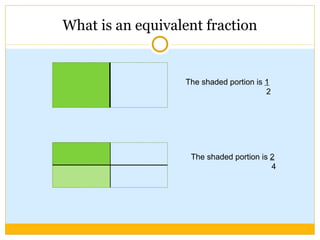
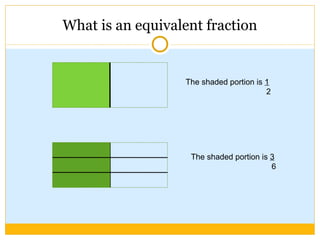
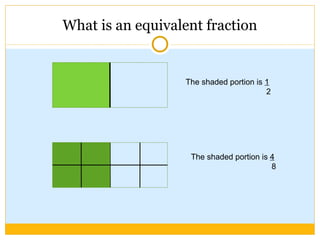
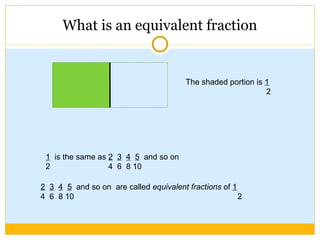
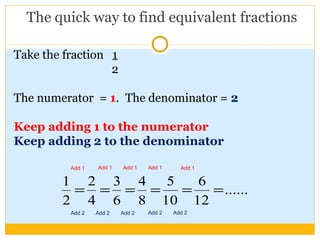
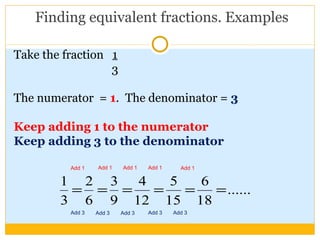
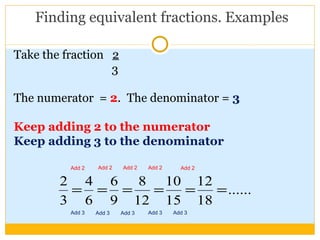
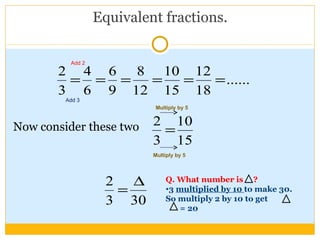
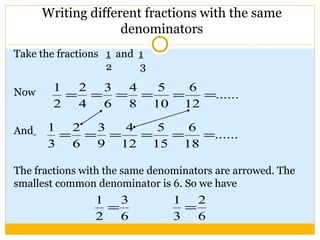
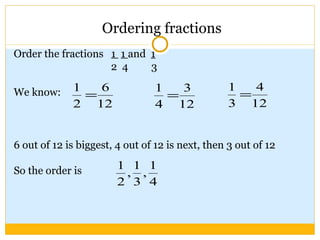
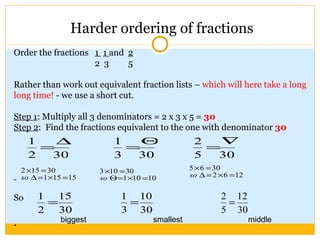
The document discusses equivalent fractions and provides examples of finding equivalent fractions by adding the same number to both the numerator and denominator. It also covers ordering fractions by finding a common denominator and writing fractions with the same denominator. Examples are given of ordering fractions and finding missing numerators or denominators of equivalent fractions.