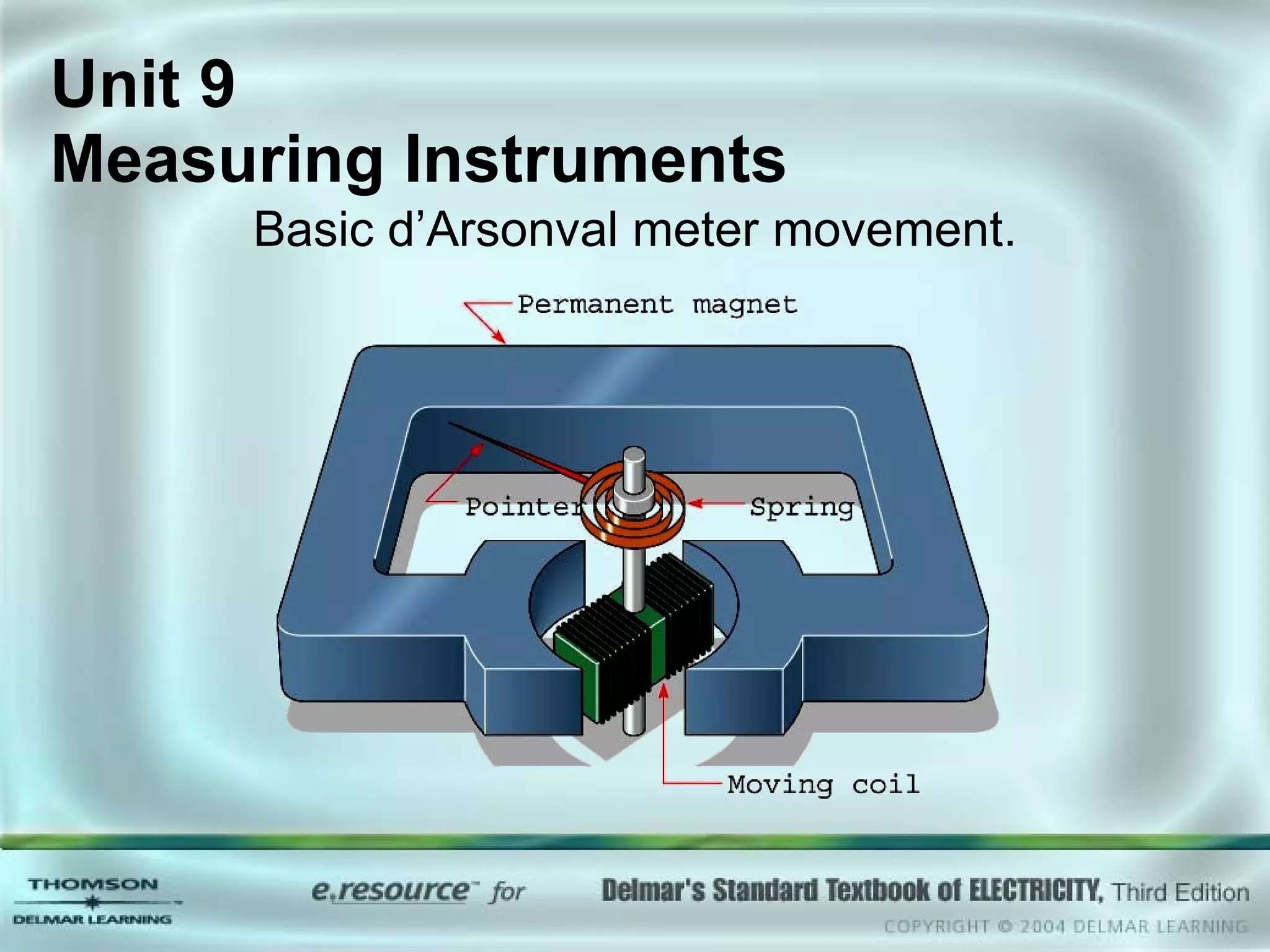
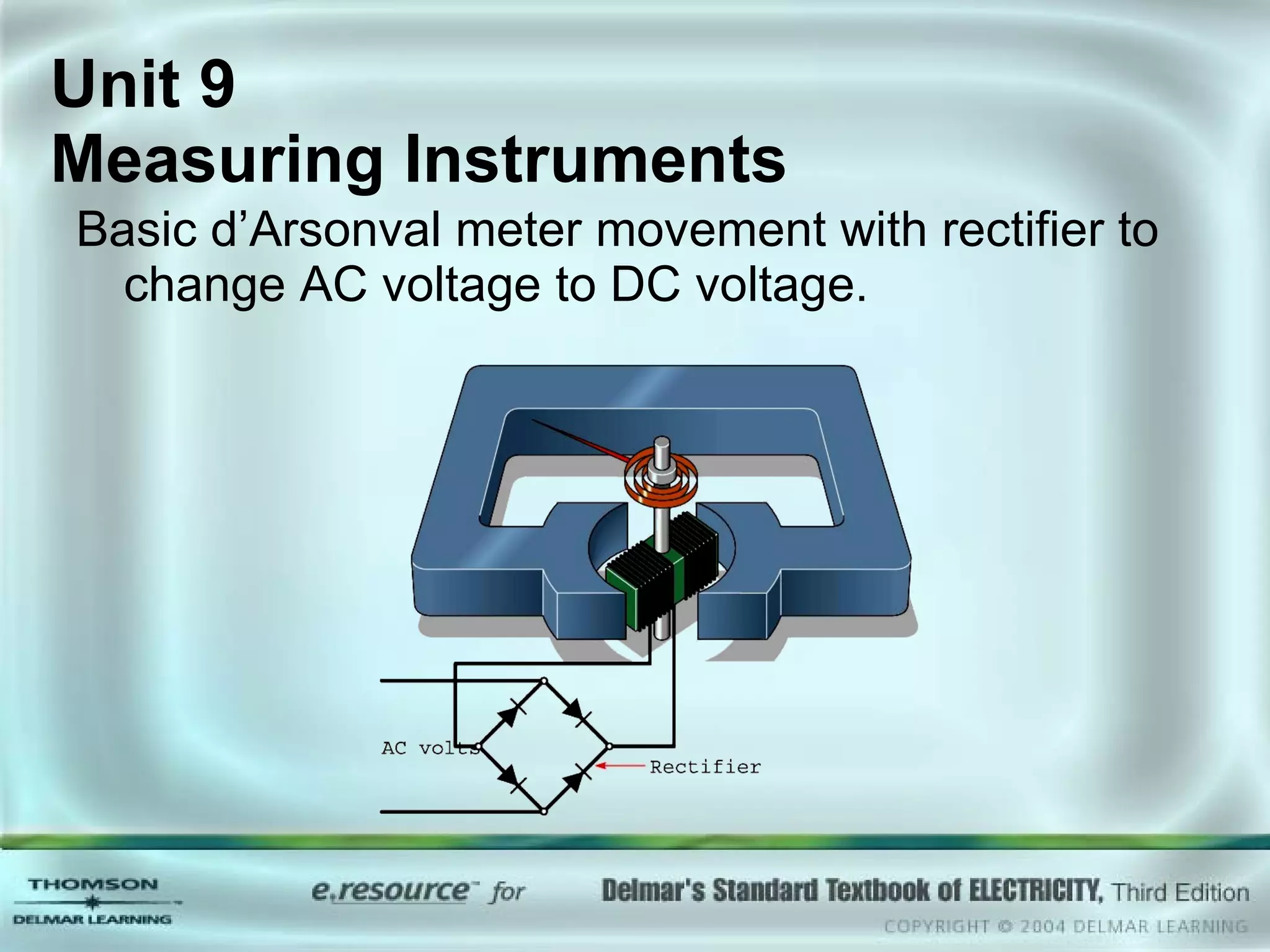
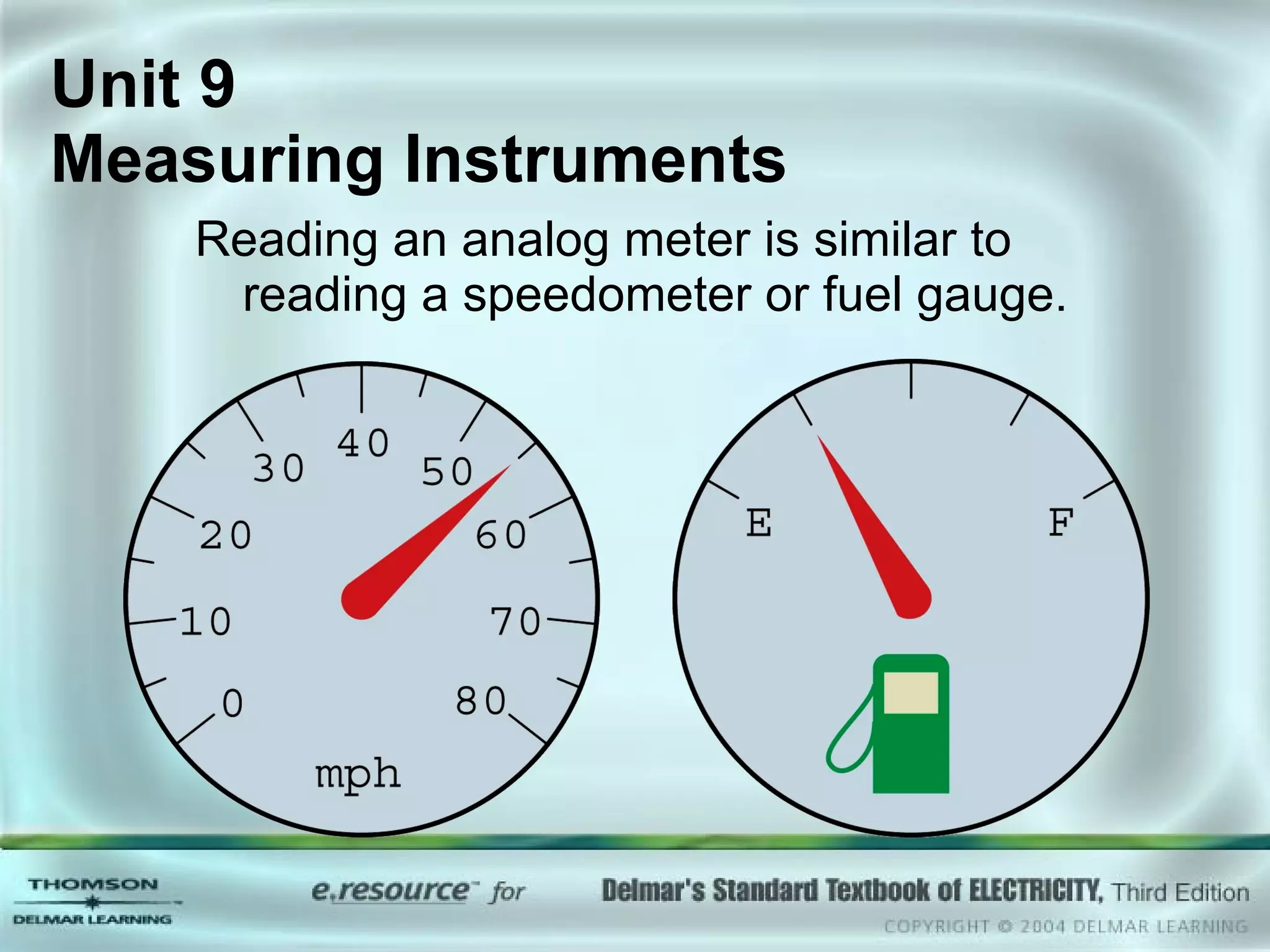
