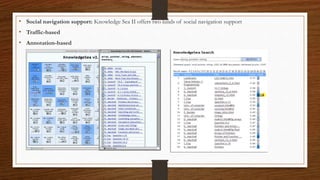
Digital libraries are collections of documents available electronically over the internet or CD-ROM. This document discusses digital libraries, their components and applications. It summarizes three research papers on digital libraries: 1) A new framework for building digital library collections that redesigns the Greenstone digital library system. 2) Rich interactions in digital libraries that aims to increase interaction between users and information. 3) Comprehensive personalized information access in an educational digital library that utilizes techniques like information retrieval, filtering, browsing and visualization.