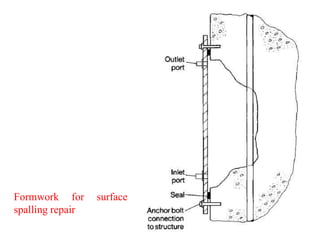
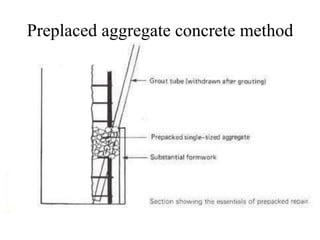
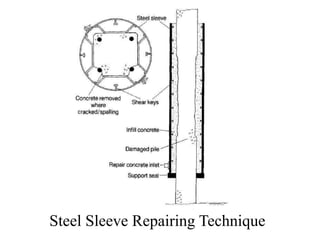
The document discusses various methods for underwater repair of concrete structures. It describes six main methods: 1) Surface spalling repair which involves clearing damaged areas and applying cementitious mortar or epoxy. 2) Large scale repair for significant damage which requires careful material selection and formwork. 3) Preplaced aggregate concrete where aggregate is compacted and grouted in place. 4) Injection techniques using cement or epoxy grouts to fill cracks or voids. 5) Guniting or shotcrete application for large surface repairs. 6) Steel sleeve technique which places a sleeve around damaged piles or columns and fills the space with concrete. Proper preparation and material compatibility are essential for effective underwater concrete structure repairs.