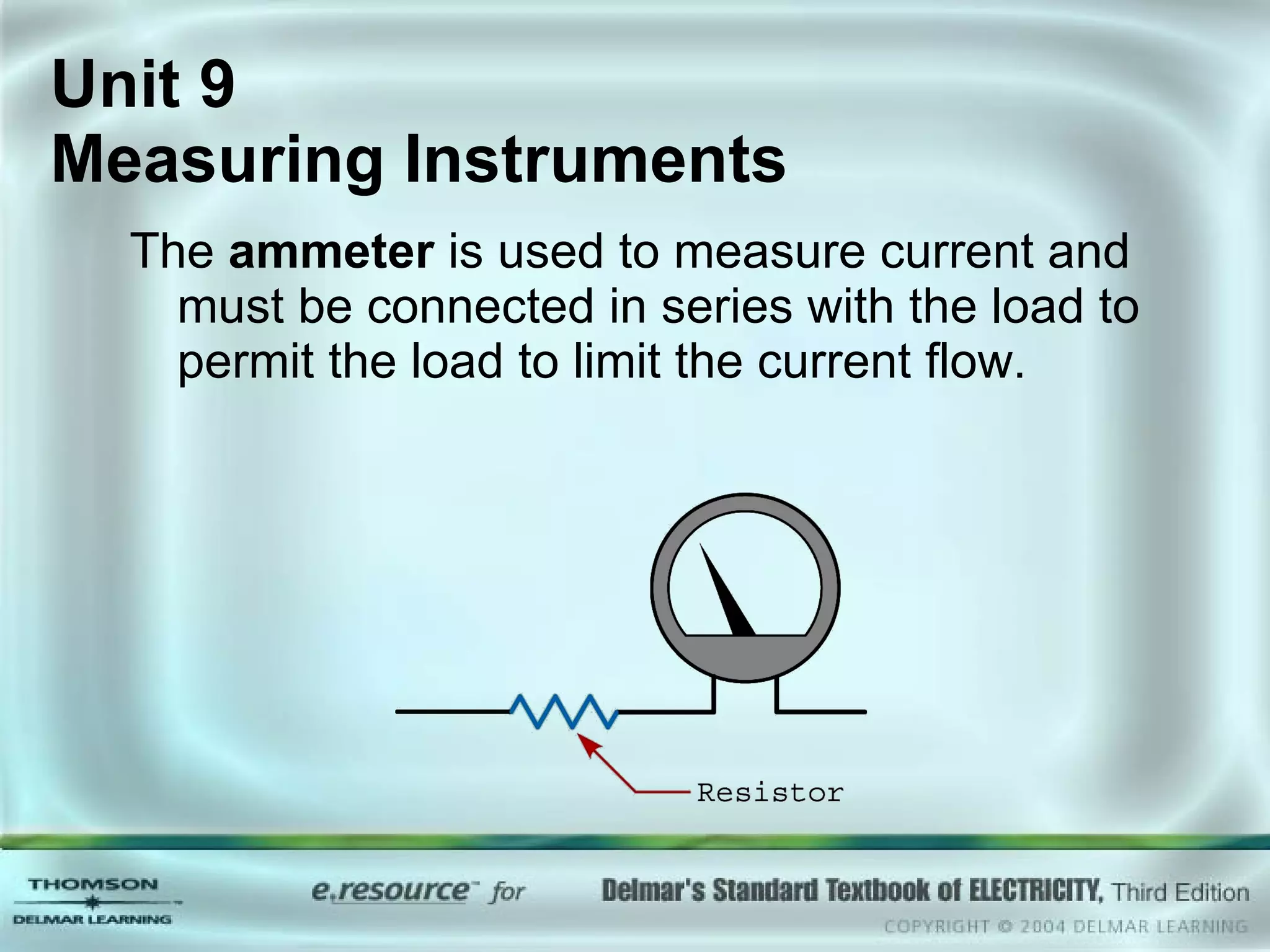
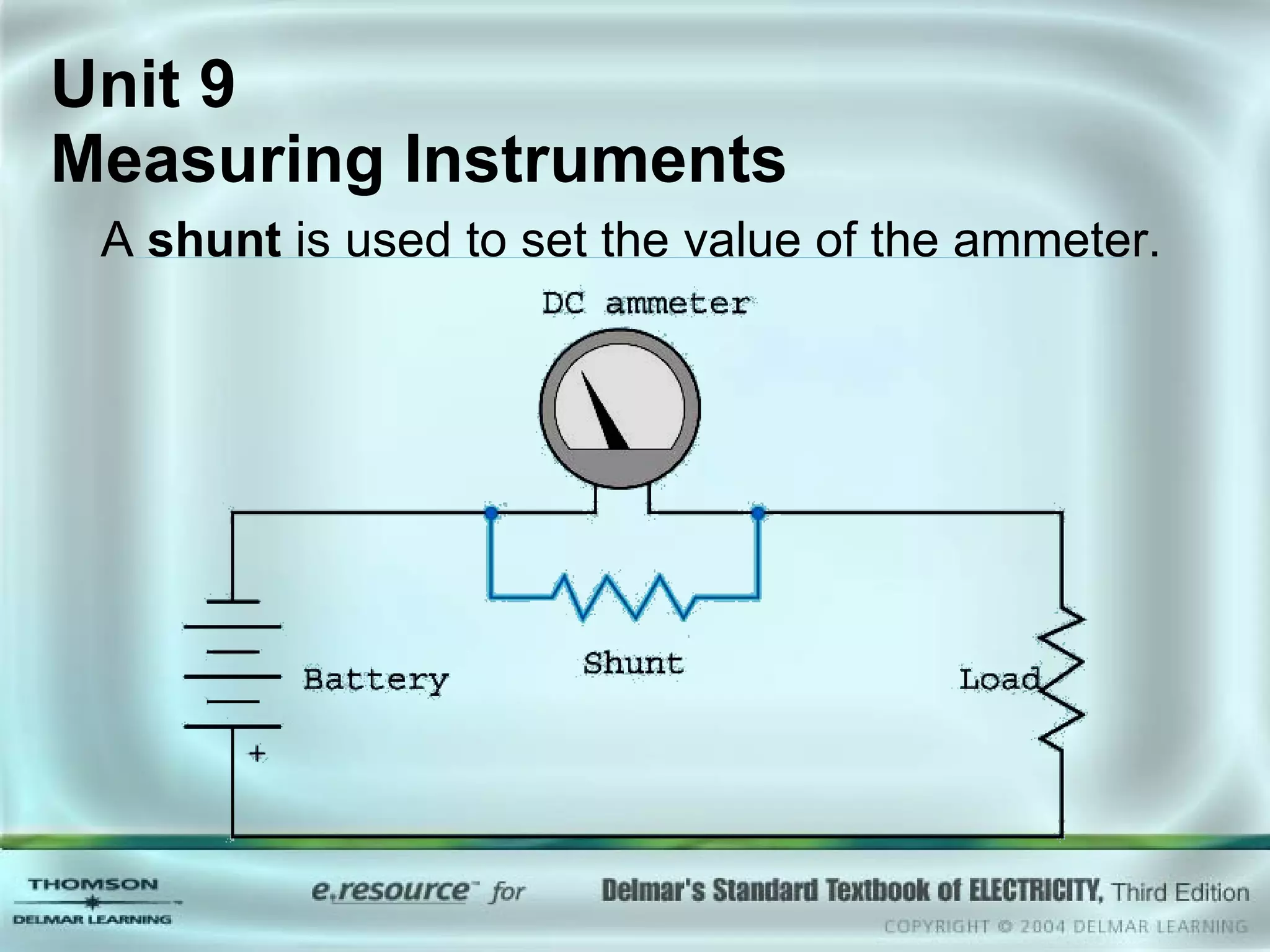
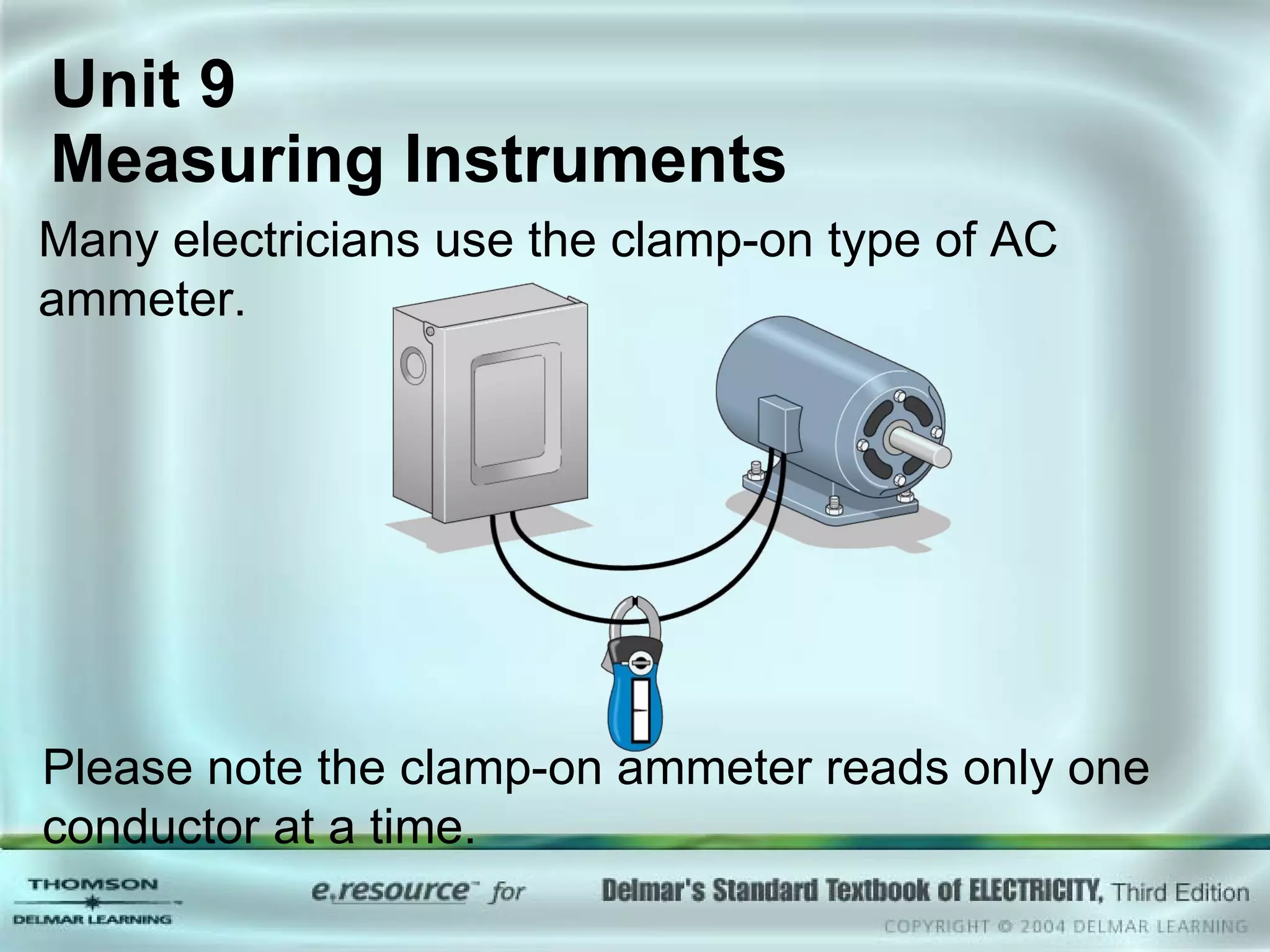
