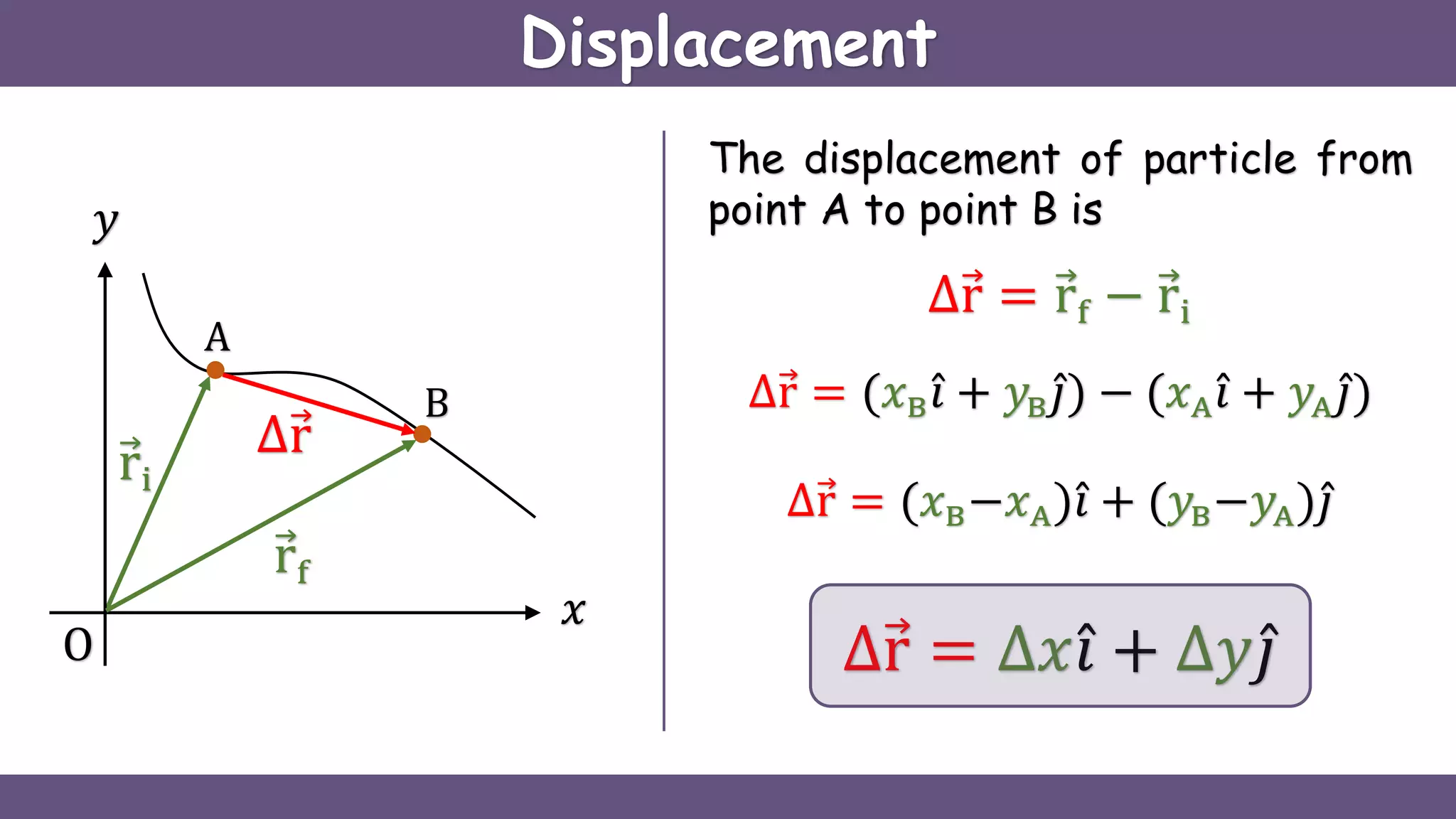
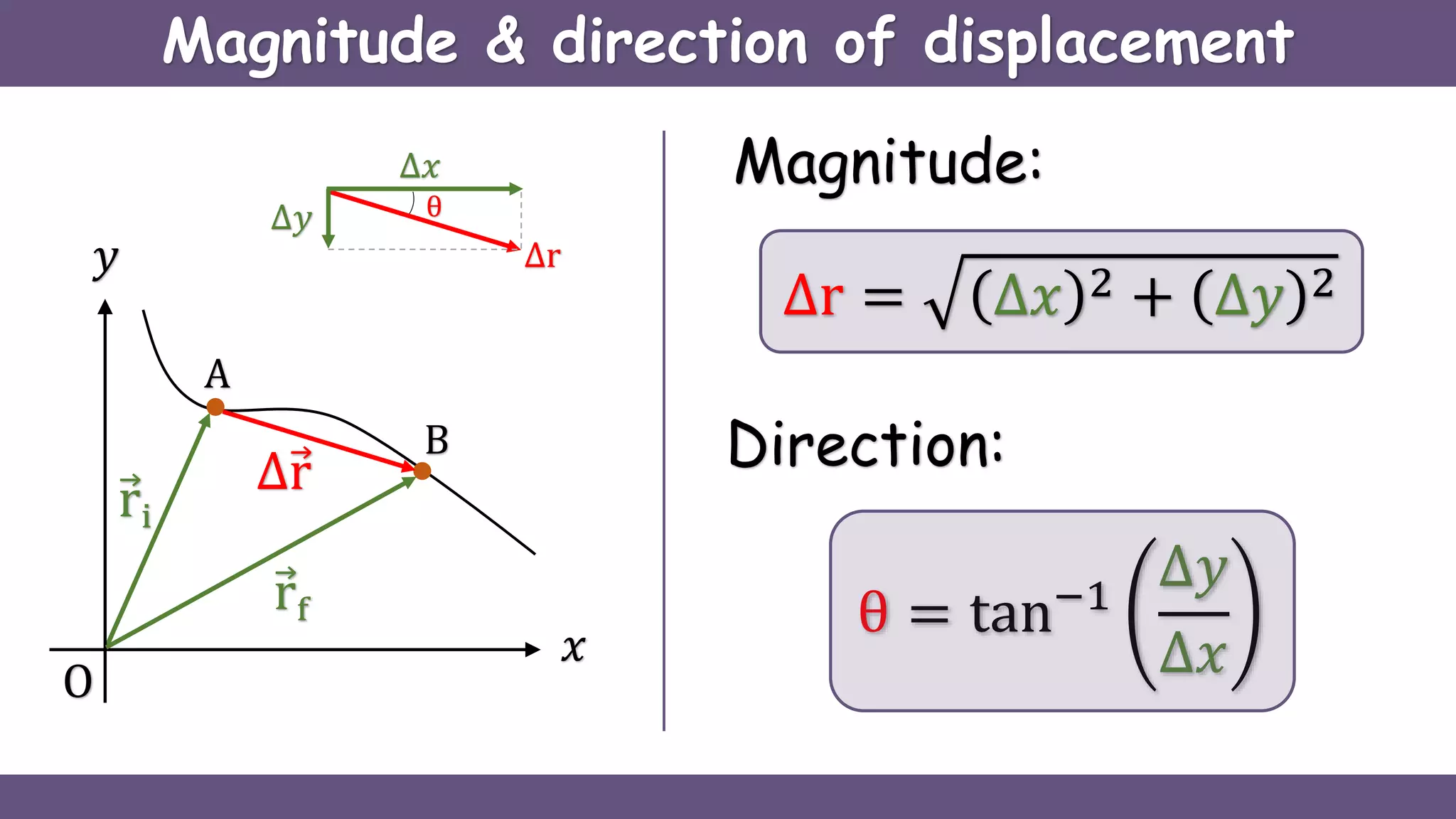
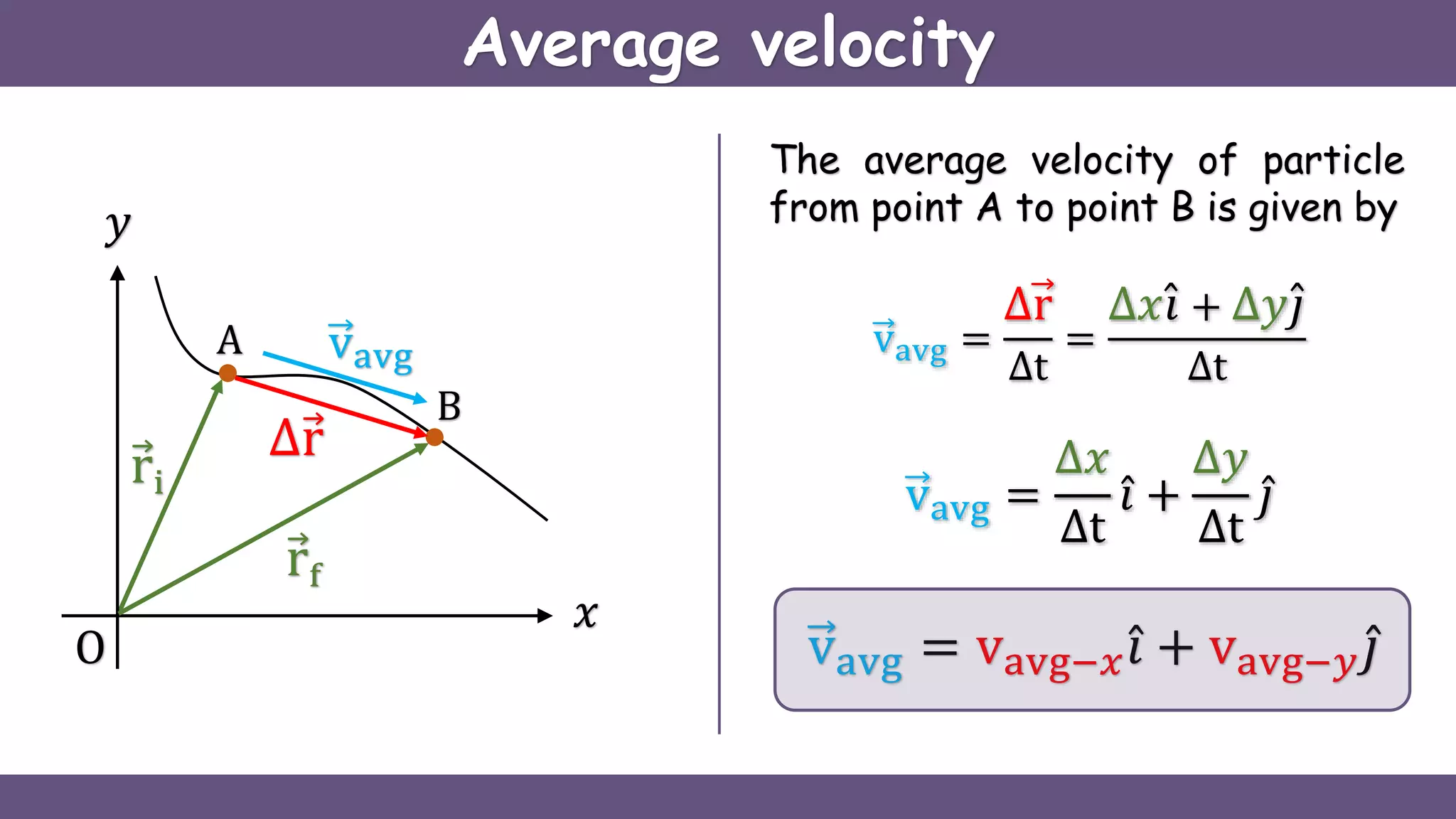
