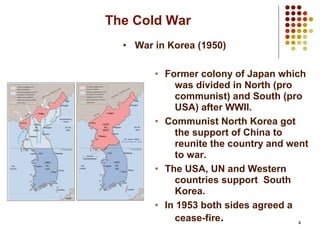
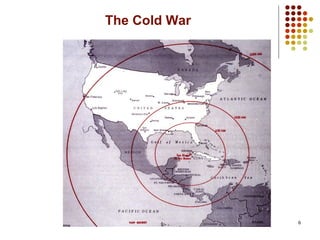
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and Soviet Union from the mid-1940s until the early 1990s. During this time, there was no direct military conflict between the two superpowers, but they supported major regional conflicts like the Korean War and the Vietnam War by proxy. Tensions escalated further in events like the Berlin Blockade and Cuban Missile Crisis, and the Cold War only ended in the late 1980s as reformist leader Gorbachev rose to power in the USSR and liberalized communist rule in Eastern Europe.