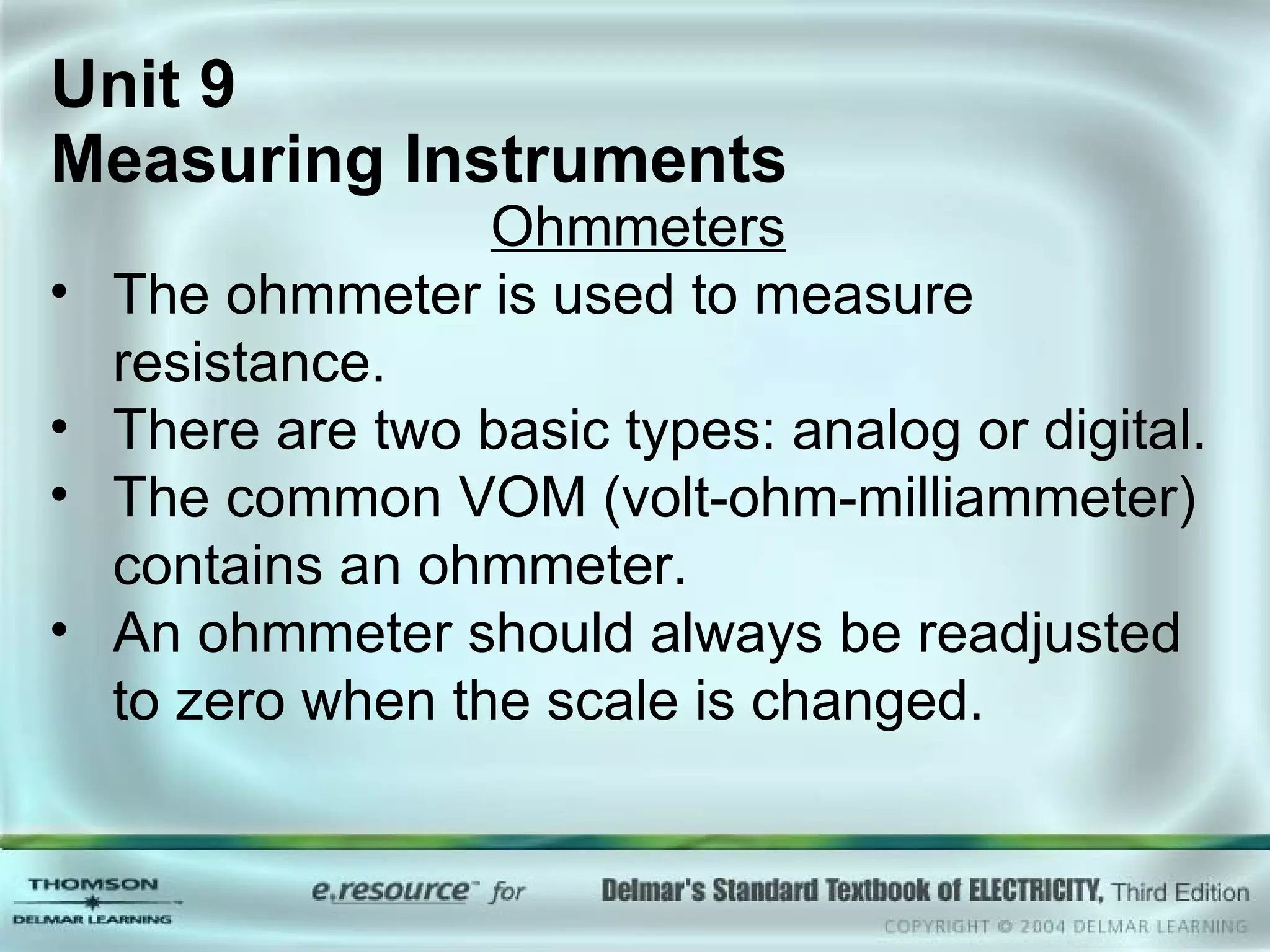
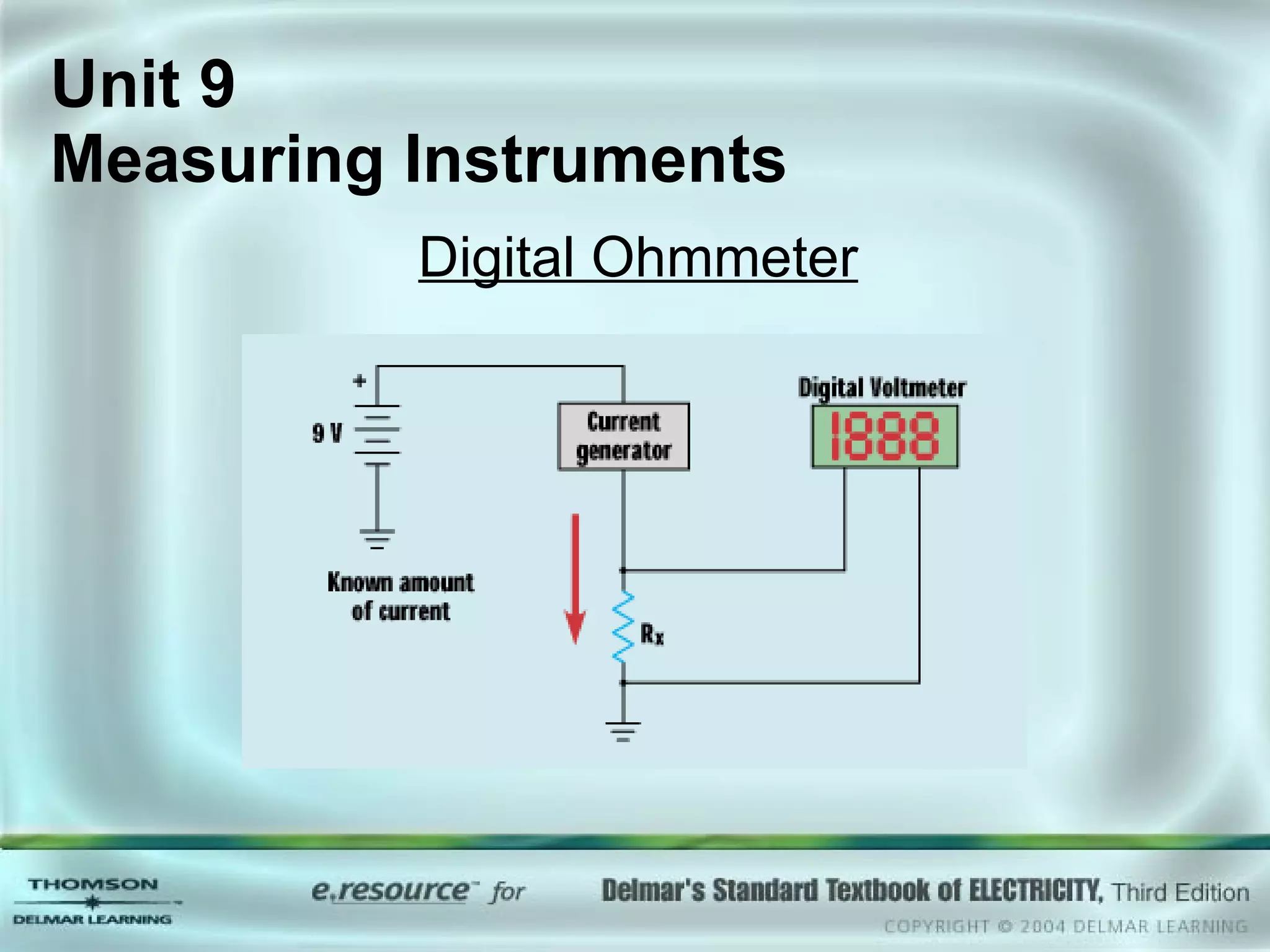