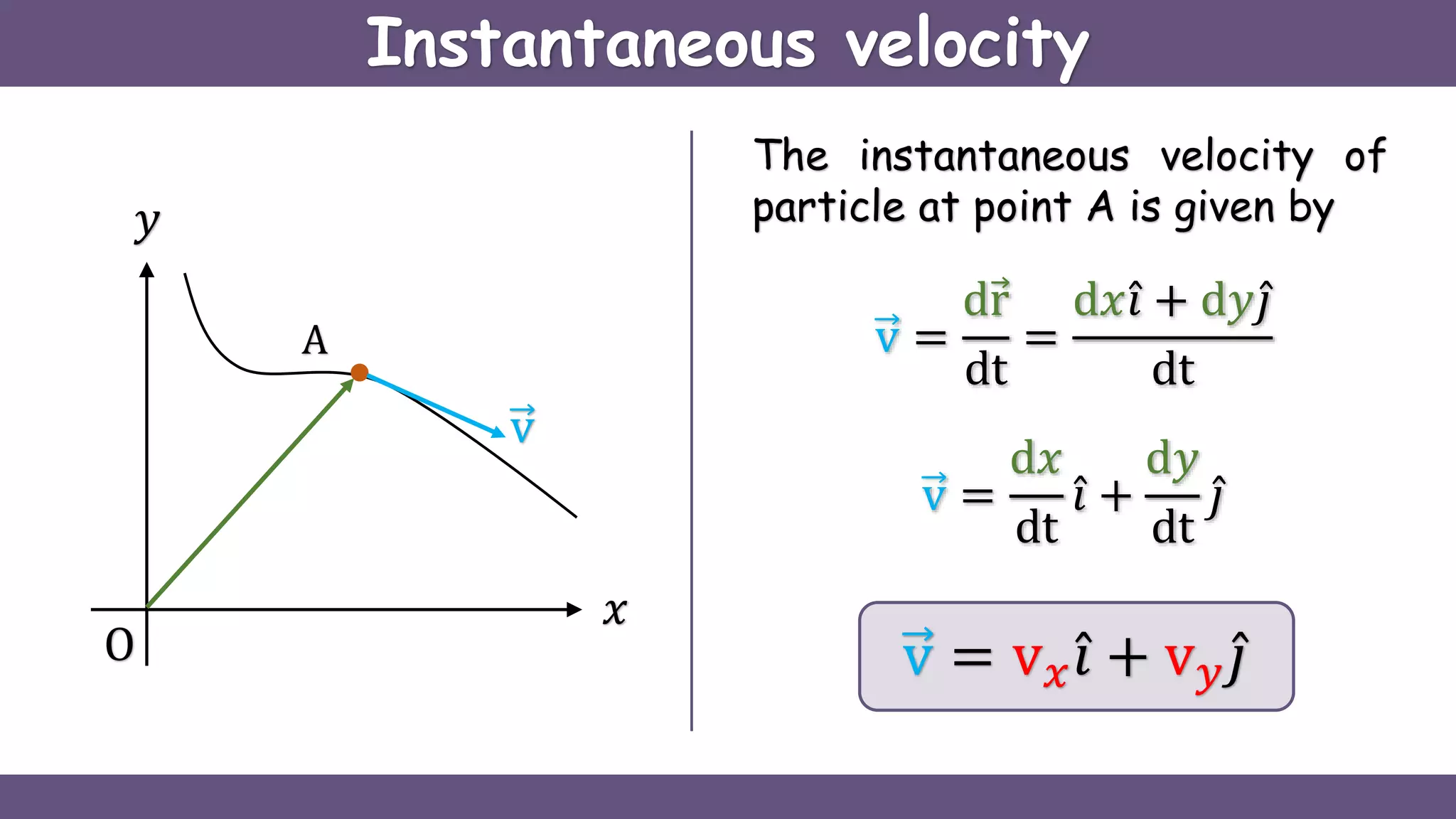
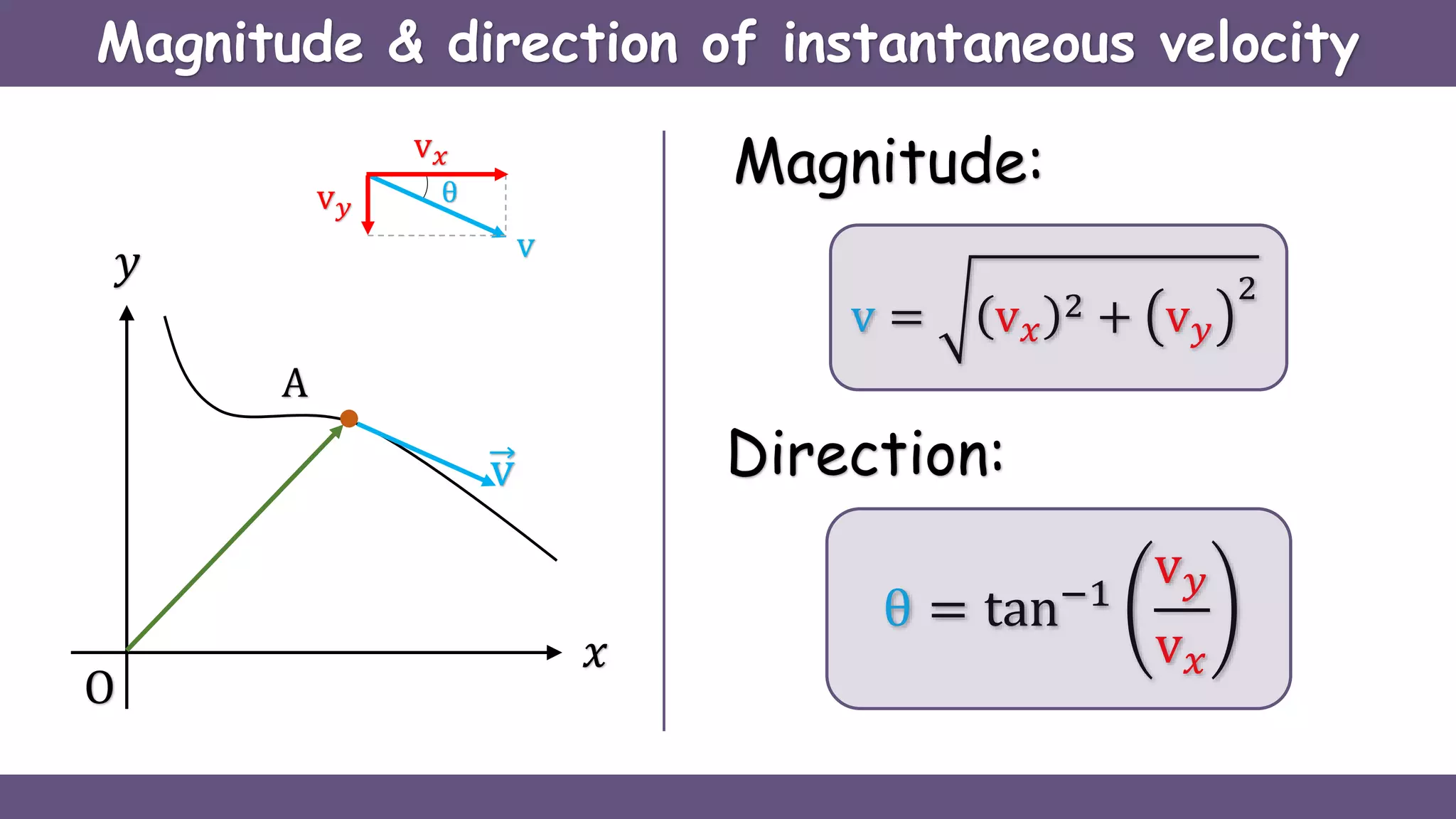
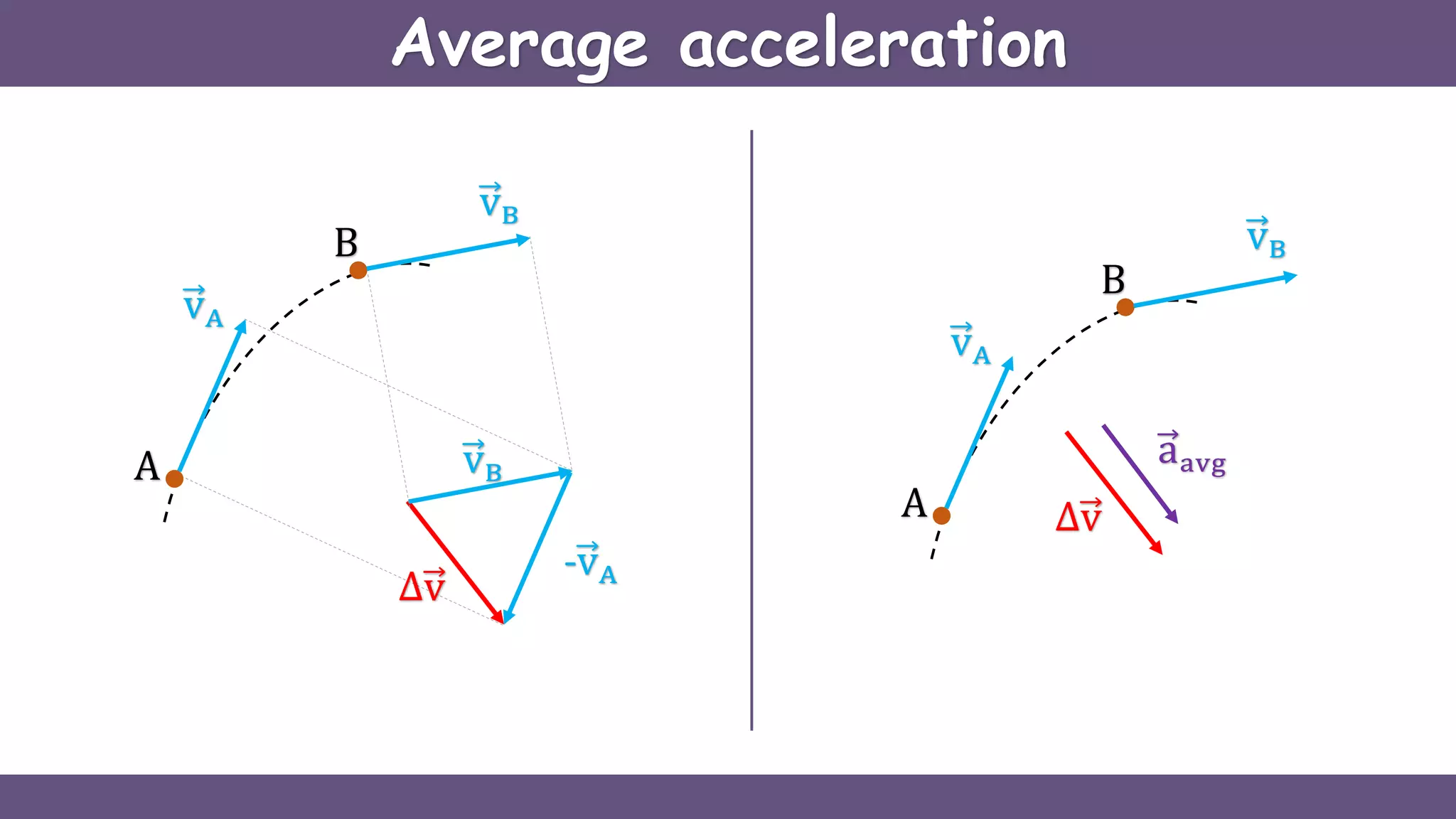
