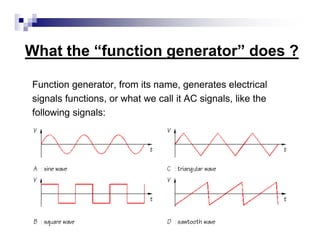
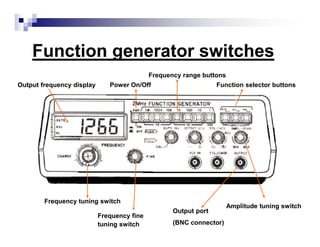
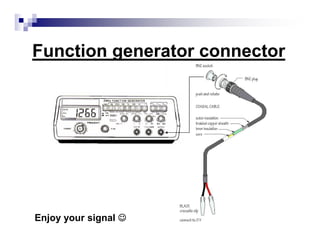
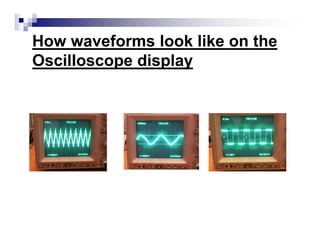
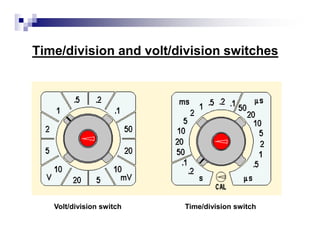
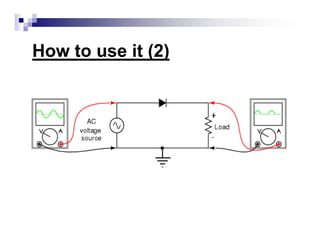
The document is a beginner's guide to using electronic measurement devices including digital multimeters, function generators, and oscilloscopes. It explains the functions, appearance, and operation of each device, providing detailed steps to measure voltage, current, resistance, and waveform characteristics. Each device's features, like connection methods and settings adjustments, are illustrated for effective usage.