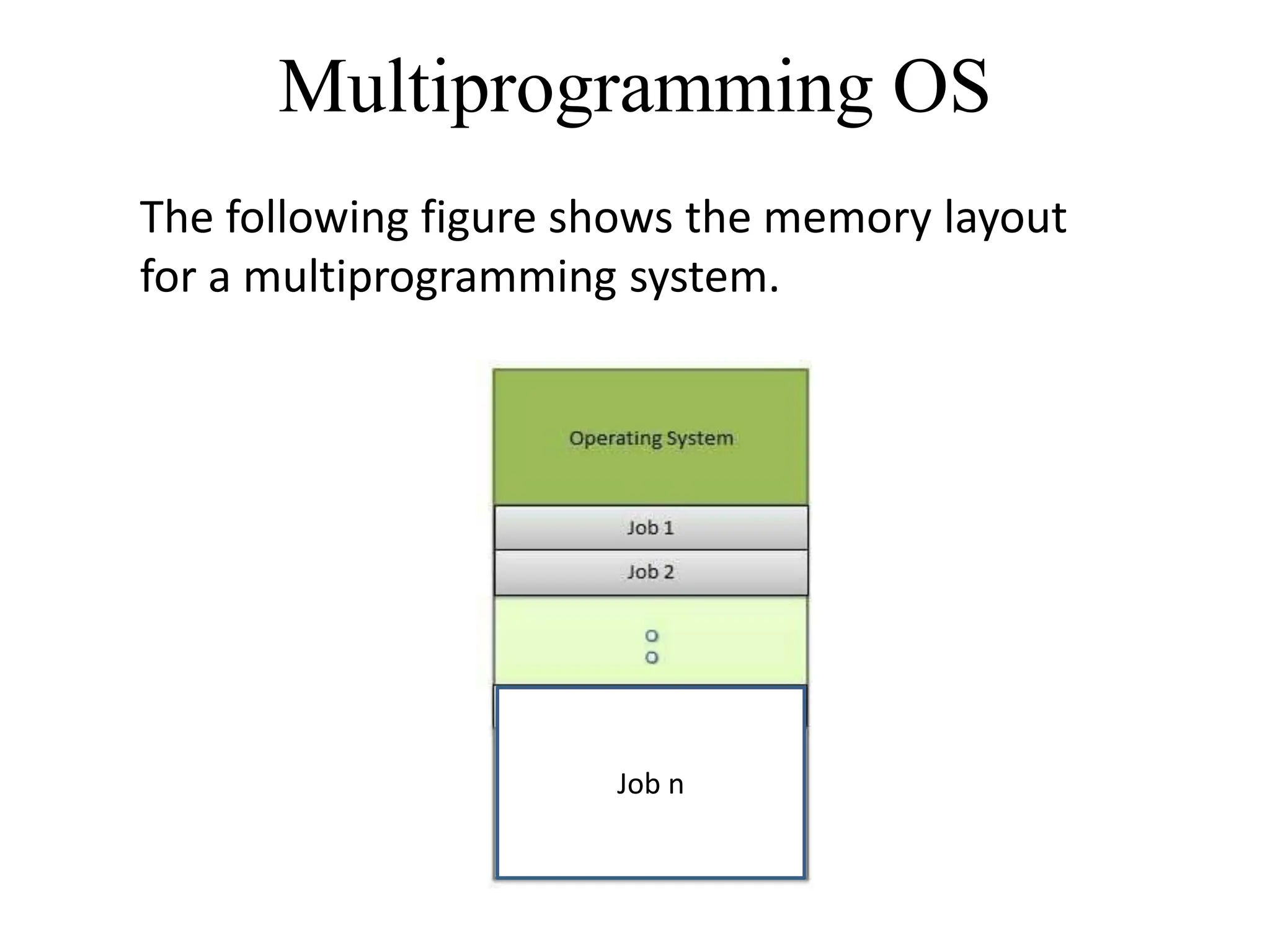
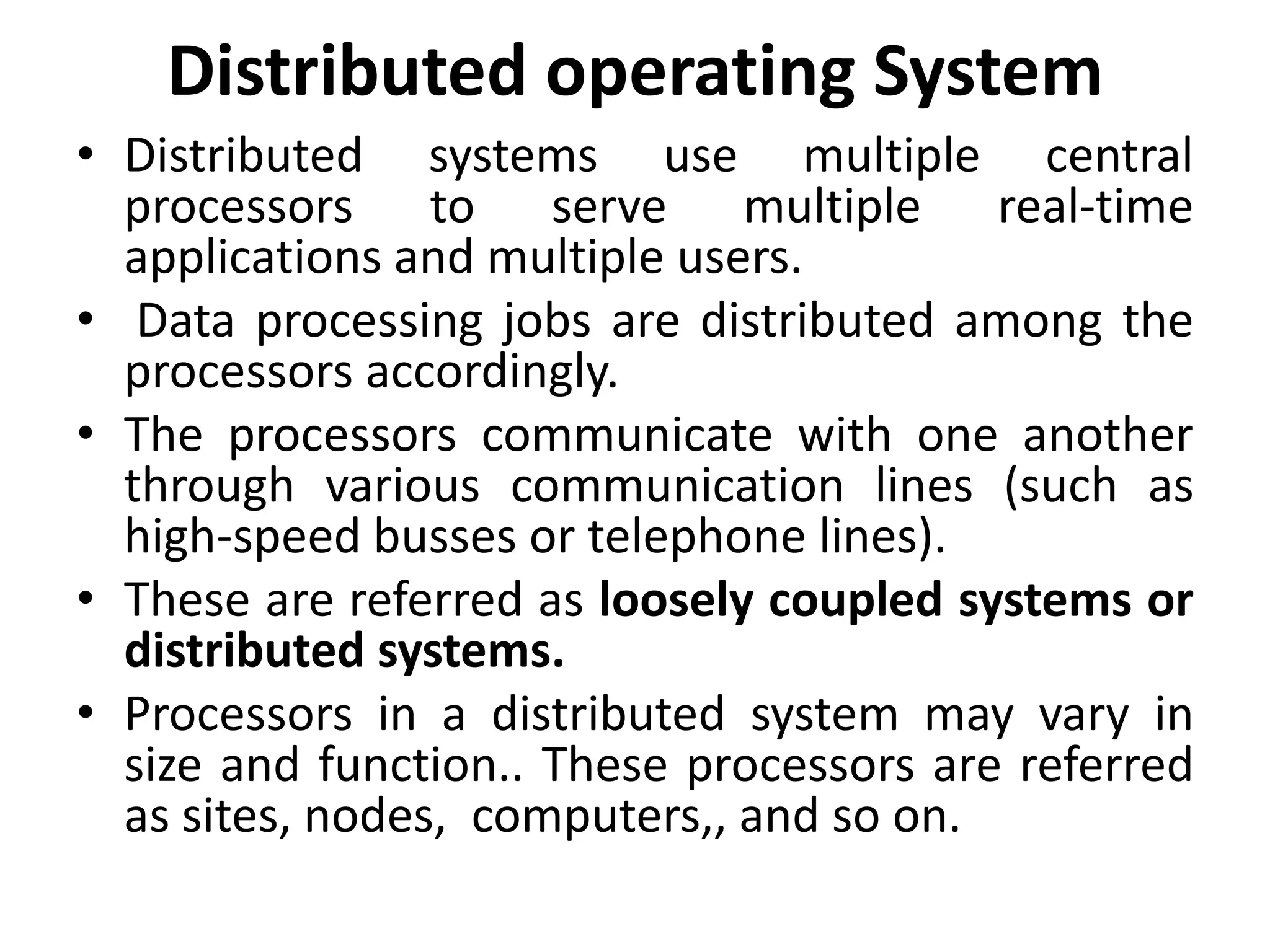
The document discusses various types of operating systems, including batch, multiprogramming, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time operating systems, each with distinct characteristics and functionalities. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each type, such as the efficiency of multiprogramming and the quick response time provided by time-sharing systems. Additionally, it touches on both hard and soft real-time systems and provides examples of mainframe and personal computer operating systems.