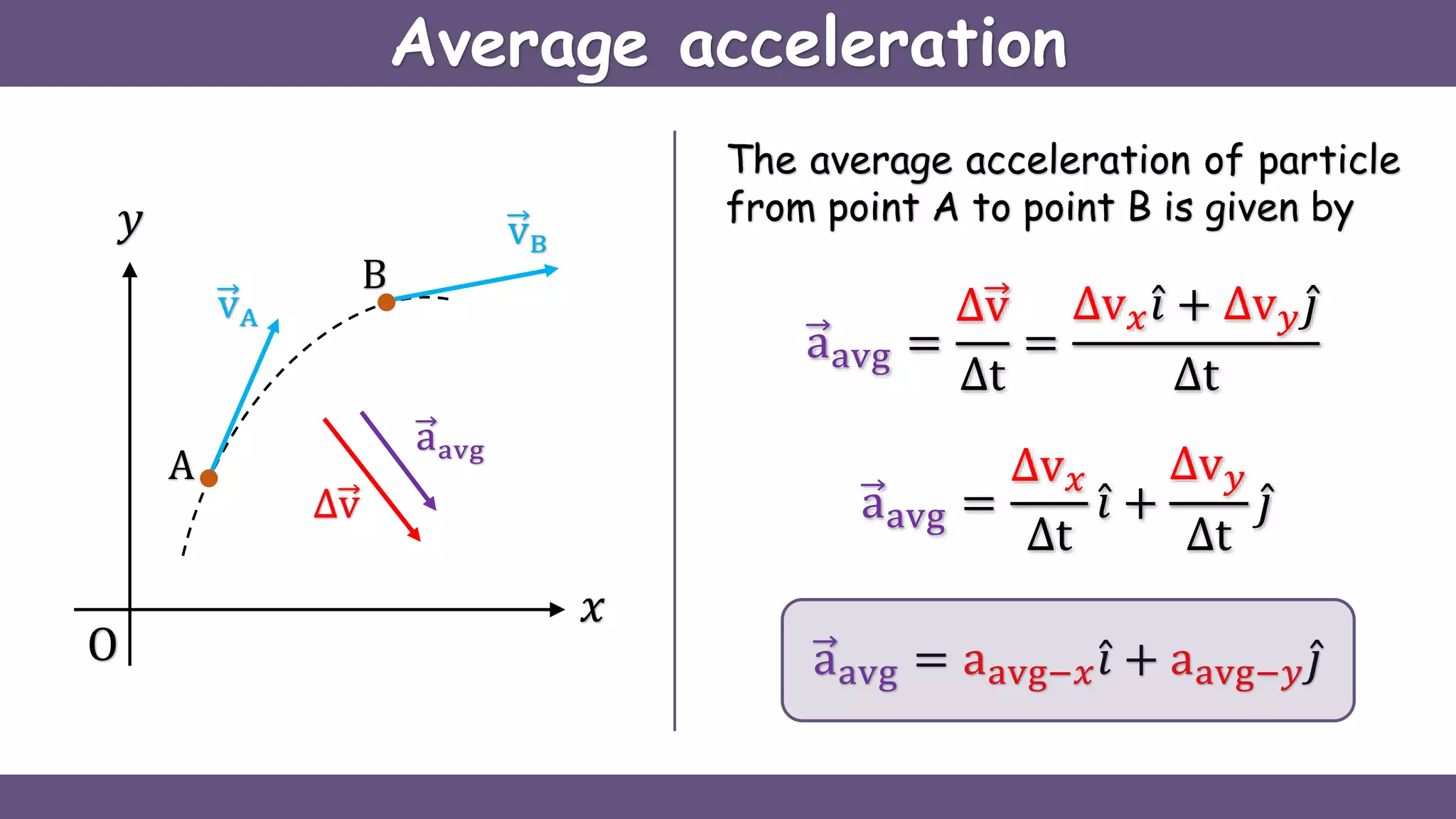
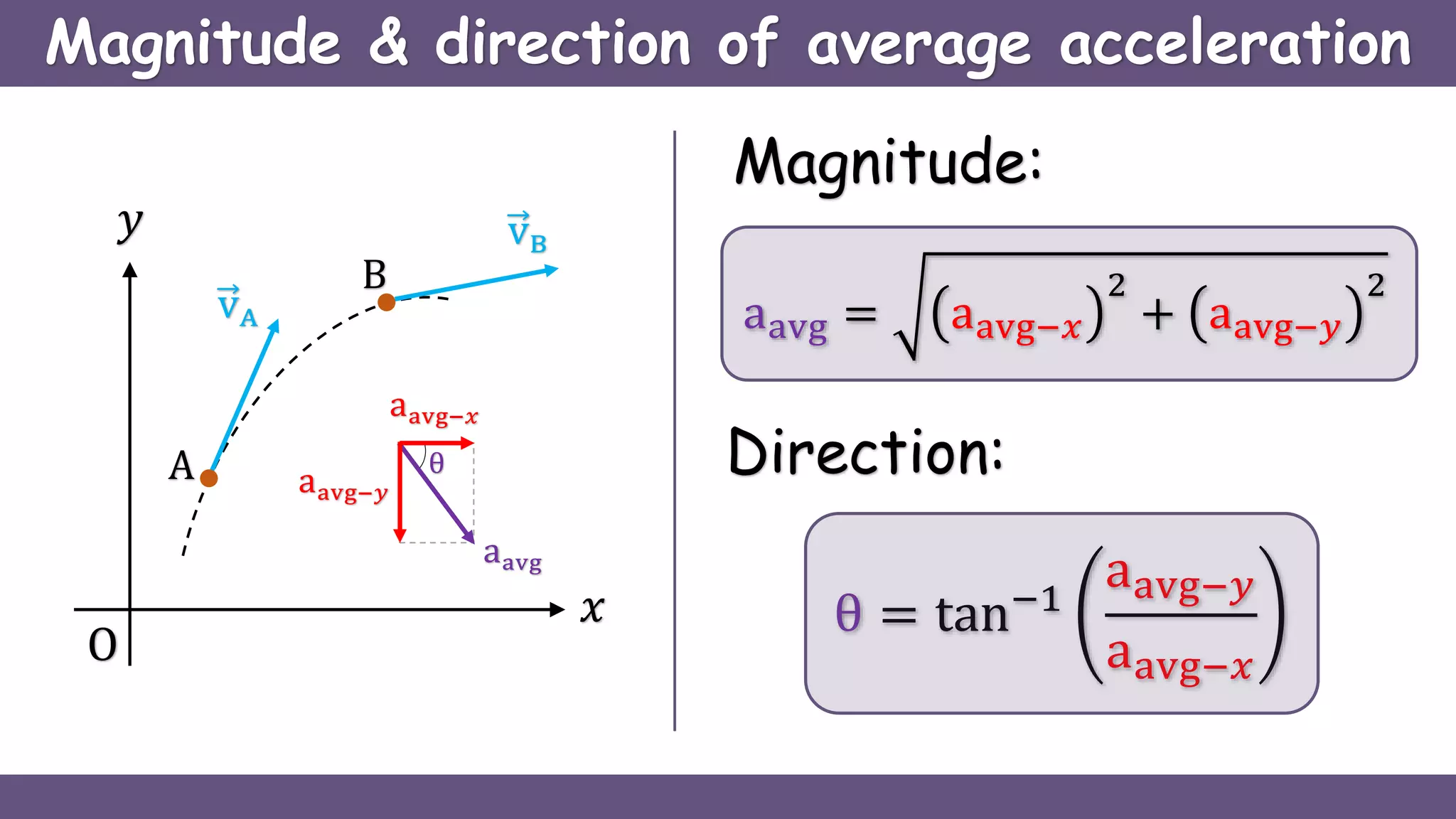
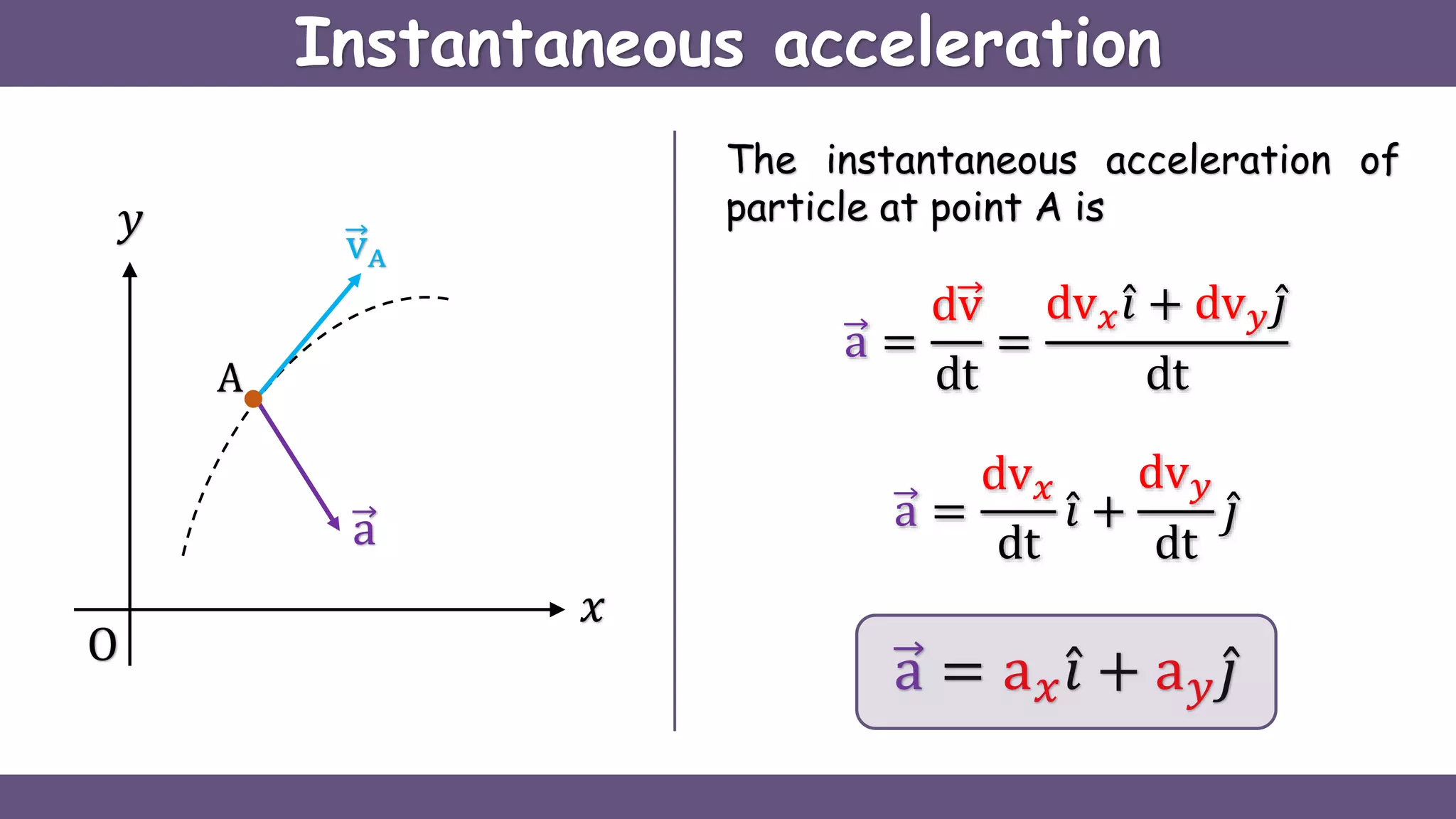