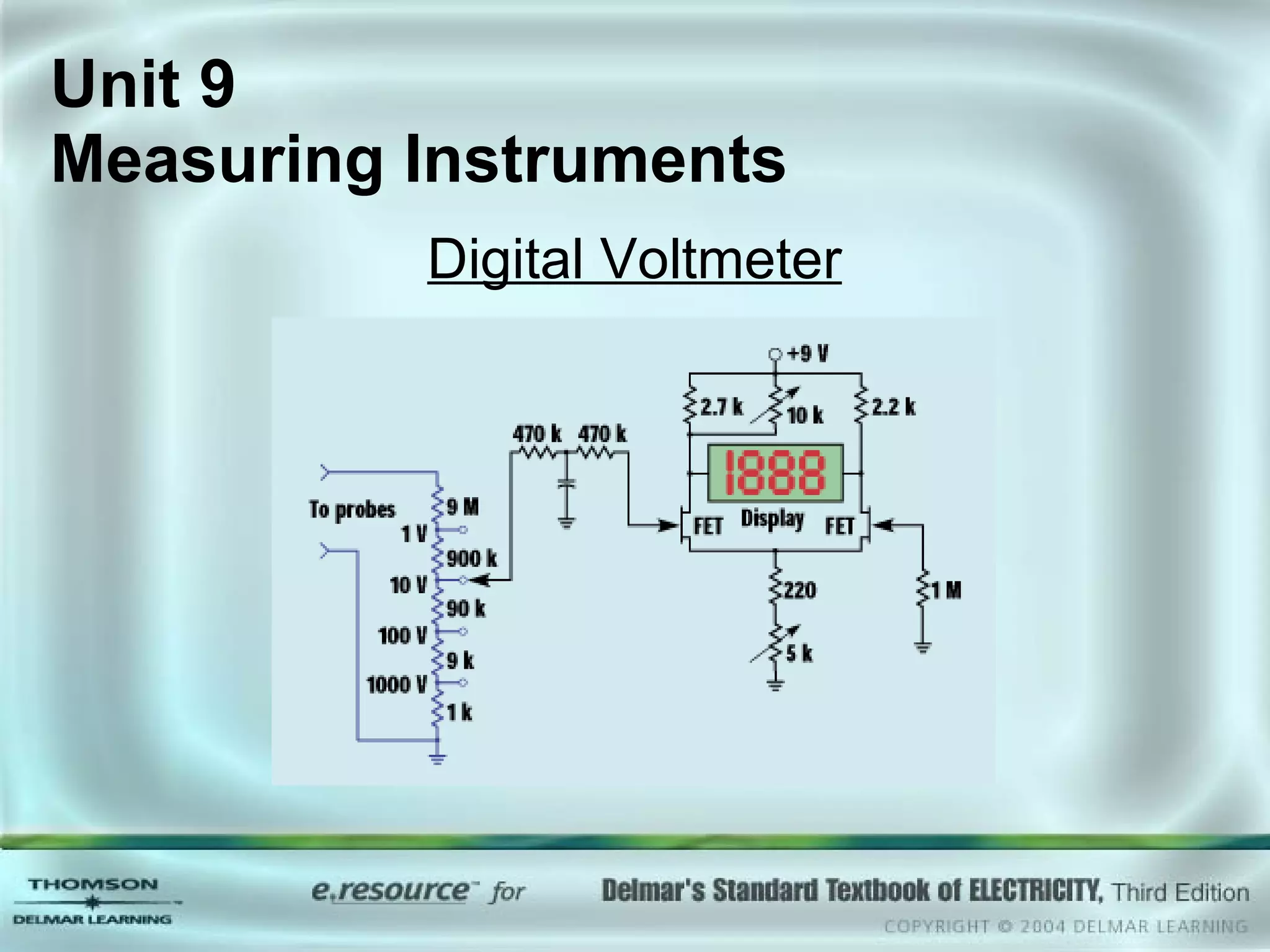
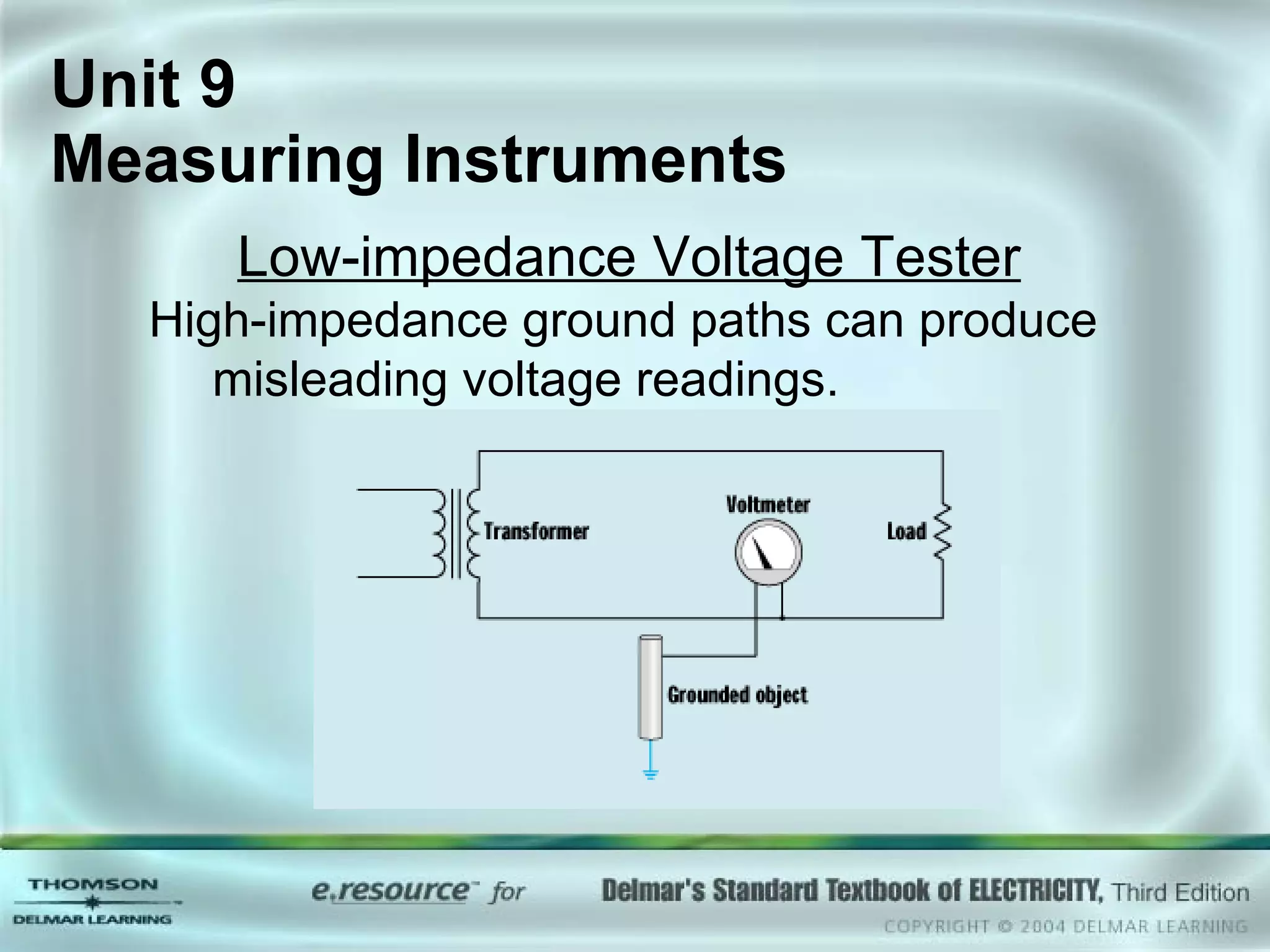
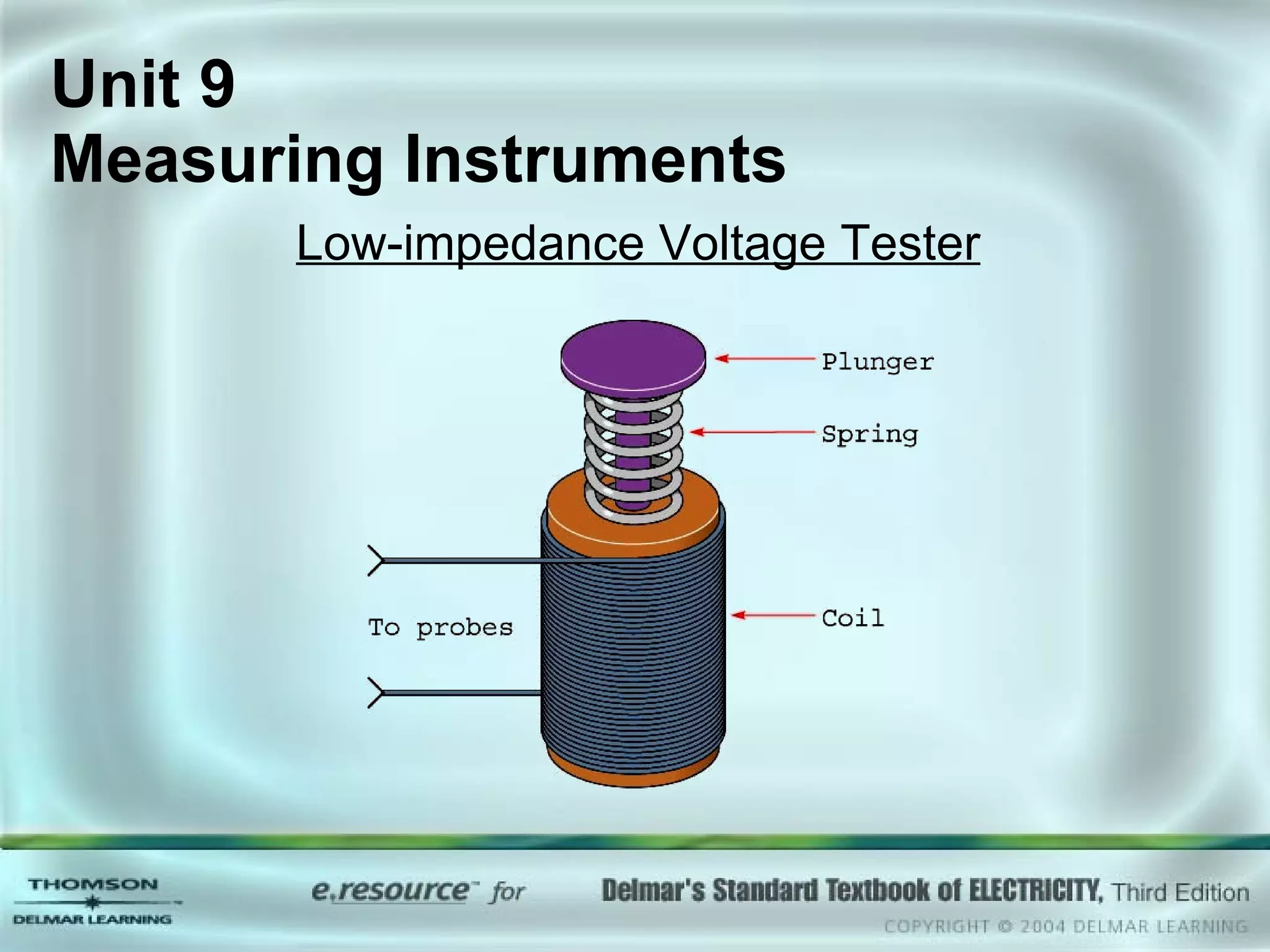
The document discusses various types of measuring instruments used in electrical work. It describes the operation of analog meters like the d'Arsonval movement and how to connect a voltmeter, ammeter, and ohmmeter. Digital multimeters and low-impedance voltage testers are also covered. Key points include how d'Arsonval meters work, the proper connections for voltmeters, ammeters, and ohmmeters, and the differences between analog and digital instruments.