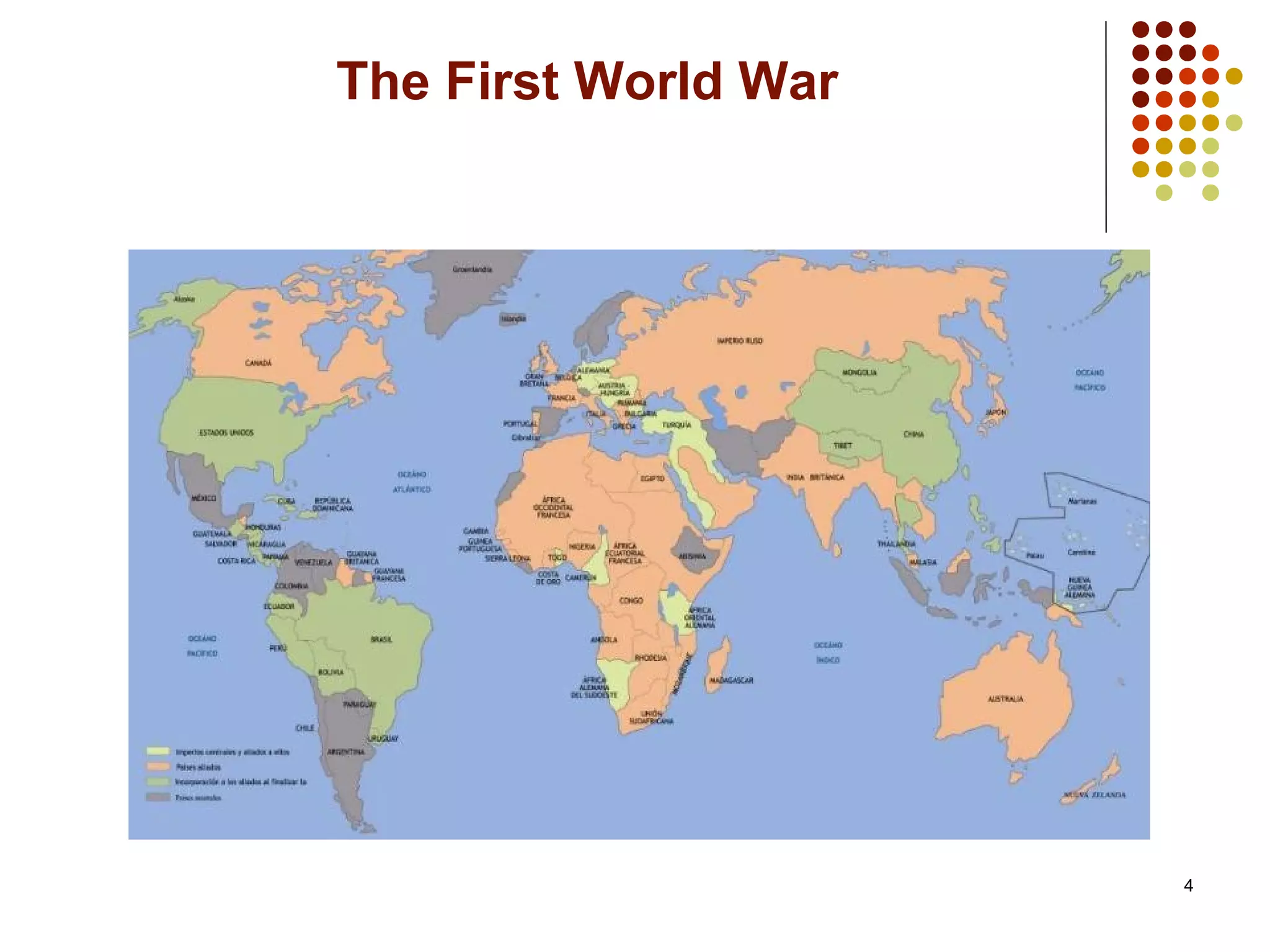
The document provides an overview of the First World War and its aftermath. It discusses the great powers in Europe in 1900 and the alliances that formed. Tensions rose due to crises over Morocco and issues in the Balkans. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand led countries to take sides and go to war in 1914. The war was fought on both the Western and Eastern fronts and included new weapons and tactics. Germany was ultimately defeated and the Treaty of Versailles imposed punishments while creating the League of Nations to promote peace. However, the League had limitations that prevented it from being fully effective.