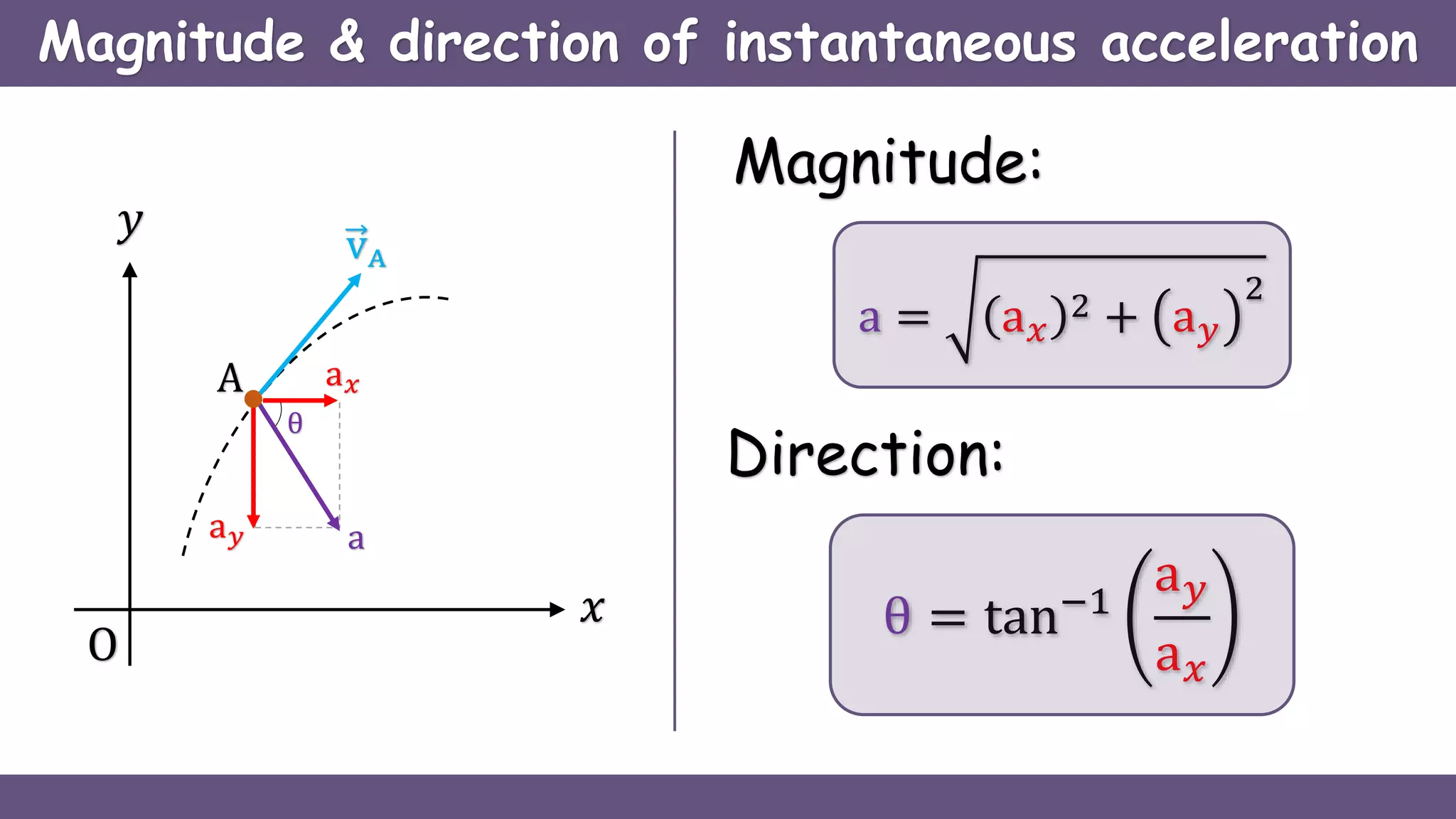
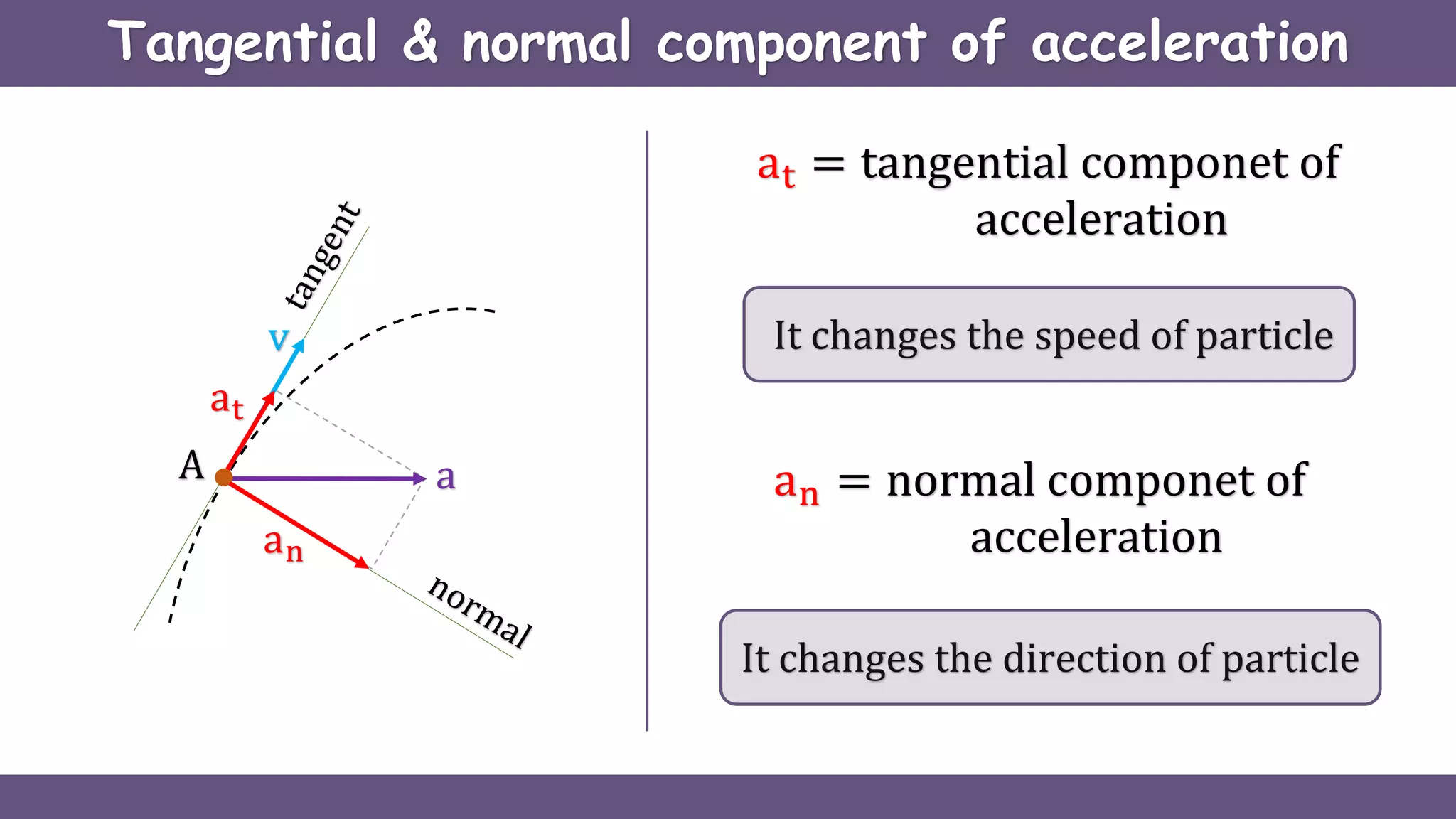
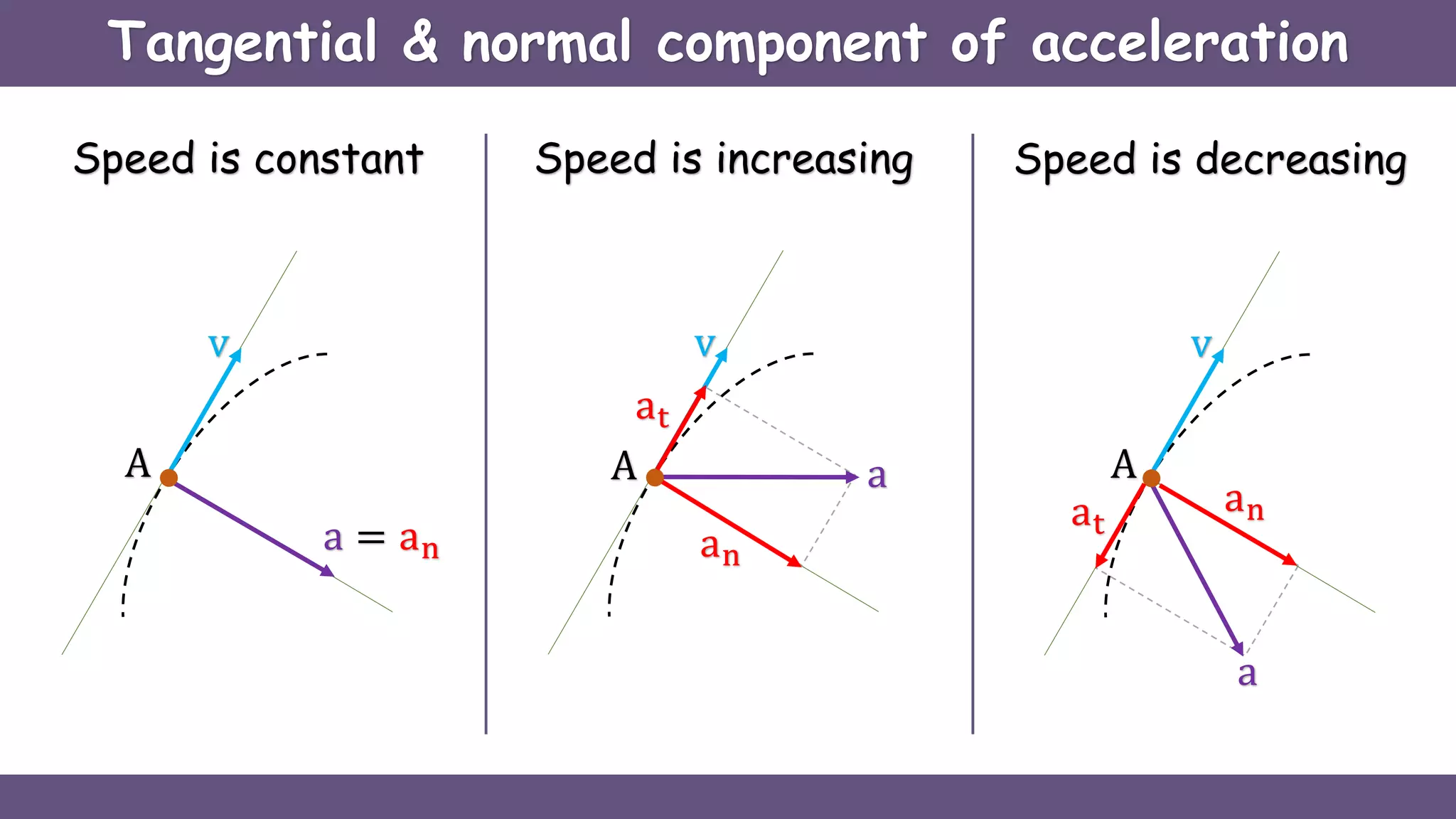
Curvilinear motion refers to the movement of objects along curved paths, exemplified by cars on winding roads or roller coasters on their tracks. The document explains vector representations for displacement, average velocity, instantaneous velocity, average acceleration, and instantaneous acceleration, along with their magnitudes and directions. It also distinguishes between tangential and normal components of acceleration, focusing on how they influence speed and direction.