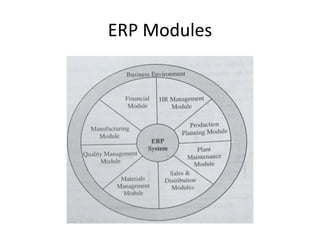
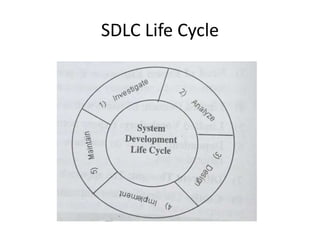
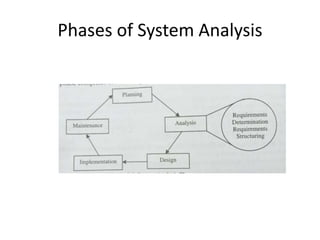
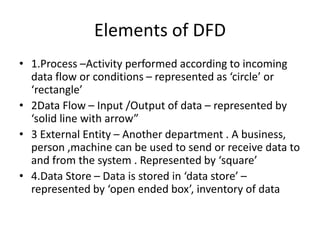
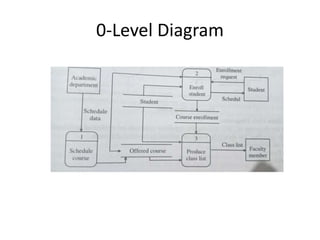
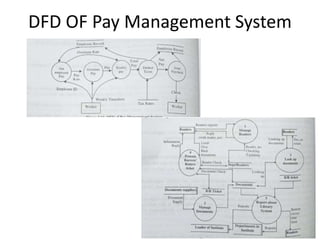
This document discusses the system development life cycle (SDLC) process for developing IT solutions within an organization. The SDLC includes 5 phases - investigation, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance. The analysis phase involves gathering requirements and modeling the system using tools like data flow diagrams to understand how data will flow through the various processes. This helps identify what needs to be done and how during the design phase.