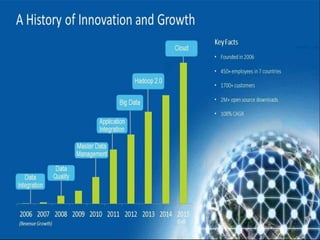
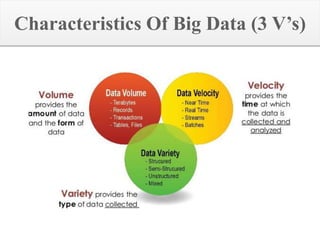
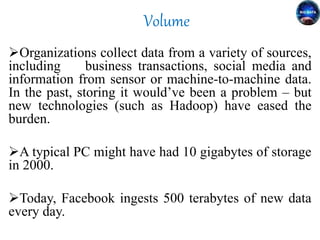
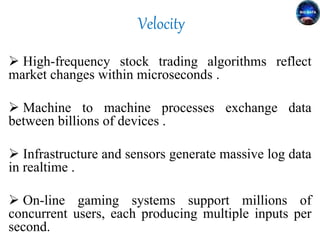
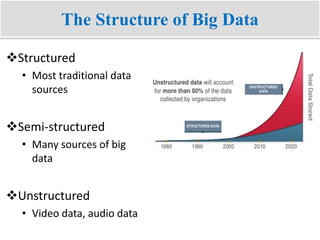
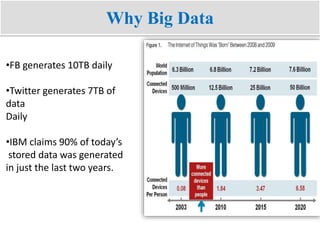
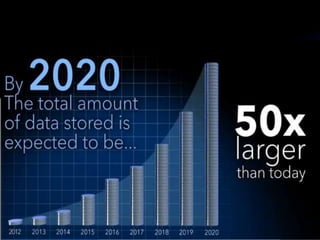
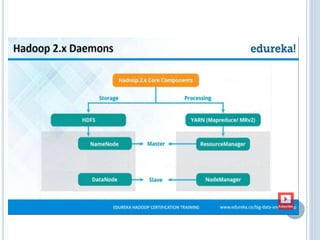
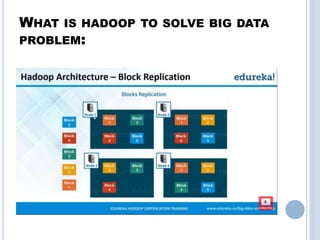
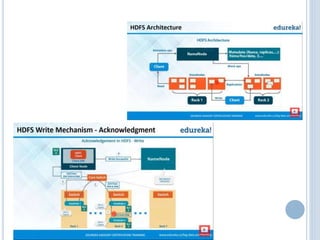
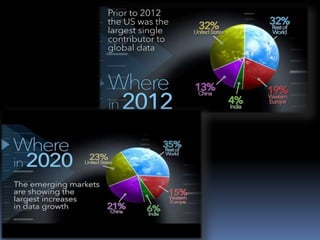
Big data refers to the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that organizations face, requiring innovative techniques for analysis. It encompasses characteristics such as volume, velocity, and variety, which necessitate advanced tools like Hadoop for effective management and insights. The growth of big data presents opportunities for improved decision-making and operational strategies, while also posing challenges for IT organizations.