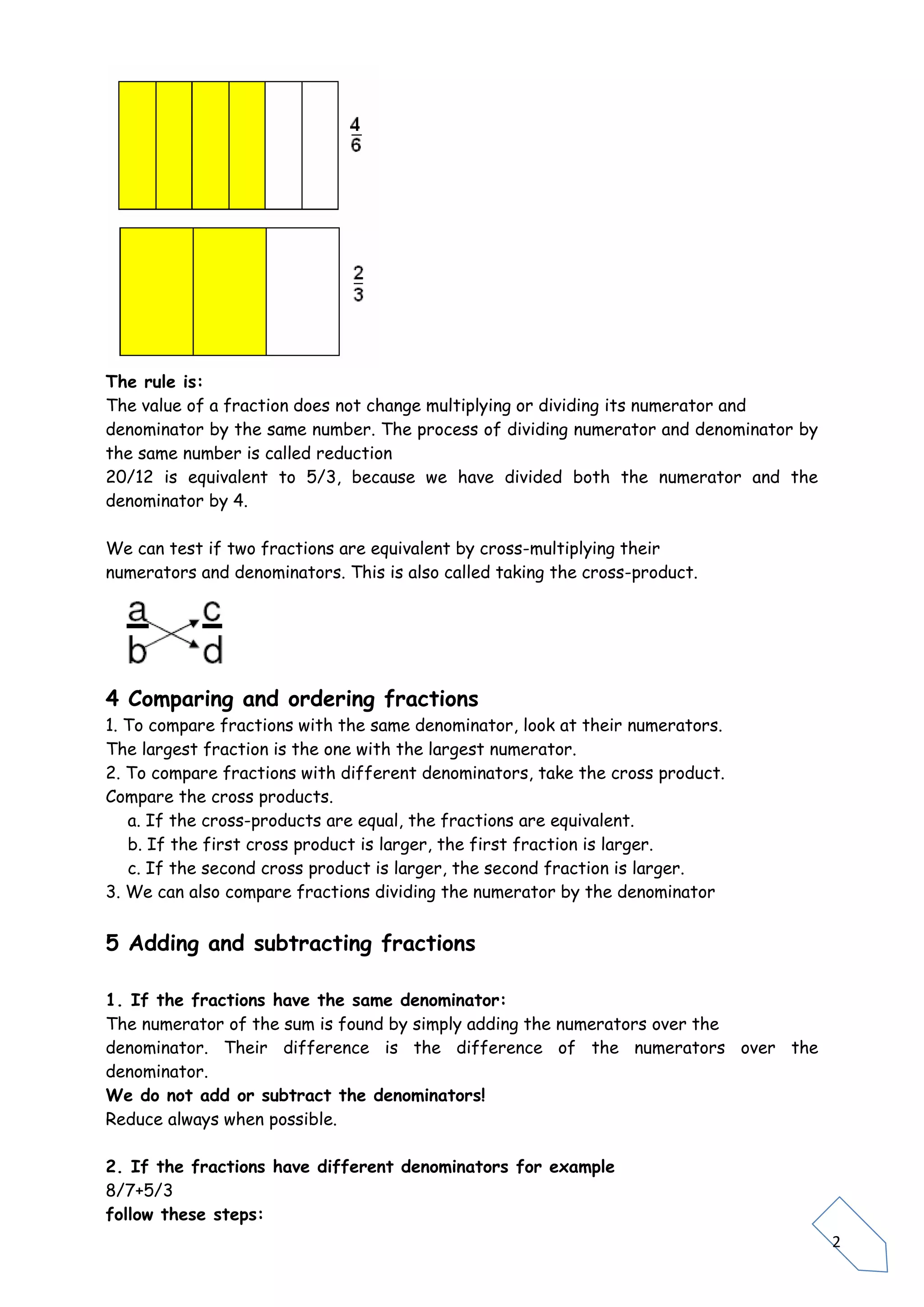
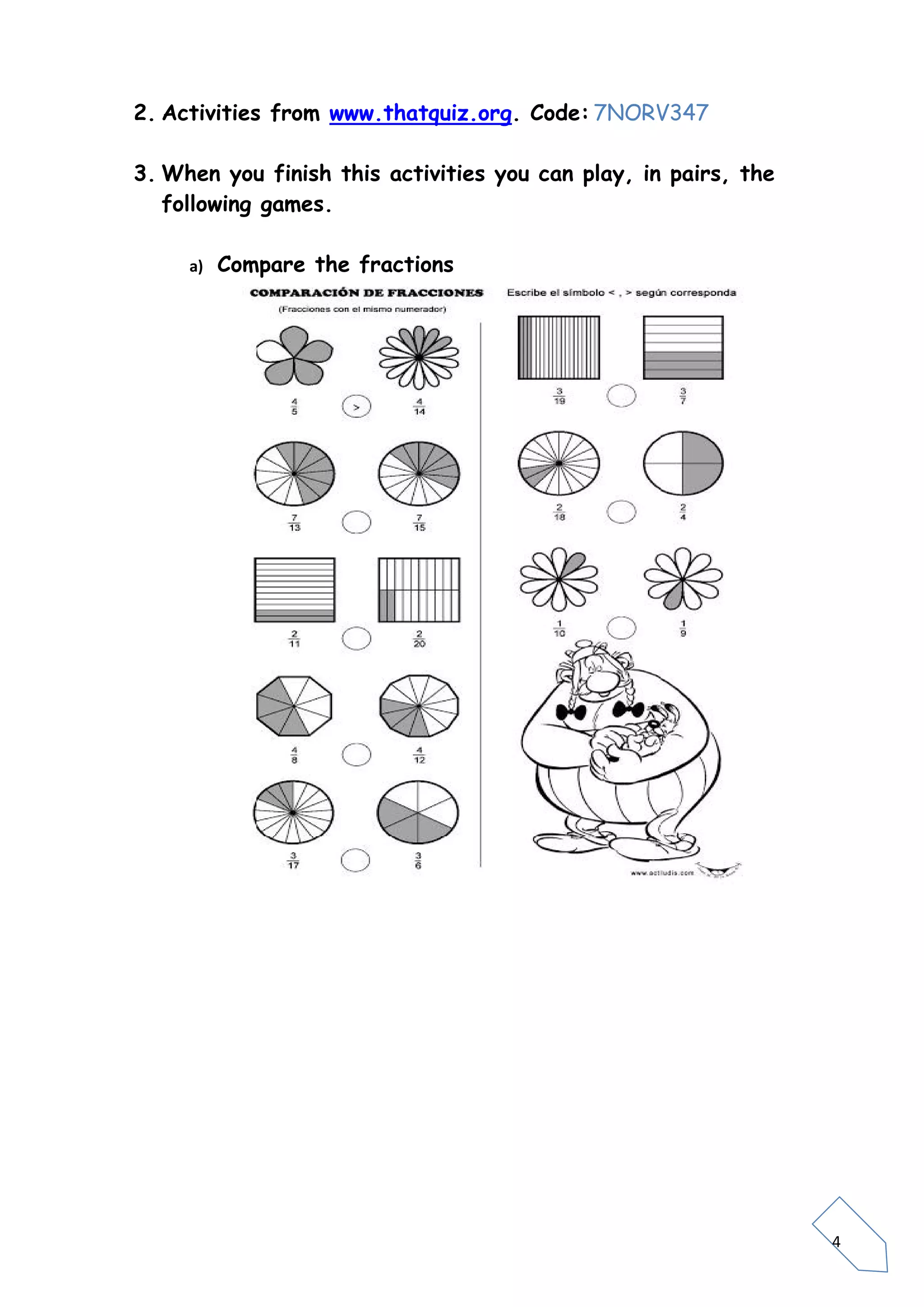
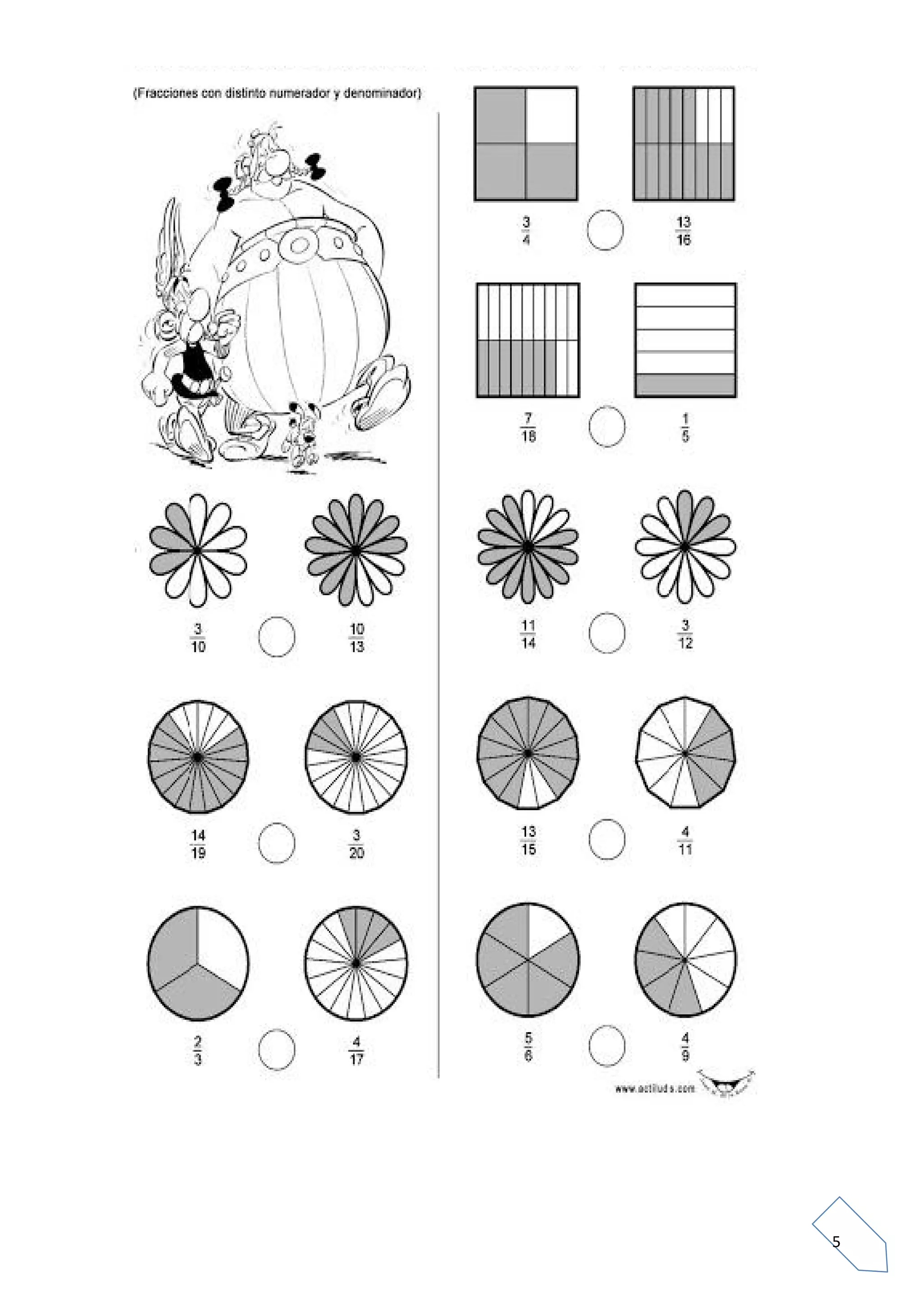
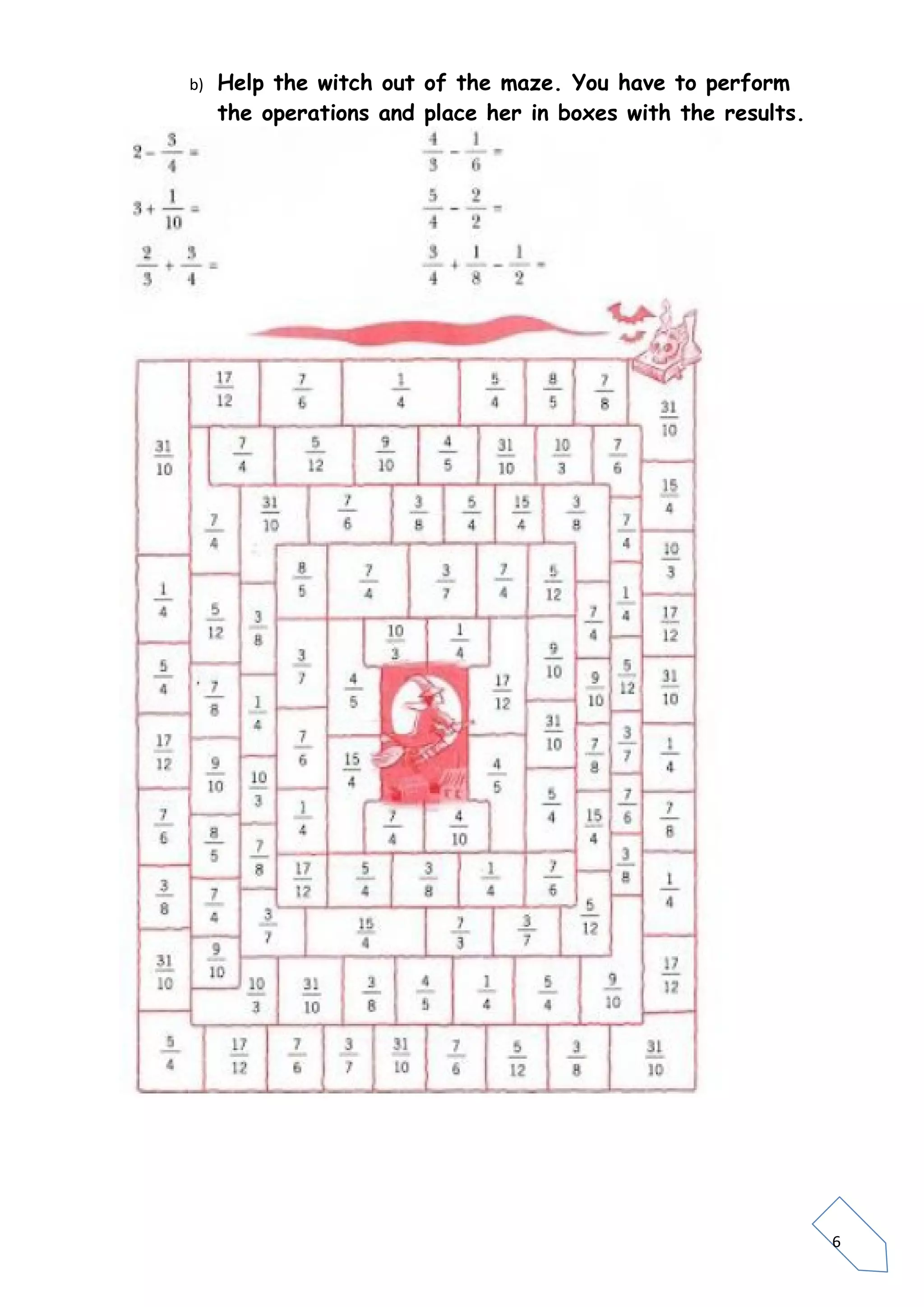
