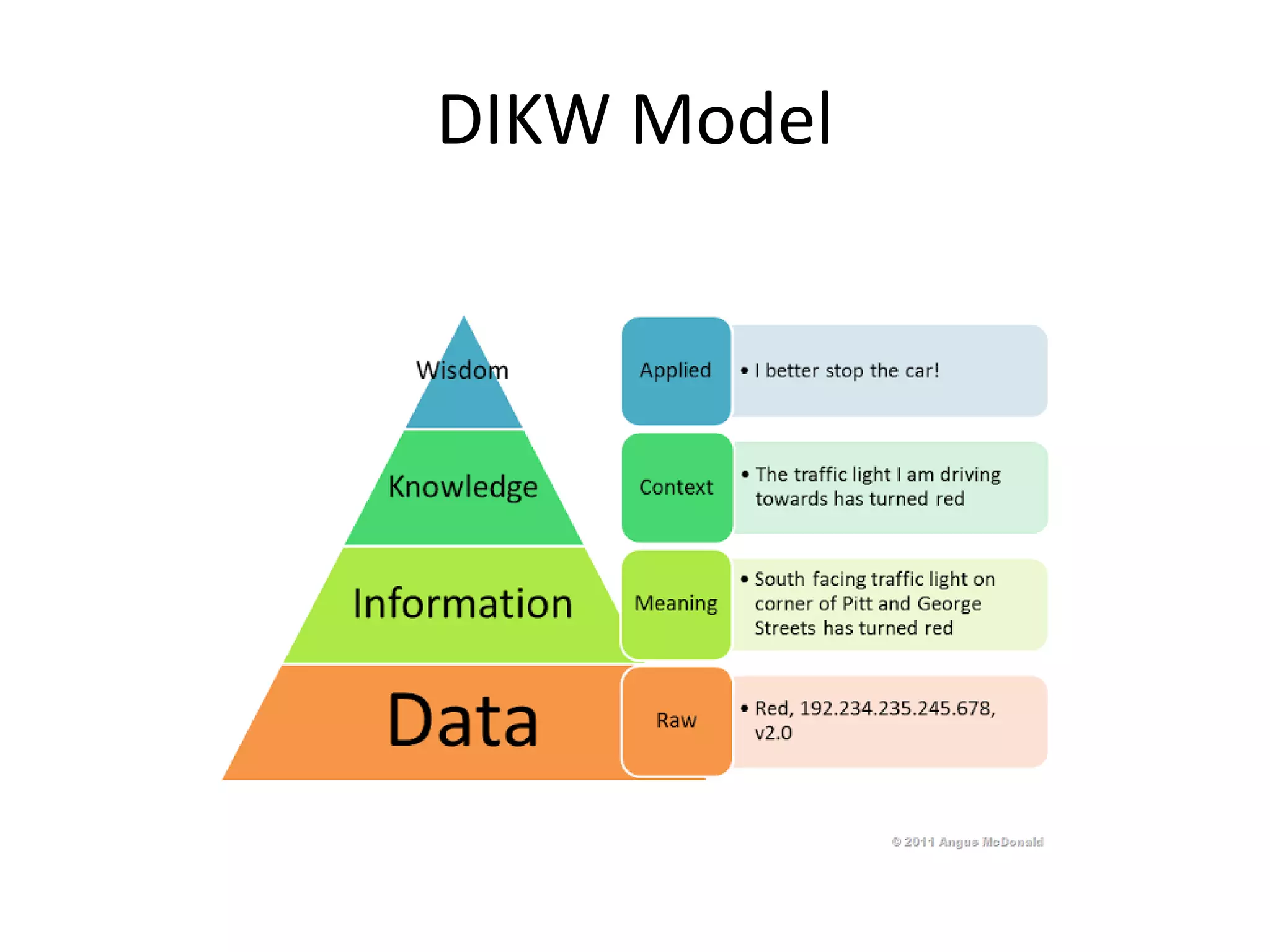
This document provides an introduction to information technology (IT) and its impact on organizations. It defines key terms like information and data, and describes how IT systems capture, process, exchange, store and present information using electrical and electromagnetic energy. Examples of how IT is used in society and businesses for communication, entertainment, commerce and operations are provided. Career opportunities in IT fields like information security, analytics, networking and software development are also summarized. The document concludes by outlining some advantages of IT for organizations like reduced costs, improved productivity and decision making.