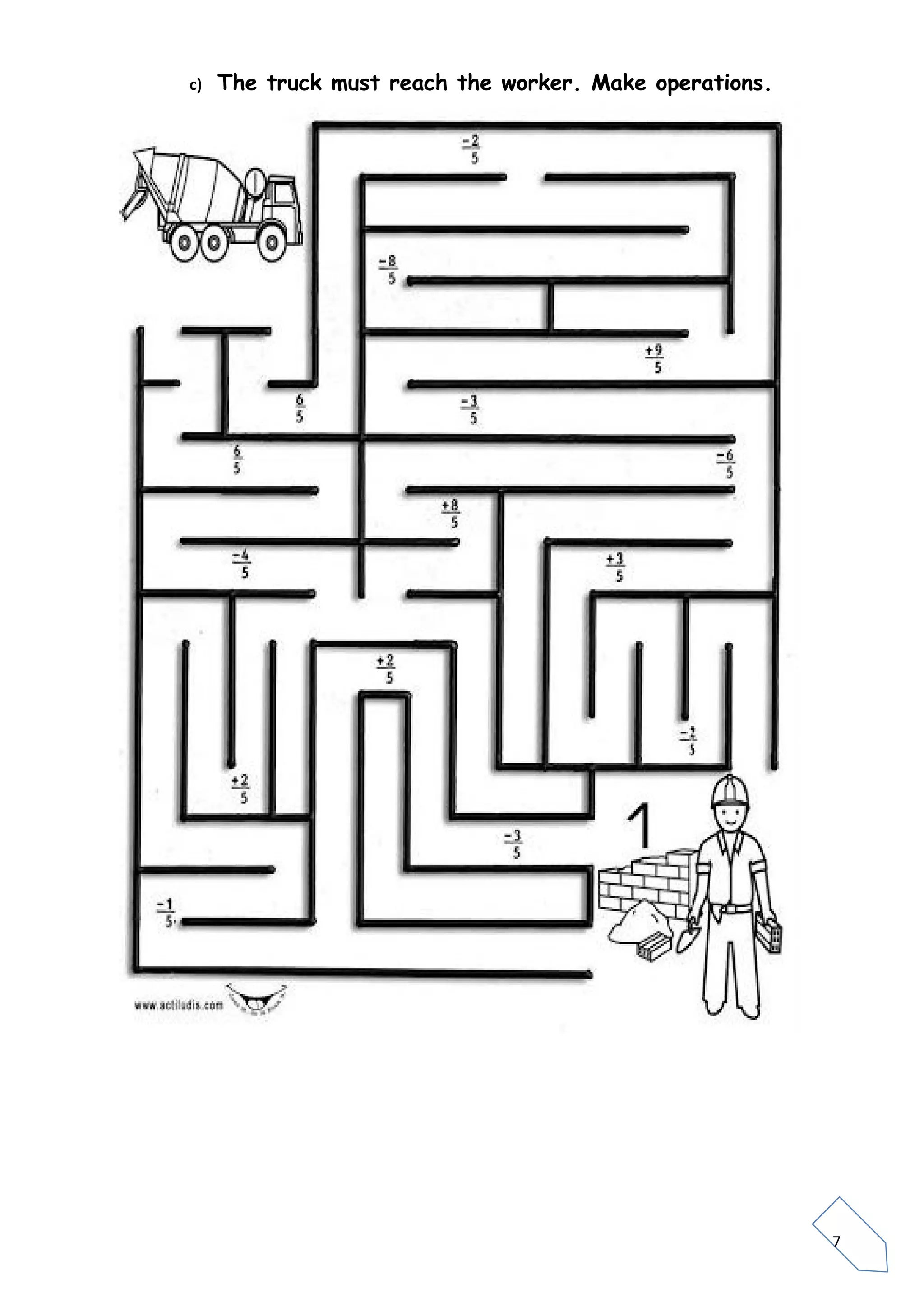
Fractions represent parts of a whole or unit. A fraction is written as a/b, where a is the numerator and b is the denominator. The denominator indicates how many equal parts the whole is divided into, while the numerator specifies how many of those parts are taken. Equivalent fractions have the same value even if they are written differently by multiplying or dividing the numerator and denominator by the same number. Fractions can be compared by considering their numerators and denominators, ordered from least to greatest, and combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division rules. Interactive online activities and games are provided to practice fraction skills.